有了光照,就应该有阴影。所以,今天我们来整个阴影。
说到阴影,我们自然而然地会想到初中里,关于阴影的产生原因:光在均匀介质中沿直线传播。
所以,我们暂且把我们的光视为平行光,从纹理角度来考虑阴影。一个显而易见的想法是:
判断一个点距离光源的远近:
设此点为A,设光源为L,设A与L距离为x,设射线LA交到的第一个点是B,那么,如果线段LB < LA,说明这个点被挡住了,那么它就处于阴影之下。
话是这么说,可是这么实现呢?让我们来一步步分析。
首先,我们要知道要获取哪些,很显然只需要两个信息:一个是LB,一个是LA。LA很好取得,已知两点坐标只需要算一下距离即可。那么LB怎么求呢?
提示:深度测试
相信已经有吊大的同学想到了,深度测试可以自动筛选出距离摄像机最近的点(深度z最小的点)来为我们绘制片元。这样,每个片元就保存了距离其最近的点。
说到片元大家一定都懂了,还记得我们之前说的帧缓冲吗?我们只需要利用一下帧缓冲和深度测试即可。
有的不认真看前面的同学就会问了,那怎么才能利用深度测试来测距离光源最近的深度大小呢?不要忘记我们之前学到的矩阵。这次只需要让MVP矩阵稍微更改一下,M不变,V,摄像机矩阵View,只需要将lookAt里摄像机的坐标改为光源的坐标。P,由于是平行光,所以阴影使用正交矩阵,由于要映射全部顶点,所以范围需要如此设置(详见下方代码)。
然后,在帧缓冲的着色器里我们gl_Position = depthMVP * (vertex_modelspace);就可以愉快地获取光源摄像机视角里的顶点了。在片元着色器里只输出低精度深度,这将大大提高我们的速度。
有了这张深度纹理之后,把它扔到正常着色器里(用于渲染场景的着色器)。对于正常顶点着色器,只需要对于每个顶点也乘上depthMVP得到光源摄像机处的坐标depthVertex,然后显然Z轴就是距离LA(不是真正的距离,但是足够我们判断了),LB就是深度纹理中UV坐标为depthVertex.xy的z属性。由此,即可简单判断。
总结一下,流程为:
1.获得以光源为摄像机的正交视角下的一张包括各个片元的深度的纹理A
2.获得以光源为摄像机的正交视角下的所有顶点的深度B
3.如果A<B,则该顶点被遮挡,对于该片元绘制阴影
彩蛋:如果把正交ortho改成透视perspective会怎样?文末揭晓。
接下来是代码,由于懒这一节没有包含新的API和新结构,代码我就全部放上去了。(注意,帧缓冲附件中必须带一个颜色附件,否则会报错,我被这个问题坑了好几个小时)
// Include standard headers #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> // Include GLEW #include <GL/glew.h> // Include GLFW #include <GLFW/glfw3.h> GLFWwindow* window; // Include GLM #include <glm/glm.hpp> #include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp> using namespace glm; #include <common/shader.hpp> #include <common/texture.hpp> #include <common/controls.hpp> #include <common/objloader.hpp> #include <common/vboindexer.hpp> int main( void ) { // Initialise GLFW if( !glfwInit() ) { fprintf( stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW " ); getchar(); return -1; } glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, 4); glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3); glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3); glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); // Open a window and create its OpenGL context window = glfwCreateWindow( 1024, 768, "Shadows", NULL, NULL); if( window == NULL ){ fprintf( stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials. " ); getchar(); glfwTerminate(); return -1; } glfwMakeContextCurrent(window); // We would expect width and height to be 1024 and 768 int windowWidth = 1024; int windowHeight = 768; // But on MacOS X with a retina screen it'll be 1024*2 and 768*2, so we get the actual framebuffer size: glfwGetFramebufferSize(window, &windowWidth, &windowHeight); // Initialize GLEW glewExperimental = true; // Needed for core profile if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW "); getchar(); glfwTerminate(); return -1; } // Ensure we can capture the escape key being pressed below glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE); // Hide the mouse and enable unlimited mouvement glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED); // Set the mouse at the center of the screen glfwPollEvents(); glfwSetCursorPos(window, 1024/2, 768/2); // Dark blue background glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.0f); // Enable depth test glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); // Accept fragment if it closer to the camera than the former one glDepthFunc(GL_LESS); // Cull triangles which normal is not towards the camera glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE); GLuint VertexArrayID; glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID); glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID); // Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders GLuint depthProgramID = LoadShaders( "DepthRTT.vertexshader", "DepthRTT.fragmentshader" ); // Get a handle for our "MVP" uniform GLuint depthMatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(depthProgramID, "depthMVP"); // Load the texture GLuint Texture = loadDDS("uvmap.DDS"); // Read our .obj file std::vector<glm::vec3> vertices; std::vector<glm::vec2> uvs; std::vector<glm::vec3> normals; bool res = loadOBJ("room_thickwalls.obj", vertices, uvs, normals); std::vector<unsigned short> indices; std::vector<glm::vec3> indexed_vertices; std::vector<glm::vec2> indexed_uvs; std::vector<glm::vec3> indexed_normals; indexVBO(vertices, uvs, normals, indices, indexed_vertices, indexed_uvs, indexed_normals); // Load it into a VBO GLuint vertexbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexed_vertices.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &indexed_vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); GLuint uvbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &uvbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexed_uvs.size() * sizeof(glm::vec2), &indexed_uvs[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); GLuint normalbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &normalbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexed_normals.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &indexed_normals[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); // Generate a buffer for the indices as well GLuint elementbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &elementbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, elementbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(unsigned short), &indices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); // --------------------------------------------- // Render to Texture - specific code begins here // --------------------------------------------- // The framebuffer, which regroups 0, 1, or more textures, and 0 or 1 depth buffer. GLuint FramebufferName = 0; glGenFramebuffers(1, &FramebufferName); glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, FramebufferName); // Depth texture. Slower than a depth buffer, but you can sample it later in your shader GLuint depthTexture; glGenTextures(1, &depthTexture); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTexture); glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0,GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT16, 1024, 1024, 0,GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, GL_FLOAT, 0); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_COMPARE_FUNC, GL_LEQUAL); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_COMPARE_MODE, GL_COMPARE_R_TO_TEXTURE); glFramebufferTexture(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, depthTexture, 0); GLuint renderedTexture; glGenTextures(1, &renderedTexture); // "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, renderedTexture); // Give an empty image to OpenGL ( the last "0" means "empty" ) glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0,GL_RGB, windowWidth, windowHeight, 0,GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, 0); // Poor filtering glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); glFramebufferTexture(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, renderedTexture, 0); // No color output in the bound framebuffer, only depth. //glDrawBuffer(GL_NONE); GLenum DrawBuffers[1] = {GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0}; glDrawBuffers(1, DrawBuffers); // "1" is the size of DrawBuffers // Always check that our framebuffer is ok if(glCheckFramebufferStatus(GL_FRAMEBUFFER) != GL_FRAMEBUFFER_COMPLETE) return false; // The quad's FBO. Used only for visualizing the shadowmap. static const GLfloat g_quad_vertex_buffer_data[] = { -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, }; GLuint quad_vertexbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &quad_vertexbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, quad_vertexbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_quad_vertex_buffer_data), g_quad_vertex_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW); // Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders GLuint quad_programID = LoadShaders( "Passthrough.vertexshader", "SimpleTexture.fragmentshader" ); GLuint texID = glGetUniformLocation(quad_programID, "texture_uniform"); // Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders GLuint programID = LoadShaders( "ShadowMapping.vertexshader", "ShadowMapping.fragmentshader" ); // Get a handle for our "myTextureSampler" uniform GLuint TextureID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "myTextureSampler"); // Get a handle for our "MVP" uniform GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP"); GLuint ViewMatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "V"); GLuint ModelMatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "M"); GLuint DepthBiasID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "DepthBiasMVP"); GLuint ShadowMapID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "shadowMap"); // Get a handle for our "LightPosition" uniform GLuint lightInvDirID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "LightInvDirection_worldspace"); do{ // Render to our framebuffer glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, FramebufferName); glViewport(0,0,1024,1024); // Render on the whole framebuffer, complete from the lower left corner to the upper right // We don't use bias in the shader, but instead we draw back faces, // which are already separated from the front faces by a small distance // (if your geometry is made this way) glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE); glCullFace(GL_BACK); // Cull back-facing triangles -> draw only front-facing triangles // Clear the screen glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Use our shader glUseProgram(depthProgramID); glm::vec3 lightInvDir = glm::vec3(0.5f,2,2); // Compute the MVP matrix from the light's point of view glm::mat4 depthProjectionMatrix = glm::ortho<float>(-10,10,-10,10,-10,20); glm::mat4 depthViewMatrix = glm::lookAt(lightInvDir, glm::vec3(0,0,0), glm::vec3(0,1,0)); // or, for spot light : //glm::vec3 lightPos(5, 20, 20); //glm::mat4 depthProjectionMatrix = glm::perspective<float>(45.0f, 1.0f, 2.0f, 50.0f); //glm::mat4 depthViewMatrix = glm::lookAt(lightPos, lightPos-lightInvDir, glm::vec3(0,1,0)); glm::mat4 depthModelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0); glm::mat4 depthMVP = depthProjectionMatrix * depthViewMatrix * depthModelMatrix; // Send our transformation to the currently bound shader, // in the "MVP" uniform glUniformMatrix4fv(depthMatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &depthMVP[0][0]); // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 0, // The attribute we want to configure 3, // size GL_FLOAT, // type GL_FALSE, // normalized? 0, // stride (void*)0 // array buffer offset ); // Index buffer glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, elementbuffer); // Draw the triangles ! glDrawElements( GL_TRIANGLES, // mode indices.size(), // count GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, // type (void*)0 // element array buffer offset ); glDisableVertexAttribArray(0); // Render to the screen glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0); glViewport(0,0,windowWidth,windowHeight); // Render on the whole framebuffer, complete from the lower left corner to the upper right glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE); glCullFace(GL_BACK); // Cull back-facing triangles -> draw only front-facing triangles // Clear the screen glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Use our shader glUseProgram(programID); // Compute the MVP matrix from keyboard and mouse input computeMatricesFromInputs(); glm::mat4 ProjectionMatrix = getProjectionMatrix(); glm::mat4 ViewMatrix = getViewMatrix(); //ViewMatrix = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(14,6,4), glm::vec3(0,1,0), glm::vec3(0,1,0)); glm::mat4 ModelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0); glm::mat4 MVP = ProjectionMatrix * ViewMatrix * ModelMatrix; glm::mat4 biasMatrix( 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0 ); glm::mat4 depthBiasMVP = biasMatrix*depthMVP; // Send our transformation to the currently bound shader, // in the "MVP" uniform glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &MVP[0][0]); glUniformMatrix4fv(ModelMatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &ModelMatrix[0][0]); glUniformMatrix4fv(ViewMatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &ViewMatrix[0][0]); glUniformMatrix4fv(DepthBiasID, 1, GL_FALSE, &depthBiasMVP[0][0]); glUniform3f(lightInvDirID, lightInvDir.x, lightInvDir.y, lightInvDir.z); // Bind our texture in Texture Unit 0 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, Texture); // Set our "myTextureSampler" sampler to use Texture Unit 0 glUniform1i(TextureID, 0); glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTexture); glUniform1i(ShadowMapID, 1); // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 0, // attribute 3, // size GL_FLOAT, // type GL_FALSE, // normalized? 0, // stride (void*)0 // array buffer offset ); // 2nd attribute buffer : UVs glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 1, // attribute 2, // size GL_FLOAT, // type GL_FALSE, // normalized? 0, // stride (void*)0 // array buffer offset ); // 3rd attribute buffer : normals glEnableVertexAttribArray(2); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 2, // attribute 3, // size GL_FLOAT, // type GL_FALSE, // normalized? 0, // stride (void*)0 // array buffer offset ); // Index buffer glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, elementbuffer); // Draw the triangles ! glDrawElements( GL_TRIANGLES, // mode indices.size(), // count GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, // type (void*)0 // element array buffer offset ); glDisableVertexAttribArray(0); glDisableVertexAttribArray(1); glDisableVertexAttribArray(2); // Optionally render the shadowmap (for debug only) // Render only on a corner of the window (or we we won't see the real rendering...) glViewport(0,0,512,512); // Use our shader glUseProgram(quad_programID); // Bind our texture in Texture Unit 0 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTexture); // Set our "renderedTexture" sampler to use Texture Unit 0 glUniform1i(texID, 0); // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, quad_vertexbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 0, // attribute 0. No particular reason for 0, but must match the layout in the shader. 3, // size GL_FLOAT, // type GL_FALSE, // normalized? 0, // stride (void*)0 // array buffer offset ); // Draw the triangle ! // You have to disable GL_COMPARE_R_TO_TEXTURE above in order to see anything ! //glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6); // 2*3 indices starting at 0 -> 2 triangles glDisableVertexAttribArray(0); // Swap buffers glfwSwapBuffers(window); glfwPollEvents(); } // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed while( glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE ) != GLFW_PRESS && glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == 0 ); // Cleanup VBO and shader glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer); glDeleteBuffers(1, &uvbuffer); glDeleteBuffers(1, &normalbuffer); glDeleteBuffers(1, &elementbuffer); glDeleteProgram(programID); glDeleteProgram(depthProgramID); glDeleteProgram(quad_programID); glDeleteTextures(1, &Texture); glDeleteTextures(1, &renderedTexture); glDeleteFramebuffers(1, &FramebufferName); glDeleteTextures(1, &depthTexture); glDeleteBuffers(1, &quad_vertexbuffer); glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID); // Close OpenGL window and terminate GLFW glfwTerminate(); return 0; }
着色器代码相当简单,这里就不放了。感兴趣的读者可以看下一篇,我将会在下一篇整体分析一个OpenGL程序应当具备的基本结构和一些具体问题。
附程序效果:
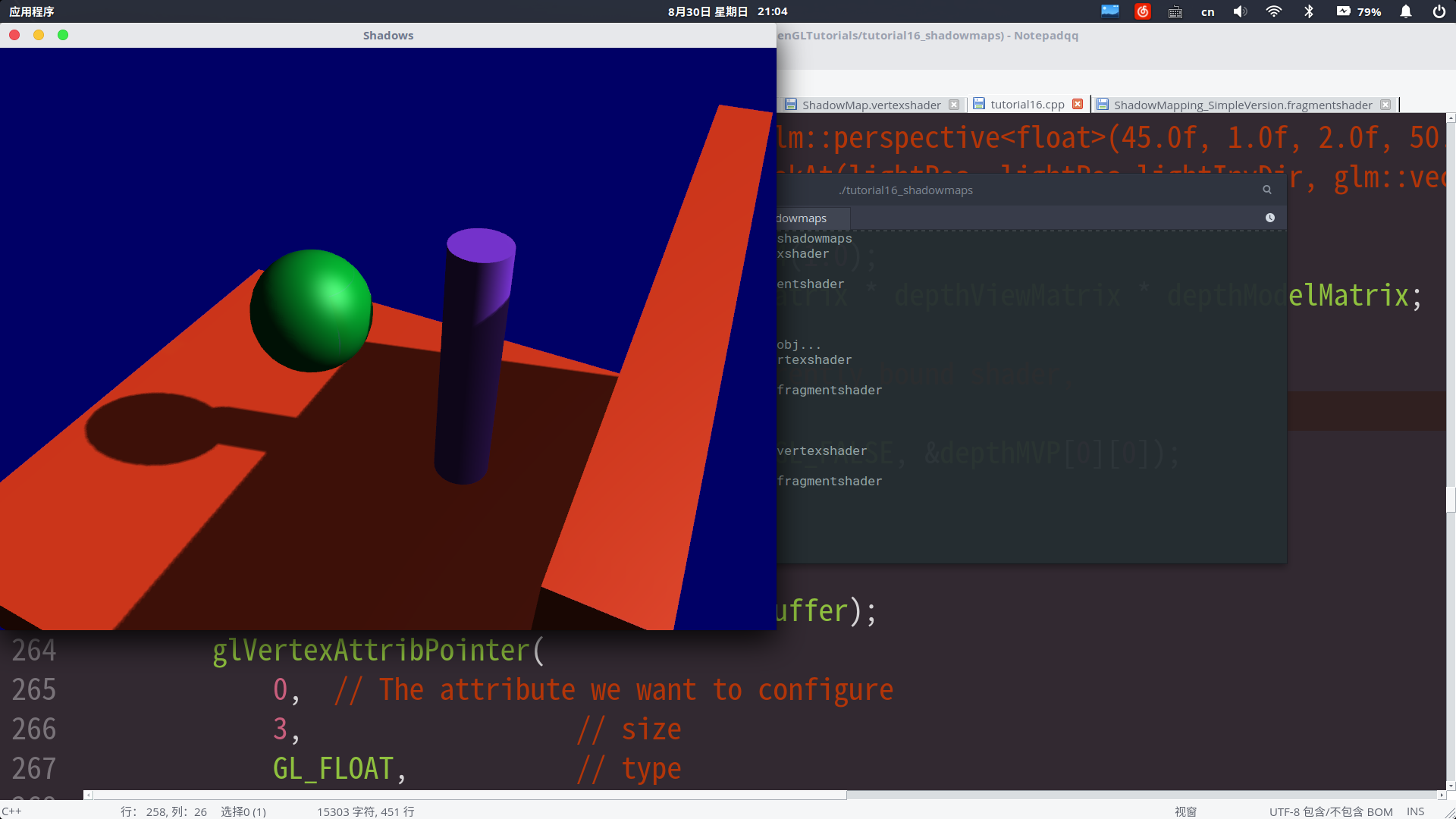 别问为什么五颜六色,问就是我把猴子的贴图不小心放进文件夹了,别说还挺好看
别问为什么五颜六色,问就是我把猴子的贴图不小心放进文件夹了,别说还挺好看
彩蛋答案:聚光灯
