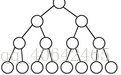
还有一种特殊的完全二叉树就是叶子节点都在同一层的,如下图
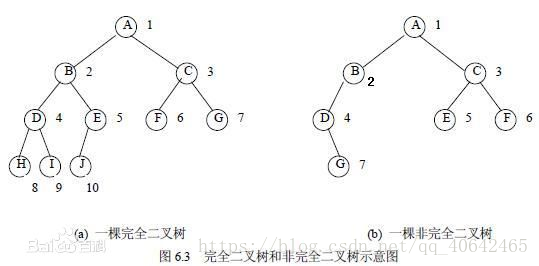
完全二叉树定义,若设二叉树的深度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
思路是:用bfs,一层一层的遍历二叉树的节点,一但遍历到空节点,那么不在往队列里加入节点了,遍历队列里的已有元素,若有一个不是空节点,那么就不是完全二叉树,若全是空节点那么就是完全二叉树
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
char v;
int num;
int depth;
struct node*ls,*rs;
};
struct node*head;
struct node*build()
{
char ch;
cin>>ch;
if(ch=='#') return NULL;
struct node*p=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->v=ch;
p->ls=build();
p->rs=build();
return p;
};
int judge()
{
if(!head) return 0; //如果树的根节点不存在,即树不存在,认为不是完全二叉树
struct node*p;
queue<struct node*>q;
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
q.push(head);//根节点入队
while(p=q.front())//队首元素不为NULL代表该节点存在,拓展这个节点的儿子节点,若为NULL,说明搜索到的节点为空节点了,那么就遍历队列里已有元素
{
q.push(p->ls);
q.push(p->rs);
q.pop();
}
while(!q.empty())
{
if(q.front()) return 0;
q.pop();
}
return 1;
}
void first(struct node *p)
{
if(!p) return ;
cout<<"/节点的值:"<<p->v<<endl;
first(p->ls);
first(p->rs);
}
int main()
{
head=build();
if(judge())
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"no"<<endl;
return 0;
}