Mybatis开源Plugin中最熟知的pagehelper,重点made in China
很多人开始用pagehelper时候,肯定很纳闷,以mysql为例,明明没有加limit语句,为什么打印出来的sql中有了limit语句了,这是怎么回事???插件在什么地方给sql加上了limit,为什么又能修改写好的sql,只能从pagehelper的源码中找到疑惑的答案了。
@Intercepts( { @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}), @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}), } ) public class PageInterceptor implements Interceptor { //缓存count查询的ms protected Cache<CacheKey, MappedStatement> msCountMap = null; private Dialect dialect; private String default_dialect_class = "com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"; private Field additionalParametersField; @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { try { Object[] args = invocation.getArgs(); MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0]; Object parameter = args[1]; RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2]; ResultHandler resultHandler = (ResultHandler) args[3]; Executor executor = (Executor) invocation.getTarget(); CacheKey cacheKey; BoundSql boundSql; //由于逻辑关系,只会进入一次 if(args.length == 4){ //4 个参数时 boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); cacheKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); } else { //6 个参数时 cacheKey = (CacheKey) args[4]; boundSql = (BoundSql) args[5]; } List resultList; //调用方法判断是否需要进行分页,如果不需要,直接返回结果 if (!dialect.skip(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) { //反射获取动态参数 Map<String, Object> additionalParameters = (Map<String, Object>) additionalParametersField.get(boundSql); //判断是否需要进行 count 查询 if (dialect.beforeCount(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) { //创建 count 查询的缓存 key CacheKey countKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, boundSql); countKey.update("_Count"); MappedStatement countMs = msCountMap.get(countKey); if (countMs == null) { //根据当前的 ms 创建一个返回值为 Long 类型的 ms countMs = MSUtils.newCountMappedStatement(ms); msCountMap.put(countKey, countMs); } //调用方言获取 count sql String countSql = dialect.getCountSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, countKey); BoundSql countBoundSql = new BoundSql(ms.getConfiguration(), countSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameter); //当使用动态 SQL 时,可能会产生临时的参数,这些参数需要手动设置到新的 BoundSql 中 for (String key : additionalParameters.keySet()) { countBoundSql.setAdditionalParameter(key, additionalParameters.get(key)); } //执行 count 查询 Object countResultList = executor.query(countMs, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, countKey, countBoundSql); Long count = (Long) ((List) countResultList).get(0); //处理查询总数 //返回 true 时继续分页查询,false 时直接返回 if (!dialect.afterCount(count, parameter, rowBounds)) { //当查询总数为 0 时,直接返回空的结果 return dialect.afterPage(new ArrayList(), parameter, rowBounds); } } //判断是否需要进行分页查询 if (dialect.beforePage(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) { //生成分页的缓存 key CacheKey pageKey = cacheKey; //处理参数对象 parameter = dialect.processParameterObject(ms, parameter, boundSql, pageKey);
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------下面就是加上limit语句的地方(方言通俗就是数据库类型)------------------------------------------------------------------ //调用方言获取分页 sql String pageSql = dialect.getPageSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, pageKey); BoundSql pageBoundSql = new BoundSql(ms.getConfiguration(), pageSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameter); //设置动态参数 for (String key : additionalParameters.keySet()) { pageBoundSql.setAdditionalParameter(key, additionalParameters.get(key)); } //执行分页查询 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, pageKey, pageBoundSql); } else { //不执行分页的情况下,也不执行内存分页 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql); } } else { //rowBounds用参数值,不使用分页插件处理时,仍然支持默认的内存分页 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql); } return dialect.afterPage(resultList, parameter, rowBounds); } finally { dialect.afterAll(); } } @Override public Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { //缓存 count ms msCountMap = CacheFactory.createCache(properties.getProperty("msCountCache"), "ms", properties); String dialectClass = properties.getProperty("dialect"); if (StringUtil.isEmpty(dialectClass)) { dialectClass = default_dialect_class; } try { Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(dialectClass); dialect = (Dialect) aClass.newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new PageException(e); } dialect.setProperties(properties); try { //反射获取 BoundSql 中的 additionalParameters 属性 additionalParametersField = BoundSql.class.getDeclaredField("additionalParameters"); additionalParametersField.setAccessible(true); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { throw new PageException(e); } } }

图中表示对 执行器Executor 的query方法进行拦截,执行器就是真正执行sql的容器
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
//拦截query方法
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
void clearLocalCache();
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
Transaction getTransaction();
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
Diagrams图:
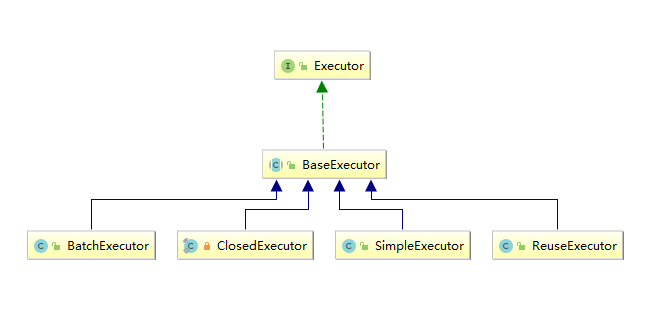
Configuration.class中有newExecutor方法
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据executorType策略,实例化对应的执行器
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
在Mybatis中可以定义四种插件类型:
ParameterHandler ResultSetHandler StatementHandler Executor
插件就是一个Interceptor比如上面的pageInterceptor
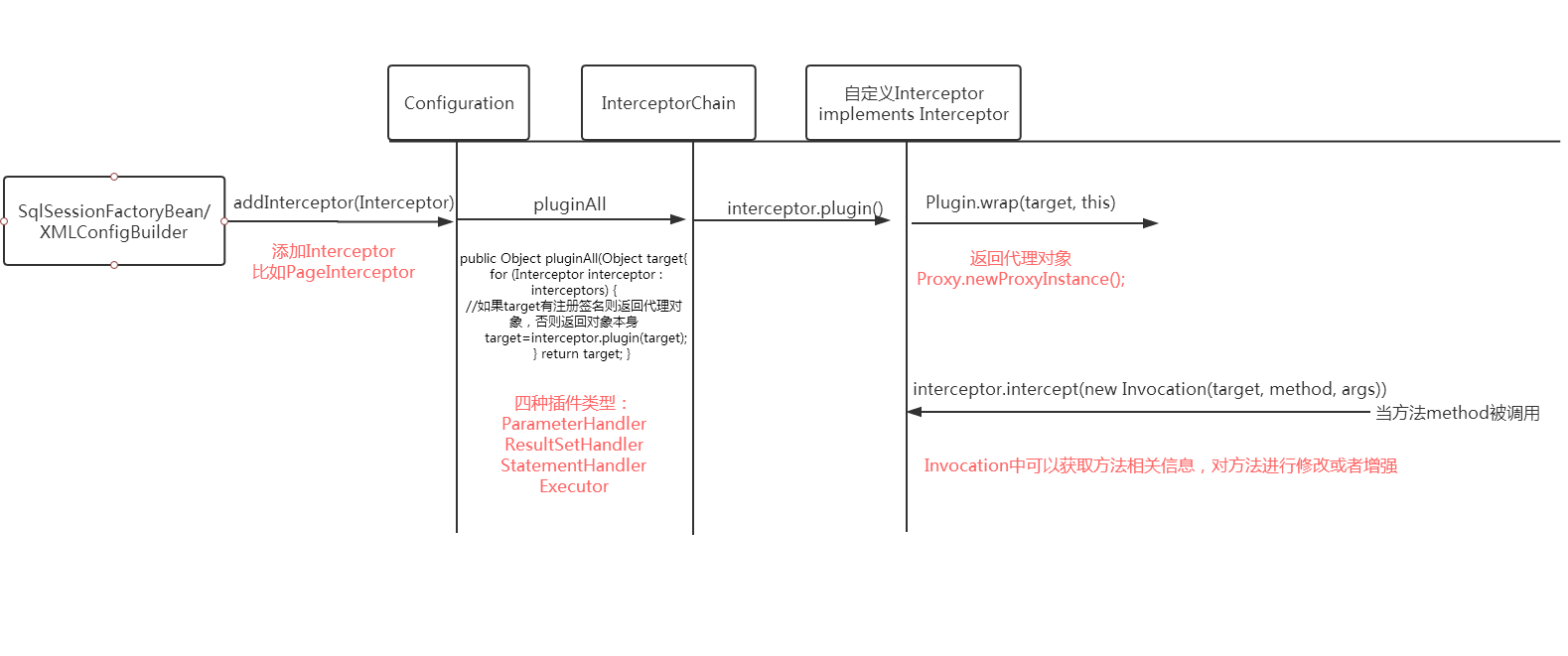
容器在实例化ParameterHander,ResultSetHandler,StatementHandler,Executor时会调用pluginAll方法进行匹配,如果签名一致则返回的就是该对象的代理对象,反之是它本身。通过AOP对方法进行了修改,增强等
自定义简单的插件(打印sql执行时间,监控慢查询)
@Intercepts({ @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "query", args = { Statement.class, ResultHandler.class}) })
public class SQLInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
System.out.println("获取到SQL语句:"+sql);
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}finally {
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("SQL执行耗时:" + (endTime-startTime) +"ms");
}
}