java为什么会引入unsafe类
sun.misc.Unsafe至少从2004年Java1.4开始就存在于Java中了。在Java9中,为了提高JVM的可维护性,Unsafe和许多其他的东西一起都被作为内部使用类隐藏起来了。但是究竟是什么取代Unsafe不得而知,个人推测会有不止一样来取代它,那么问题来了,到底为什么要使用Unsafe?
做一些Java语言不允许但是又十分有用的事情
JDK底层的unsafe开始讲起,concurrent包下的很多都是依赖于unsafe提供的操作。
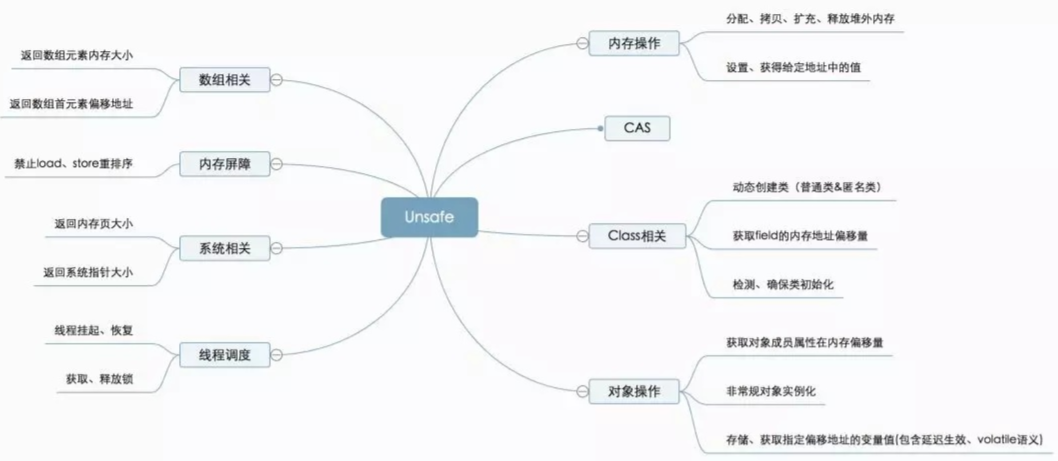
一、Unsafe简介
sun.misc.Unsafe类型从名字看,这个类应该是封装了一些不安全的操作。是JDK提供的一个工具类,unsafe里面的方法大多是native方法,你可以理解为unsafe类是JDK给你提供的一个直接调用操作系统底层功能的一个工具类,unsafe提供了非常多操作系统级别的方法。
(1)比如说通过unsafe可以让操作系统直接给你分配内存、释放内存。提供便利的同时也隐藏着很多风险。
(2)突破java语法本身的限制,直接从内存级别去操作堆里面的某个对象的数据;
(3)调用操作系统的CAS指令,实现CAS的功能
(4)操作系统层次将线程挂起和恢复
(5)提供操作系统级别的内存屏障(之前说过的Load屏障和Store屏障),读取数据强制走主存,修改数据直接刷新到主存
总之unsafe就相当于JDK给你提供的一个直接跟操作系统打交道的一个工具类,通过unsafe可做一些非常底层的指令和行为。
这个类尽管里面的方法都是public的,但是并没有办法使用它们,JDK API文档也没有提供任何关于这个类的方法的解释。总而言之,对于Unsafe类的使用都是受限制的,只有授信的代码才能获得该类的实例,当然JDK库里面的类是可以随意使用的。
unsafe提供的这些操作系统级别的方法对于JDK底层的一些工具类、上层的一些框架来说在实现层方便了许多。比如著名的并发基础工具类AQS底层就是通过unsafe提供的CAS操作来进行加锁的,加锁失败的线程又是通过unsafe提供的park、unpark操作将线程挂起和唤醒的。还有一些非常著名的开源框架比如netty分配直接内存的方式底层也还是通过unsafe分配直接内存。
例如:concurrent包是基于AQS (AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)框架的,AQS(JAVA CAS原理、unsafe、AQS)框架借助于两个类:
- Unsafe(提供CAS操作)------------------------------------《AQS之:Unsafe(java可直接操作内存(),挂起与恢复,CAS操作)》
- LockSupport(提供park/unpark操作)-------------------《Java多线程系列--AQS之 LockSupport》
从第一行的描述可以了解到Unsafe提供了硬件级别的操作,比如说获取某个属性在内存中的位置,比如说修改对象的字段值,即使它是私有的。不过Java本身就是为了屏蔽底层的差异,对于一般的开发而言也很少会有这样的需求。
举两个例子,比方说:
public native long staticFieldOffset(Field paramField);
这个方法可以用来获取给定的paramField的内存地址偏移量,这个值对于给定的field是唯一的且是固定不变的。
二、Unsafe源码分析
2.1、类图结构
2.2、数据结构
2.2、Unsafe中的lock
2.3、成员变量
2.3、构造函数
private Unsafe() {} private static final Unsafe theUnsafe = new Unsafe(); @CallerSensitive public static Unsafe getUnsafe() { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); //调用者Class对象 if (!VM.isSystemDomainLoader(caller.getClassLoader())) //判断调用者的类加载器是否为系统类加载器 //不是JAVA_HOME/jre/lib目录下jar包中的类来调用此方法getUnsafe()就会抛出异常 throw new SecurityException("Unsafe"); return theUnsafe; }
*不能直接new Unsafe(),原因是Unsafe被设计成单例模式,构造方法是私有的;
*不能通过调用Unsafe.getUnsafe()获取,因为getUnsafe被设计成只能从引导类加载器(bootstrap class loader)加载,从getUnsafe的源码中也可以看出来;
JDK的开发人员并不希望大家使用这个类。获得Unsafe实例的方法是只能调用其工厂方法getUnsafe()。上面其中的if(!VM.isSystemDomainLoader(class1.getClassLoader()))的判断是为了只有JDK内部类调用。其它应用层调用它都报错。
示例1:通过下面的例子可以测试:
package com.dxz.unsafe; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { sun.misc.Unsafe u = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); System.out.println(u); } }
在if(!VM.isSystemDomainLoader(class1.getClassLoader()))处打个断点,然后watch下Reflection.getCallerClass()的值,如下图:
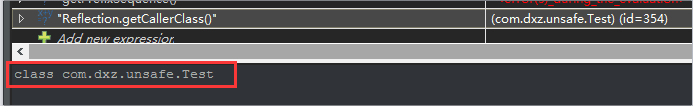
说明:根据Java 类加载器的工作原理,应用程序的类由AppLoader加载。而系统核心类,如rt.jar中的类由Bootstrap类加载器加载。Bootstrap加载器没有Java对象的对象,因此试图获得这个类加载器会返回null。所以,当一个类的类加载器为null时,说明它是由Bootstrap加载的,而这个类也极有可能是rt.jar中的类。
三、Unsafe类提供了硬件级别的原子操作,主要提供了以下功能:
1、通过Unsafe类可以分配内存,可以释放内存;
类中提供的3个本地方法allocateMemory、reallocateMemory、freeMemory分别用于分配内存,扩充内存和释放内存,与C语言中的3个方法对应。
// 分配bytes大小的堆外内存 public native long allocateMemory(long bytes); // 还可以执行从address处开始分配,分配bytes大小的堆外内存 public native long reallocateMemory(long address, long bytes); // 释放allocateMemory和reallocateMemory申请的内存块 public native void freeMemory(long address); // 将指定对象的给定offset偏移量内存块中的所有字节设置为固定值 // 相当于直接让你在内存级别直接给这个对象的变量赋值了 public native void setMemory(Object o, long offset, long bytes, byte value);
2、可以定位对象某字段的内存位置,也可以修改对象的字段值,即使它是私有的;
// 设置给定内存地址的long值 // 相当于直接在内存级别给address后面的8个字节赋值 public native void putLong(long address, long x); // 获取指定内存地址的long值 // 相当于获取address后面的8个字节的值,然后转化为十进制的long值给你 public native long getLong(long address); // 设置或获取指定内存的byte值 // 相当于获取address后面一个字节的数据,转化成十进制返回给你 public native byte getByte(long address); // 直接在内存级别给adderess地址后面的1个字节设置 public native void putByte(long address, byte x);
字段的定位:
JAVA中对象的字段的定位可能通过native staticFieldOffset方法实现,该方法返回给定field的内存地址偏移量,这个值对于给定的filed是唯一的且是固定不变的。
native getIntVolatile方法获取对象中offset偏移地址对应的整型field的值,支持volatile load语义。
native getLong方法获取对象中offset偏移地址对应的long型field的值。
数组元素定位:
Unsafe类中有很多以BASE_OFFSET结尾的常量,比如ARRAY_INT_BASE_OFFSET,ARRAY_BYTE_BASE_OFFSET等,这些常量值是通过arrayBaseOffset方法得到的。arrayBaseOffset方法是一个本地方法,可以获取数组第一个元素的偏移地址。Unsafe类中还有很多以INDEX_SCALE结尾的常量,比如 ARRAY_INT_INDEX_SCALE , ARRAY_BYTE_INDEX_SCALE等,这些常量值是通过arrayIndexScale方法得到的。arrayIndexScale方法也是一个本地方法,可以获取数组的转换因子,也就是数组中元素的增量地址。将arrayBaseOffset与arrayIndexScale配合使用,可以定位数组中每个元素在内存中的位置。
public final class Unsafe { public static final int ARRAY_INT_BASE_OFFSET; public static final int ARRAY_INT_INDEX_SCALE; public native long staticFieldOffset(Field field); public native int getIntVolatile(Object obj, long l); public native long getLong(Object obj, long l); public native int arrayBaseOffset(Class class1); public native int arrayIndexScale(Class class1); static { ARRAY_INT_BASE_OFFSET = theUnsafe.arrayBaseOffset([I); ARRAY_INT_INDEX_SCALE = theUnsafe.arrayIndexScale([I); } }
3、挂起与恢复
unsafe类提供类将一个线程挂起、讲一个挂起的线程唤醒的方法,分别是park和unpark。
park方法:
//线程调用该方法,线程将一直阻塞直到被唤醒,或者超时, //或者中断条件出现。 public native void park(boolean isAbsolute, long time);
(1) isAbsolute是否是绝对时间,当isAbsolute == true ,后面time的时间单位是ms;当为false的时候,后面time参数的时间单位是ns。
(2)time > 0时候,表示大概要将线程挂起time的时间,过了时间后自动将线程唤醒。当time = 0的时候,表示一直将线程挂起,直到有人调用unpark方法将线程唤醒。
unpark方法:
public native void unpark(Object thread);
直接将正在被挂起的thread线程唤醒,让它继续干活.
整个并发框架中对线程的阻塞和唤醒功能操作被封装在LockSupport类中,LockSupport类中有各种版本pack方法,但最终都调用了Unsafe.park()方法。
public class LockSupport { public static void unpark(Thread thread) { if (thread != null) unsafe.unpark(thread); } public static void park(Object blocker) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); setBlocker(t, blocker); unsafe.park(false, 0L); setBlocker(t, null); } public static void parkNanos(Object blocker, long nanos) { if (nanos > 0) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); setBlocker(t, blocker); unsafe.park(false, nanos); setBlocker(t, null); } } public static void parkUntil(Object blocker, long deadline) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); setBlocker(t, blocker); unsafe.park(true, deadline); setBlocker(t, null); } public static void park() { unsafe.park(false, 0L); } public static void parkNanos(long nanos) { if (nanos > 0) unsafe.park(false, nanos); } public static void parkUntil(long deadline) { unsafe.park(true, deadline); } }
由于我们自己编写的java程序不能直接使用unsafe工具类,所以啊JDK还是有一些工具类对unsafe类的功能进行封装,然后我们就直接使用这些封装的工具类即可。
4、CAS操作
这块内容比较重要,JUC提供的很多Atomic原子类、基于AQS实现的并发工具,底层都是通过CAS操作去实现的。下面我们就说说unsafe提供的cas操作:
是通过compareAndSwapXXX方法实现的
/** * 比较obj的offset处内存位置中的值和期望的值,如果相同则更新。此更新是不可中断的。 * * @param obj 需要更新的对象 * @param offset obj中整型field的偏移量 * @param expect 希望field中存在的值 * @param update 如果期望值expect与field的当前值相同,设置filed的值为这个新值 * @return 如果field的值被更改返回true */ public native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object obj, long offset, int expect, int update);
简单来说CAS操作涉及三个值,分别是待修改的值E,要修改后的新值V,以及待修改值所对应的内存位置的取值N。
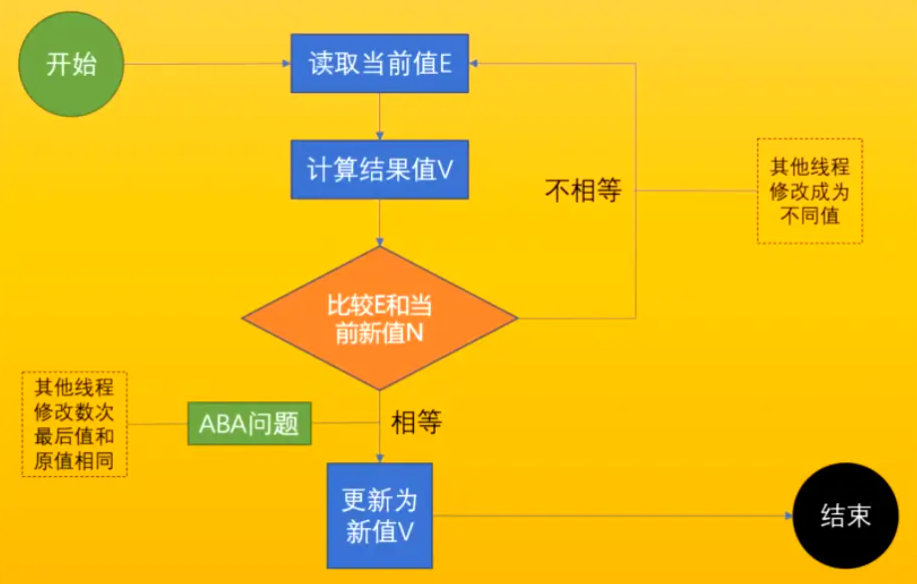
(1)首先读取并记录待修改的值E
(2)然后计算新值V
(3)比较E和该内存位置的值,如果相等->(4);如果不相等->(5);
(4)更新为新值
(5)更新失败
看下natUnsafe.cc中的c++实现吧,加深理解,其实就是将内存值与预期值作比较,判断是否相等,相等的话,写入数据,不相等不做操作,返回旧数据;
static inline bool compareAndSwap (volatile jint *addr, jint old, jint new_val) { jboolean result = false; spinlock lock; if ((result = (*addr == old))) *addr = new_val; return result; }
5、putLong,putInt,putDouble,putChar,putObject等方法,直接修改内存数据(可以越过访问权限)
上面的这些方法不受java语法的限制,提供内存级别的直接获取数据,修改数据的方式;unsafe操作内存这块内存我们目前只需要了解即可,对我们后续并发的学习影响不大。
比如说某个对象的private int value属性,这里的value属性是private的,如果这个对象没有提供对应的访问方法,在对象外部是访问不到这个value属性的对不对?
正常来说只有在对象的内部可以访问这个private属性,外部是访问不到的。
然而这个对象的数据本质上还是保存在内存里面的,而unsafe提供了直接对某个内存地址读取、修改的操作,这样就可以突破java语法的限制了。

相当于就是直接通过内存地址address,找到这块内存然后直接操作这个内存块的数据了。就是直接操作内存块的数据,接下来我们再讲讲unsafe提供的cas操作。
这里,还有put对应的get方法,很简单就是直接读取内存地址处的数据,不做举例;
我们可以举个putLong(Object, long, long)方法详细看下其具体实现,其它的类似,先看Java的源码,没啥好看的,就声明了一个native本地方法:
三个参数说明下:
Object o//对象引用
long offset//对象内存地址的偏移量
long x//写入的数据
public native void putLong(Object o, long offset, long x);
还是看下natUnsafe.cc中的c++实现吧,很简单,就是计算要写入数据的内存地址,然后写入数据,如下:
void sun::misc::Unsafe::putLong (jobject obj, jlong offset, jlong value) { jlong *addr = (jlong *) ((char *) obj + offset);//计算要修改的数据的内存地址=对象地址+成员属性地址偏移量 spinlock lock;//自旋锁,通过循环来获取锁, i386处理器需要加锁访问64位数据,如果是int,则不需要改行代码 *addr = value;//往该内存地址位置直接写入数据 }
示例2:即使User类的成员属性是私有的且没有提供对外的public方法,我们还是可以直接在它们的内存地址位置处写入数据,并成功;
package com.dxz.unsafe; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import sun.misc.Unsafe; class User { private String name = "test"; private long id = 1; private int age = 2; private double height = 1.72; @Override public String toString() { return name + "," + id + "," + age + "," + height; } } public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException { // 通过反射得到theUnsafe对应的Field对象 Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); // 设置该Field为可访问 field.setAccessible(true); // 通过Field得到该Field对应的具体对象,传入null是因为该Field为static的 Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null); User user = new User(); System.out.println(user); // 打印test,1,2,1.72 Class userClass = user.getClass(); Field name = userClass.getDeclaredField("name"); Field id = userClass.getDeclaredField("id"); Field age = userClass.getDeclaredField("age"); Field height = userClass.getDeclaredField("height"); // 直接往内存地址写数据 unsafe.putObject(user, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(name), "midified-name"); unsafe.putLong(user, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(id), 100l); unsafe.putInt(user, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(age), 101); unsafe.putDouble(user, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(height), 100.1); System.out.println(user);// 打印midified-name,100,101,100.1 } }
结果:
test,1,2,1.72
midified-name,100,101,100.1
6、getLongVolatile/putLongVolatile等等方法
这类方法使用volatile语义去存取数据,我的理解就是各个线程不缓存数据,直接在内存中读取数据;
7、unsafe提供了几种内存屏障
// 在该方法之前的所有读操作,一定在load屏障之前执行完成 public native void loadFence(); // 在该方法之前的所有写操作,一定在store屏障之前执行完成 public native void storeFence(); // 在该方法之前的所有读写操作,一定在full屏障之前执行完成,这个内存屏障相当于上面两个的合体功能 public native void fullFence();
四、unsafe的cas功能底层是怎么保证原子性的
CAS操作的时候,是直接通过( 对象地址 + 对象内部属性偏移量offset )直接定位到要修改的变量在内存的位置,然后在内存级别的比较数据和修改数据。
操作的时候直接根据 o对象地址 + offset偏移量地址,定位到demo属性在内存的位置,然后直接操作内存修改数据。
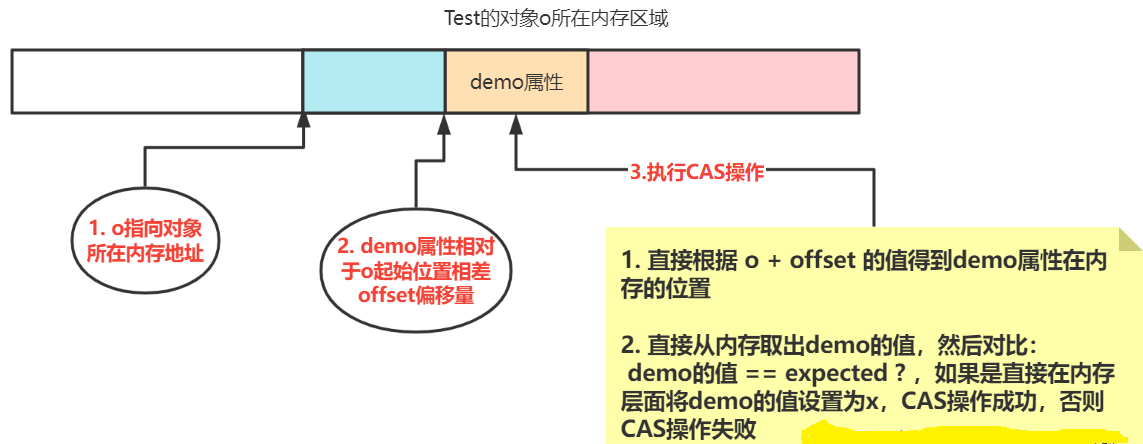
由于CPU是不会直接读写主存的,数据读取的时候还是先将数据读取到高速缓存,然后通过高速缓存传递给CPU.写数据的时候也是先高速缓存,然后再将高速缓存的数据写入内存;于是可以得到下面的图形:
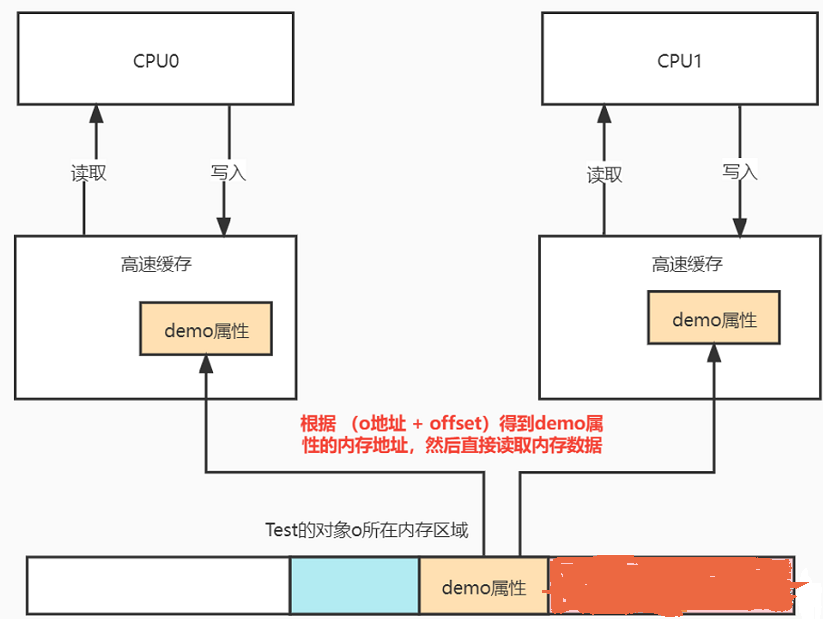
多个线程或者多个CPU同时读取demo属性的时候,可能会导致数据不一致。
CAS底层硬件使用锁保证原子性
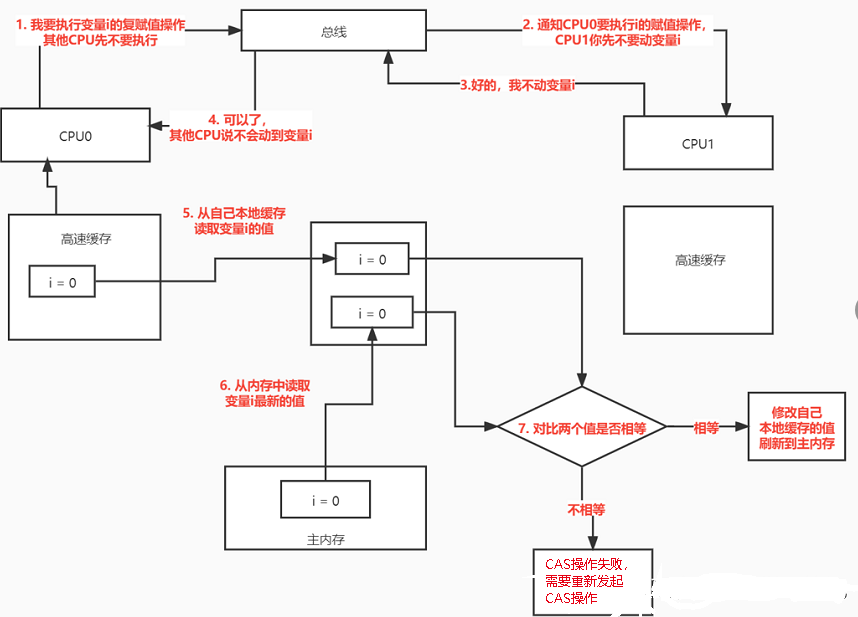
(1)首先CPU0要执行CAS操作对变量 i 进行赋值,然后CPU0告诉总线说我要申请单独操作变量 i 的权限,帮我告诉一下CPU1等其它的CPU
(2)总线通知到了CPU1,CPU1告诉总线,好的,我不会操作数据,让CPU0大胆的去操作吧
(3)然后总线告诉CPU0,你可以独占变量i的操作了,其它的cpu表示不会干扰你
(4)然后CPU0从自己的缓存读取 变量 i 的值;然后又根据 (o对象地址 + offset偏移量地址) 直接定位到变量 i 在内存的位置,直接读取变量i在内存的值
(5)接下来的操作就简单了,由于不会有人干扰,直接对比缓存的值和内存的值是否一致就可以了,如果一致,我直接修改,然后刷回主内存;如果不一致,说明我本地的数据不是最新的,需要重新申请CAS操作。
这个就是CAS在底层操作的原理,它底层还是通过加锁来保证原子性的,这个加锁是在硬件级别的,非常轻量级的。
Unsafe中CAS部分的实现
unsafe.cpp,这个就是对应jvm相关的c++实现类了。
在该文件中搜索compareAndSwapInt,此时可以看到对应的JNI方法为Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt,具体代码如下
UNSAFE_ENTRY(jboolean, Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt(JNIEnv *env, jobject unsafe, jobject obj, jlong offset, jint e, jint x)) UnsafeWrapper("Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt"); oop p = JNIHandles::resolve(obj); // 查找要指定的对象 jint* addr = (jint *) index_oop_from_field_offset_long(p, offset); // 获取操作对象偏移量为offset的字段的地址 return (jint)(Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e)) == e; //执行Atomic类中的cmpxchg UNSAFE_END
可以看到最后会调用到Atomic::cmpxchg里面的函数,这个根据不同操作系统和不同CPU会有不同的实现,比如linux_64x的,对应类就是hotspot\src\os_cpu\linux_x86\vm\atomic_linux_x86.inline.hpp, 而windows_64x的,对应类就是hotspot\src\os_cpu\windows_x86\vm\atomic_windows_x86.inline.hpp。这里我们以linux_64x的为例,查看Atomic::cmpxchg的实现,atomic_linux_x86.inline.hpp。
inline jint Atomic::cmpxchg (jint exchange_value, volatile jint* dest, jint compare_value) { int mp = os::is_MP(); __asm__ volatile (LOCK_IF_MP(%4) "cmpxchgl %1,(%3)" : "=a" (exchange_value) : "r" (exchange_value), "a" (compare_value), "r" (dest), "r" (mp) : "cc", "memory"); return exchange_value;
os::is_MP():判断当前系统是否为多核系统,如果是就给总线加锁,所以同一芯片上的其他处理器就暂时不能通过总线访问内存,保证了该指令在多处理器环境下的原子性。
LOCK_IF_MP(mp):LOCK_IF_MP 是一个宏定义,
宏定义用"cmp $0, " #mp "检查核心是否为单核:
- 是:跳到
1f,执行CPU指令cmpxchgl %1,(%3)。 - 不是:则跳到
1f前先通过lock给总线上锁,令物理处理器的其他核心不能通过总线访存,保证指令操作的原子性。
LOCK_IF_MP根据当前操作系统是否为多核处理器,来决定是否为cmpxchg指令添加lock前缀。如果有lock前缀的话,则会根据CPU不同会采用锁总线或者锁cache line的方式,来实现缓存一致性。
四、JDK或开源框架中使用
LockSupport中park阻塞,和unpark解除阻塞。
concurrent中中的cas调用。
五、源码
Unsafe源码:
//下面是sun.misc.Unsafe.java类源码 package sun.misc; import java.lang.reflect.Field; /*** * This class should provide access to low-level operations and its * use should be limited to trusted code. Fields can be accessed using * memory addresses, with undefined behaviour occurring if invalid memory * addresses are given. * 这个类提供了一个更底层的操作并且应该在受信任的代码中使用。可以通过内存地址 * 存取fields,如果给出的内存地址是无效的那么会有一个不确定的运行表现。 * * @author Tom Tromey (tromey@redhat.com) * @author Andrew John Hughes (gnu_andrew@member.fsf.org) */ public class Unsafe { // Singleton class. private static Unsafe unsafe = new Unsafe(); /*** * Private default constructor to prevent creation of an arbitrary * number of instances. * 使用私有默认构造器防止创建多个实例 */ private Unsafe() { } /*** * Retrieve the singleton instance of <code>Unsafe</code>. The calling * method should guard this instance from untrusted code, as it provides * access to low-level operations such as direct memory access. * 获取<code>Unsafe</code>的单例,这个方法调用应该防止在不可信的代码中实例, * 因为unsafe类提供了一个低级别的操作,例如直接内存存取。 * * @throws SecurityException if a security manager exists and prevents * access to the system properties. * 如果安全管理器不存在或者禁止访问系统属性 */ public static Unsafe getUnsafe() { SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) sm.checkPropertiesAccess(); return unsafe; } /*** * Returns the memory address offset of the given static field. * The offset is merely used as a means to access a particular field * in the other methods of this class. The value is unique to the given * field and the same value should be returned on each subsequent call. * 返回指定静态field的内存地址偏移量,在这个类的其他方法中这个值只是被用作一个访问 * 特定field的一个方式。这个值对于 给定的field是唯一的,并且后续对该方法的调用都应该 * 返回相同的值。 * * @param field the field whose offset should be returned. * 需要返回偏移量的field * @return the offset of the given field. * 指定field的偏移量 */ public native long objectFieldOffset(Field field); /*** * Compares the value of the integer field at the specified offset * in the supplied object with the given expected value, and updates * it if they match. The operation of this method should be atomic, * thus providing an uninterruptible way of updating an integer field. * 在obj的offset位置比较integer field和期望的值,如果相同则更新。这个方法 * 的操作应该是原子的,因此提供了一种不可中断的方式更新integer field。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the integer field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中整型field的偏移量 * @param expect the expected value of the field. * 希望field中存在的值 * @param update the new value of the field if it equals <code>expect</code>. * 如果期望值expect与field的当前值相同,设置filed的值为这个新值 * @return true if the field was changed. * 如果field的值被更改 */ public native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object obj, long offset, int expect, int update); /*** * Compares the value of the long field at the specified offset * in the supplied object with the given expected value, and updates * it if they match. The operation of this method should be atomic, * thus providing an uninterruptible way of updating a long field. * 在obj的offset位置比较long field和期望的值,如果相同则更新。这个方法 * 的操作应该是原子的,因此提供了一种不可中断的方式更新long field。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the long field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @param expect the expected value of the field. * 希望field中存在的值 * @param update the new value of the field if it equals <code>expect</code>. * 如果期望值expect与field的当前值相同,设置filed的值为这个新值 * @return true if the field was changed. * 如果field的值被更改 */ public native boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object obj, long offset, long expect, long update); /*** * Compares the value of the object field at the specified offset * in the supplied object with the given expected value, and updates * it if they match. The operation of this method should be atomic, * thus providing an uninterruptible way of updating an object field. * 在obj的offset位置比较object field和期望的值,如果相同则更新。这个方法 * 的操作应该是原子的,因此提供了一种不可中断的方式更新object field。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the object field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中object型field的偏移量 * @param expect the expected value of the field. * 希望field中存在的值 * @param update the new value of the field if it equals <code>expect</code>. * 如果期望值expect与field的当前值相同,设置filed的值为这个新值 * @return true if the field was changed. * 如果field的值被更改 */ public native boolean compareAndSwapObject(Object obj, long offset, Object expect, Object update); /*** * Sets the value of the integer field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value. This is an ordered or lazy * version of <code>putIntVolatile(Object,long,int)</code>, which * doesn't guarantee the immediate visibility of the change to other * threads. It is only really useful where the integer field is * <code>volatile</code>, and is thus expected to change unexpectedly. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的整型field的值为指定值。这是一个有序或者 * 有延迟的<code>putIntVolatile</cdoe>方法,并且不保证值的改变被其他线程立 * 即看到。只有在field被<code>volatile</code>修饰并且期望被意外修改的时候 * 使用才有用。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the integer field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中整型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 * @see #putIntVolatile(Object,long,int) */ public native void putOrderedInt(Object obj, long offset, int value); /*** * Sets the value of the long field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value. This is an ordered or lazy * version of <code>putLongVolatile(Object,long,long)</code>, which * doesn't guarantee the immediate visibility of the change to other * threads. It is only really useful where the long field is * <code>volatile</code>, and is thus expected to change unexpectedly. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的long型field的值为指定值。这是一个有序或者 * 有延迟的<code>putLongVolatile</cdoe>方法,并且不保证值的改变被其他线程立 * 即看到。只有在field被<code>volatile</code>修饰并且期望被意外修改的时候 * 使用才有用。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the long field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 * @see #putLongVolatile(Object,long,long) */ public native void putOrderedLong(Object obj, long offset, long value); /*** * Sets the value of the object field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value. This is an ordered or lazy * version of <code>putObjectVolatile(Object,long,Object)</code>, which * doesn't guarantee the immediate visibility of the change to other * threads. It is only really useful where the object field is * <code>volatile</code>, and is thus expected to change unexpectedly. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的object型field的值为指定值。这是一个有序或者 * 有延迟的<code>putObjectVolatile</cdoe>方法,并且不保证值的改变被其他线程立 * 即看到。只有在field被<code>volatile</code>修饰并且期望被意外修改的时候 * 使用才有用。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the object field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 */ public native void putOrderedObject(Object obj, long offset, Object value); /*** * Sets the value of the integer field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value, with volatile store semantics. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的整型field的值为指定值。支持volatile store语义 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the integer field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中整型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 */ public native void putIntVolatile(Object obj, long offset, int value); /*** * Retrieves the value of the integer field at the specified offset in the * supplied object with volatile load semantics. * 获取obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的整型field的值,支持volatile load语义。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to read. * 包含需要去读取的field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the integer field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中整型field的偏移量 */ public native int getIntVolatile(Object obj, long offset); /*** * Sets the value of the long field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value, with volatile store semantics. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的long型field的值为指定值。支持volatile store语义 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the long field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 * @see #putLong(Object,long,long) */ public native void putLongVolatile(Object obj, long offset, long value); /*** * Sets the value of the long field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的long型field的值为指定值。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the long field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 * @see #putLongVolatile(Object,long,long) */ public native void putLong(Object obj, long offset, long value); /*** * Retrieves the value of the long field at the specified offset in the * supplied object with volatile load semantics. * 获取obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的long型field的值,支持volatile load语义。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to read. * 包含需要去读取的field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the long field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @see #getLong(Object,long) */ public native long getLongVolatile(Object obj, long offset); /*** * Retrieves the value of the long field at the specified offset in the * supplied object. * 获取obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的long型field的值 * * @param obj the object containing the field to read. * 包含需要去读取的field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the long field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中long型field的偏移量 * @see #getLongVolatile(Object,long) */ public native long getLong(Object obj, long offset); /*** * Sets the value of the object field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value, with volatile store semantics. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的object型field的值为指定值。支持volatile store语义 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the object field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中object型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 * @see #putObject(Object,long,Object) */ public native void putObjectVolatile(Object obj, long offset, Object value); /*** * Sets the value of the object field at the specified offset in the * supplied object to the given value. * 设置obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的object型field的值为指定值。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to modify. * 包含需要修改field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the object field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中object型field的偏移量 * @param value the new value of the field. * field将被设置的新值 * @see #putObjectVolatile(Object,long,Object) */ public native void putObject(Object obj, long offset, Object value); /*** * Retrieves the value of the object field at the specified offset in the * supplied object with volatile load semantics. * 获取obj对象中offset偏移地址对应的object型field的值,支持volatile load语义。 * * @param obj the object containing the field to read. * 包含需要去读取的field的对象 * @param offset the offset of the object field within <code>obj</code>. * <code>obj</code>中object型field的偏移量 */ public native Object getObjectVolatile(Object obj, long offset); /*** * Returns the offset of the first element for a given array class. * To access elements of the array class, this value may be used along with * with that returned by * <a href="#arrayIndexScale"><code>arrayIndexScale</code></a>, * if non-zero. * 获取给定数组中第一个元素的偏移地址。 * 为了存取数组中的元素,这个偏移地址与<a href="#arrayIndexScale"><code>arrayIndexScale * </code></a>方法的非0返回值一起被使用。 * @param arrayClass the class for which the first element's address should * be obtained. * 第一个元素地址被获取的class * @return the offset of the first element of the array class. * 数组第一个元素 的偏移地址 * @see arrayIndexScale(Class) */ public native int arrayBaseOffset(Class arrayClass); /*** * Returns the scale factor used for addressing elements of the supplied * array class. Where a suitable scale factor can not be returned (e.g. * for primitive types), zero should be returned. The returned value * can be used with * <a href="#arrayBaseOffset"><code>arrayBaseOffset</code></a> * to access elements of the class. * 获取用户给定数组寻址的换算因子.一个合适的换算因子不能返回的时候(例如:基本类型), * 返回0.这个返回值能够与<a href="#arrayBaseOffset"><code>arrayBaseOffset</code> * </a>一起使用去存取这个数组class中的元素 * * @param arrayClass the class whose scale factor should be returned. * @return the scale factor, or zero if not supported for this array class. */ public native int arrayIndexScale(Class arrayClass); /*** * Releases the block on a thread created by * <a href="#park"><code>park</code></a>. This method can also be used * to terminate a blockage caused by a prior call to <code>park</code>. * This operation is unsafe, as the thread must be guaranteed to be * live. This is true of Java, but not native code. * 释放被<a href="#park"><code>park</code></a>创建的在一个线程上的阻塞.这个 * 方法也可以被使用来终止一个先前调用<code>park</code>导致的阻塞. * 这个操作操作时不安全的,因此线程必须保证是活的.这是java代码不是native代码。 * @param thread the thread to unblock. * 要解除阻塞的线程 */ public native void unpark(Thread thread); /*** * Blocks the thread until a matching * <a href="#unpark"><code>unpark</code></a> occurs, the thread is * interrupted or the optional timeout expires. If an <code>unpark</code> * call has already occurred, this also counts. A timeout value of zero * is defined as no timeout. When <code>isAbsolute</code> is * <code>true</code>, the timeout is in milliseconds relative to the * epoch. Otherwise, the value is the number of nanoseconds which must * occur before timeout. This call may also return spuriously (i.e. * for no apparent reason). * 阻塞一个线程直到<a href="#unpark"><code>unpark</code></a>出现、线程 * 被中断或者timeout时间到期。如果一个<code>unpark</code>调用已经出现了, * 这里只计数。timeout为0表示永不过期.当<code>isAbsolute</code>为true时, * timeout是相对于新纪元之后的毫秒。否则这个值就是超时前的纳秒数。这个方法执行时 * 也可能不合理地返回(没有具体原因) * * @param isAbsolute true if the timeout is specified in milliseconds from * the epoch. * 如果为true timeout的值是一个相对于新纪元之后的毫秒数 * @param time either the number of nanoseconds to wait, or a time in * milliseconds from the epoch to wait for. * 可以是一个要等待的纳秒数,或者是一个相对于新纪元之后的毫秒数直到 * 到达这个时间点 */ public native void park(boolean isAbsolute, long time); }
六、示例
下面这个例子演示了简单的修改一个byte[]的数据。
这个例子在eclipse里不能直接编译,要到项目的属性,Java Compiler,Errors/Warnings中Forbidden reference(access rules)中设置为warning。
另外,因为sun.misc.Unsafe包不能直接使用,所有代码里用反射的技巧得到了一个Unsafe的实例。
package com.dxz.unsafe; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.Arrays; import sun.misc.Unsafe; public class Test3 { private static int byteArrayBaseOffset; public static void main(String[] args) throws SecurityException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { // 通过反射得到theUnsafe对应的Field对象 Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); // 设置该Field为可访问 theUnsafe.setAccessible(true); // 通过Field得到该Field对应的具体对象,传入null是因为该Field为static的 Unsafe UNSAFE = (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null); System.out.println(UNSAFE); byte[] data = new byte[10]; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); //arrayBaseOffset方法是一个本地方法,可以获取数组第一个元素的偏移地址 byteArrayBaseOffset = UNSAFE.arrayBaseOffset(byte[].class); System.out.println(byteArrayBaseOffset); //putByte直接修改内存数据 UNSAFE.putByte(data, byteArrayBaseOffset, (byte) 1); UNSAFE.putByte(data, byteArrayBaseOffset + 5, (byte) 5); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); } }
运行结果:
sun.misc.Unsafe@15db9742 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] 16 [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0]
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/lizc_lizc/article/details/107883070?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.1&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7EBlogCommendFromBaidu%7ERate-1.pc_relevant_paycolumn_v3&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7EBlogCommendFromBaidu%7ERate-1.pc_relevant_paycolumn_v3&utm_relevant_index=2
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ch5FxxNnB2C96cfdrvofRQ