可以使用pytest.mark.parametrize装饰器来对测试用例进行参数化。
对列表中的对象进行循环,然后一一赋值,这个对象可以是列表,元组,字典。
import pytest def add(a, b): return a + b @pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,expect", [ [1, 1, 2], [2, 3, 5], [4, 5, 7] ]) def test_add(a, b, expect): assert add(a, b) == expect
执行结果:

还可以对每组参数进行标识,如下:
import pytest def add(a, b): return a + b @pytest.mark.parametrize('a,b,expect', [ pytest.param(1, 1, 2, id="first case"), pytest.param(2, 3, 5, id="second case"), pytest.param(4, 5, 8, id="third case") ]) def test_add(a, b, expect): assert add(a, b) == expect
使用mark.xfail对参数进行标识
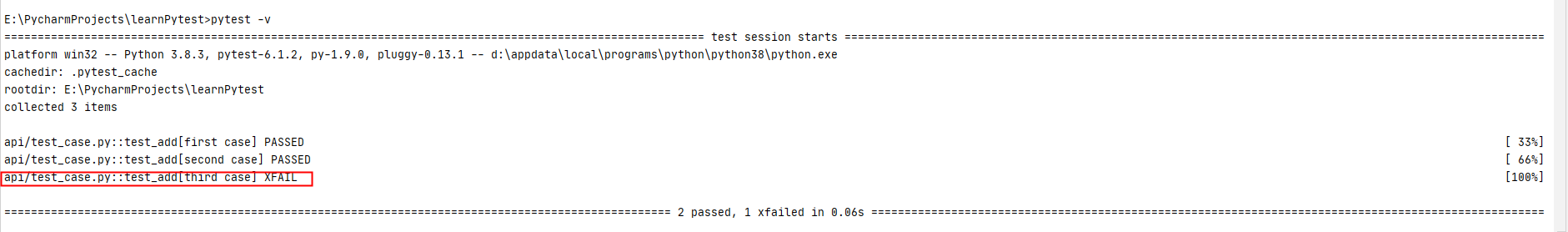
import pytest def add(a, b): return a + b @pytest.mark.parametrize('a,b,expect', [ pytest.param(1, 1, 2, id="first case"), pytest.param(2, 3, 5, id="second case"), pytest.param(4, 5, 8, id="third case", marks=pytest.mark.xfail(reason="这是个bug")) ]) def test_add(a, b, expect): assert add(a, b) == expect
执行结果:
读取外部数据进行参数化
在自动化测试用例编写中,我们一般遵循数据分离的原则,在使用pytest.mark.parametrize装饰器进行参数化时,数据来源也可以是json,yaml,csv等文件。
如下:
我们把数据放在json文件中
# param.json { "par": [ {"a": 1,"b": 2,"expect": 3}, {"a": 2,"b": 4,"expect": 6}, {"a": 4,"b": 5,"expect": 9} ] }
测试用例:
import pytest import json def read_json(): with open("param.json", "r") as f: return json.load(f)["par"] def add(a, b): return a + b @pytest.mark.parametrize('data', read_json()) def test_add(data): a = data.get("a") b = data.get("b") expect = data.get("expect") assert add(a, b) == expect