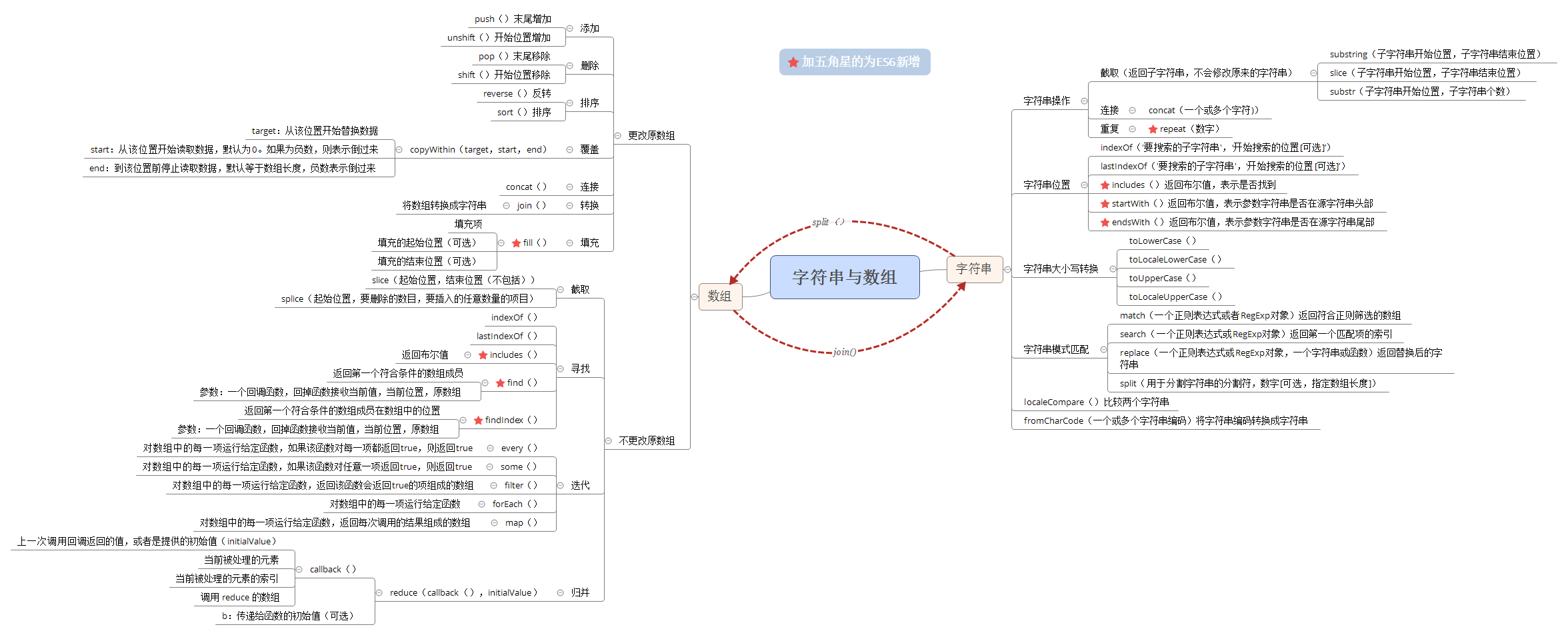
字符方法
chartAt()与charCodeAt()
参数:基于0的字符位置
chartAt()以单字符字符串的形式返回给定位置的那个字符。而charCodeAt()返回的是字符编码。
var stringValue = 'hello world';
/*chartAt()*/
console.log(stringValue.chartAt(1)); // 'e'字符串操作方法
concat()(数组中也有该方法)
参数:一个或多个字符串
将一个会多个字符串拼接起来,当然更常用的是使用 “+” 进行拼接
substring()与slice()(数组中也有此方法)
参数:指定子字符串的开始位置,子字符串到哪里结束
作用:创建新的子字符串(可以理解为字符串截取)
substr()
参数:指定子字符串的开始位置,返回的子字符串的字符个数
作用:创建新的子字符串(可以理解为字符串截取)
repeat()(ES6新增)
参数:数字(表示重复的次数)
作用:将原字符串重复n次
如果传入负数,则报错,传入小数和NaN等同于传入0
substring,slice,substr,repeat均返回子字符串,不会修改原来的字符串
var stringValue = "hello world";
alert(stringValue.slice(3)); //"lo world"
alert(stringValue.substring(3)); //"lo world"
alert(stringValue.substr(3)); //"lo world"
alert(stringValue.slice(3, 7)); //"lo w"
alert(stringValue.substring(3,7)); //"lo w"
alert(stringValue.substr(3, 7)); //"lo worl"
/*repeat()*/
var a = 'he';
var b = a.repeat(3);
console.log(`${a}---${b}`); / //"he---hehehe"当给这三个方法传入负值的时候,三个的表现不同:
-
slice()会将传入的负值与字符串的长度相加
-
substr()会将第一个位置的负值参数加上字符串长度后转为正数,而第二个位置的负值将转化为0
-
substring()会把所有的负参数转化为0
-
repeat()会报错
字符串位置方法
indexOf()和lastIndexOf()(数组中也有该方法)
参数:要搜索的子字符串,开始搜索的位置(可选)
搜索给定的子字符串,如果找到则返回位置,否则返回-1
var stringValue = "hello world";
alert(stringValue.indexOf("o")); //4
alert(stringValue.lastIndexOf("o")); //7 这两个方法在搜索到第一个匹配的子字符串后就停止运行,所以如果想找到字符串中所有的
子字符串出现的位置,可以循环调用indexOf或lastIndexOf。
var stringValue = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit";
var positions = new Array();
var pos = stringValue.indexOf("e");
while(pos > -1){
positions.push(pos);
pos = stringValue.indexOf("e", pos + 1);
}
alert(positions); //"3,24,32,35,52"ES6新增includes()、startsWith()、endsWith()
-
includes():返回布尔值,表示是否找到了参数字符串
-
startsWith():返回布尔值,表示参数字符串是否在源字符串的头部
-
endsWith():返回布尔值,表示参数字符串是否在源字符串的尾部
这三个方法的参数与indexOf(),lastIndexOf()一样
var s = 'Hello world';
s.startsWith('world',6); // true
s.endsWith('Hello',5); // true
s.includes('Hello',6); //false注意:
使用第2个参数n时,endsWith的行为与其他两个方法有所不同。它针对前面n个字符,而其他两个方法针对从第n个位置开始直到字符串结束的字符。
去空格--trim()
ES5中新增trim()方法用于去除字符串的左右空格,该方法会创建一个字符串的副本,不会改变原有的字符串,此外,Firefox 3.5+、Safari 5+
和 Chrome 8+还支持非标准的 trimLeft()和 trimRight()方法,分别用于删除字符串开头和末尾的
空格。
其实去空格可以使用正则去匹配的去掉,这里写一个去空格函数
/*trim 去掉空白
str要处理的字符串
[type] 类型:l 去除左边的空白 r去除右边空白 b去掉两边的空白 a去除所有空白*/
function trim (str,type) {
var type=type||"b";
if(type=="b"){
return str.replace(/^s*|s*$/g,"");
}else if(type=="l"){
return str.replace(/^s*/g,"");
}else if(type=="r"){
return str.replace(/s*$/g,"");
}else if(type=="a"){
return str.replace(/s*/g,"");
}
}字符串大小写转换
toLowerCase()、toLocaleLowerCase()、toUpperCase()和 toLocaleUpperCase()
字符串的模式匹配方法
match()
参数:一个正则表达式或RegExp对象
返回一个数组。在字符串上调用这个方法本质上与调用RegExp的exec()方法相同。
var text = "cat, bat, sat, fat";
var pattern = /.at/;
//与 pattern.exec(text)相同
var matches = text.match(pattern);
alert(matches.index); //0
alert(matches[0]); //"cat"
alert(pattern.lastIndex); //0 search()
参数:一个正则表达式或RegExp对象
返回字符串中第一个匹配项的索引,如果没有找到,则返回-1
var text = "cat, bat, sat, fat";
var pos = text.search(/at/);
alert(pos); //1 replace()
参数:一个RegExp对象或者一个字符串(这个字符串不会被转换成正则表达式),一个字符串或一个函数
利用replace()进行替换的时候,如果传入的是字符串,则只会替换第一个子字符串,要想替换所有的子字符串,则需要传入一个正则表达式,而且要指定全局(g)标志
var text = 'cat , bat , sat , fat';
var result = text.replace('at','ond');
console.log(result); // =>'cont , bat , sat , fat'
result = text.replace(/at/g,'ond');
console.log(result); //=>'cont , bont , sont , font'该方法并不改变调用它的字符串本身,只是返回一个新的替换后的字符串。
当第二个参数为函数时函数的返回值作为替换字符串。与第二个参数是字符串一样,如果第一个参数是正则表达式,并且全局匹配,则这个函数的方法将被多次调用,每次匹配都会被调用。
该函数的参数:
-
match:匹配的子串
-
p1,p2...:假如
replace()方法的第一个参数是RegExp对象,则代表第n个括号匹配的字符串。 -
offset:匹配到的子字符串在原字符串中的偏移量。(比如,如果原字符串是“abcd”,匹配到的子字符串时“bc”,那么这个参数是1)
-
被匹配的原字符串
function replacer(match , p1 , p2 , p3 , offset , string){
// p1 is nondigits, p2 digits, and p3 non-alphanumerics
console.log(`${match}
${p1}
${p2}
${p3}
${offset}
${string}`);
/* => abc12345#$*%
abc
12345
#$*%
0
abc12345#$*%" */
console.log([p1, p2, p3].join(' - ')); // => "abc - 12345 - #$*%"
return [p1, p2, p3].join(' - ');
}
var newString = 'abc12345#$*%'.replace(/([^d]*)(d*)([^w]*)/, replacer); // =>"abc - 12345 - #$*%"split()
参数:用于分隔字符串的分隔符,数字(可选,用于指定数组的大小)
作用:基于指定的分隔符将一个字符串分割成多个子字符串,并将结果放在一个数组中,分隔符可以是字符串,也可以是RegExp对象
var color = 'red,blue,yellow,black';
var color1 = color.split(','); // =>['red','blue','yellow','black']
var color2 = color.split(',',2); // =>['red','blue']
var color3 = color.split(/[^\,]+/); // =>["", ",", ",", ",", ""] 最后一个调用split的时候,出现了前后的两个空白,是因为通过正则表达式指定的分隔符出现在了字符串的开头和结尾。
localeCompare()
这个方法用于比较两个字符串,并返回下列值中的一个:
-
如果字符串在字母表中应该排在字符串参数之前,则返回负数(大多情况下为-1)
-
如果相等,则返回0
-
如果排在字符串参数之前,则返回正数(大多数情况下为1)
fromCharCode()
String构造函数的一个静态方法
参数:一个或多个字符串编码
作用:将接收到的一个或多个字符串编码转换成一个字符串,这个方法与实例方法charCodeAt()执行相反的操作。
/*fromCharCode*/
String.fromCharCode(104,101,108,108,111); // =>hello
/*charCodeAt*/
let s = 'hello';
for(let i=0;i<s.length;i++){
console.log(`${s[i]}----${s[i].charCodeAt()}`);
}
/*
"h----104"
"e----101"
"l----108"
"l----108"
"o----111"
*/最后写一个字符串与数组方法应用的一个例子,熟悉它们方法的话很简单,不熟悉就会觉得有点儿乱。
let s = 'hello';
let news = s.split('').reverse().join('');
console.log(news); // => "olleh"另附js中String和Array方法的总结图: