基于 3.10.90 内核代码
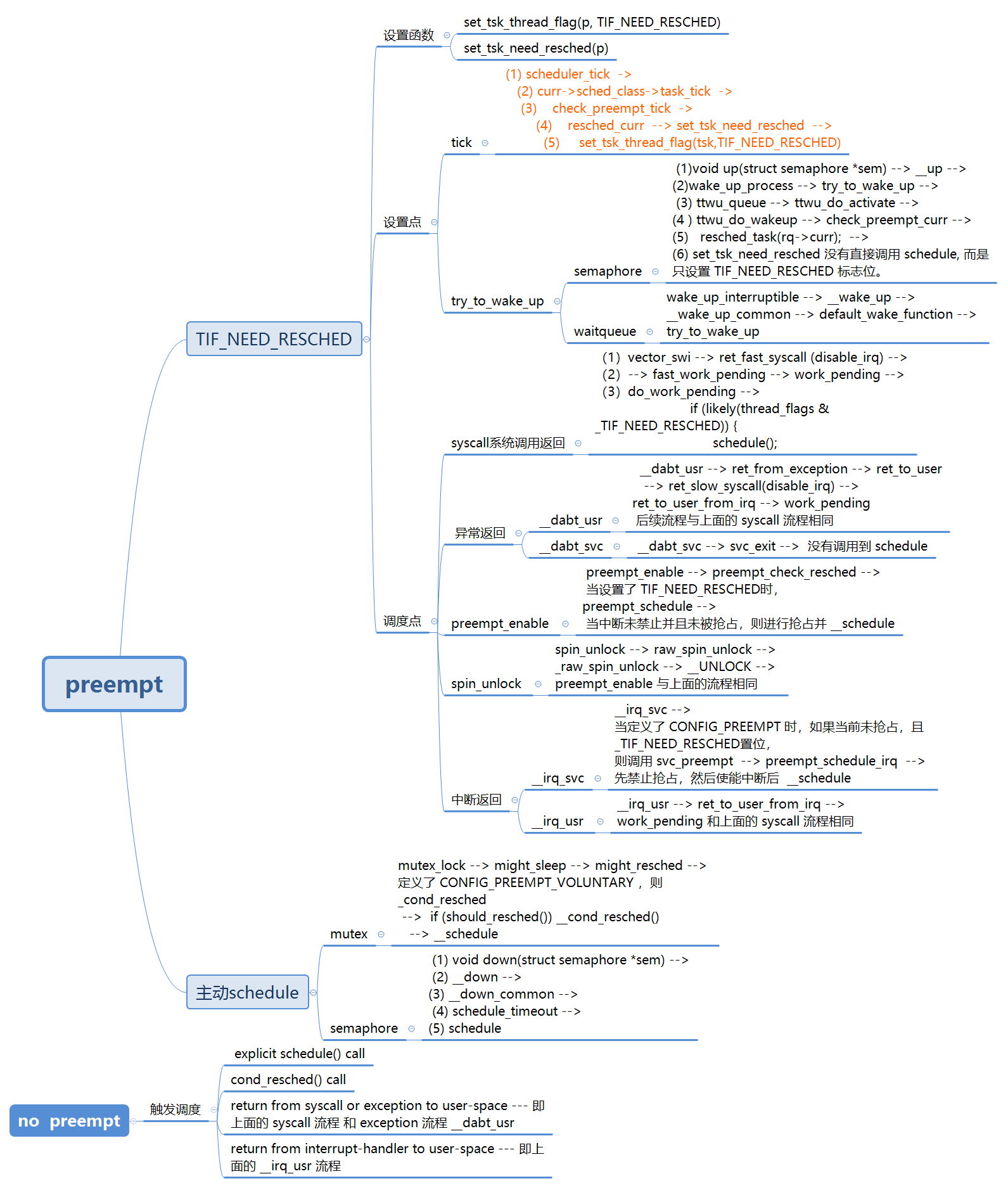
在 kernel\sched\core.c 里, 对于 __schedule 有如下注释:
/*
* __schedule() is the main scheduler function.
*
* The main means of driving the scheduler and thus entering this function are:
*
* 1. Explicit blocking: mutex, semaphore, waitqueue, etc.
* (1) mutext:
* mutex_lock --> might_sleep --> might_resched --> 定义了 CONFIG_PREEMPT_VOLUNTARY ,则 _cond_resched
* --> if (should_resched()) __cond_resched() --> __schedule
* (2) semaphore:
* void down(struct semaphore *sem) --> __down --> __down_common --> schedule_timeout --> schedule
* void up(struct semaphore *sem) --> __up --> wake_up_process --> try_to_wake_up --> ttwu_queue
* --> ttwu_do_activate --> ttwu_do_wakeup --> check_preempt_curr
* --> resched_task(rq->curr); --> set_tsk_need_resched 没有直接调用 schedule, 而是只设置 TIF_NEED_RESCHED 标志位。
* (3) waitqueue
* wake_up_interruptible --> __wake_up --> __wake_up_common --> default_wake_function --> try_to_wake_up
*
* 2. TIF_NEED_RESCHED flag is checked on interrupt and userspace return
* paths. For example, see arch/x86/entry_64.S.
*
* To drive preemption between tasks, the scheduler sets the flag in timer
* interrupt handler scheduler_tick().
* scheduler_tick 设置 TIF_NEED_RESCHED 的流程如下:
* scheduler_tick --> curr->sched_class->task_tick --> task_tick_fair
* --> check_preempt_tick --> resched_task --> set_tsk_need_resched
* --> set_tsk_thread_flag(tsk,TIF_NEED_RESCHED);
*
* 3. Wakeups don't really cause entry into schedule(). They add a
* task to the run-queue and that's it.
* wakeups 设置 TIF_NEED_RESCHED 的过程为:
* wake_up_process --> try_to_wake_up --> ttwu_queue
* --> ttwu_do_activate --> ttwu_do_wakeup --> check_preempt_curr
* --> resched_task(rq->curr); --> set_tsk_need_resched
*
* Now, if the new task added to the run-queue preempts the current
* task, then the wakeup sets TIF_NEED_RESCHED and schedule() gets
* called on the nearest possible occasion: *
*
* - If the kernel is preemptible (CONFIG_PREEMPT=y):
*
* - in syscall or exception context, at the next outmost
* preempt_enable(). (this might be as soon as the wake_up()'s
* spin_unlock()!)
* (1) syscall 流程: vector_swi --> ret_fast_syscall (disable_irq) -->
* --> fast_work_pending --> work_pending --> do_work_pending -->
* if (likely(thread_flags & _TIF_NEED_RESCHED)) {
* schedule();
* (2) exception 流程:
* __dabt_usr --> ret_from_exception --> ret_to_user
* --> ret_slow_syscall(disable_irq) --> ret_to_user_from_irq --> work_pending
* 后续流程与上面的 syscall 流程相同
* __dabt_svc --> svc_exit --> 没有调用到 schedule
* (3) preempt_enable --> preempt_check_resched -->
* 当设置了 TIF_NEED_RESCHED 时,preempt_schedule -->
* 当中断未禁止并且未被抢占,则进行抢占并 __schedule
*
* (4) spin_unlock --> raw_spin_unlock --> _raw_spin_unlock --> __UNLOCK --> preempt_enable 与上面的流程相同
*
* - in IRQ context, return from interrupt-handler to
* preemptible context
* (1) __irq_svc --> 当定义了 CONFIG_PREEMPT 时,如果当前未抢占,且 _TIF_NEED_RESCHED置位,则
* 调用 svc_preempt --> preempt_schedule_irq --> 先禁止抢占,然后使能中断后 __schedule 。
* (2) __irq_usr --> ret_to_user_from_irq --> work_pending 和上面的 syscall 流程相同
*
* - If the kernel is not preemptible (CONFIG_PREEMPT is not set)
* then at the next:
*
* - cond_resched() call
* - explicit schedule() call
* - return from syscall or exception to user-space --- 即上面的 syscall 流程 和 exception 流程 __dabt_usr
* - return from interrupt-handler to user-space --- 即上面的 __irq_usr 流程
*/
spinlock
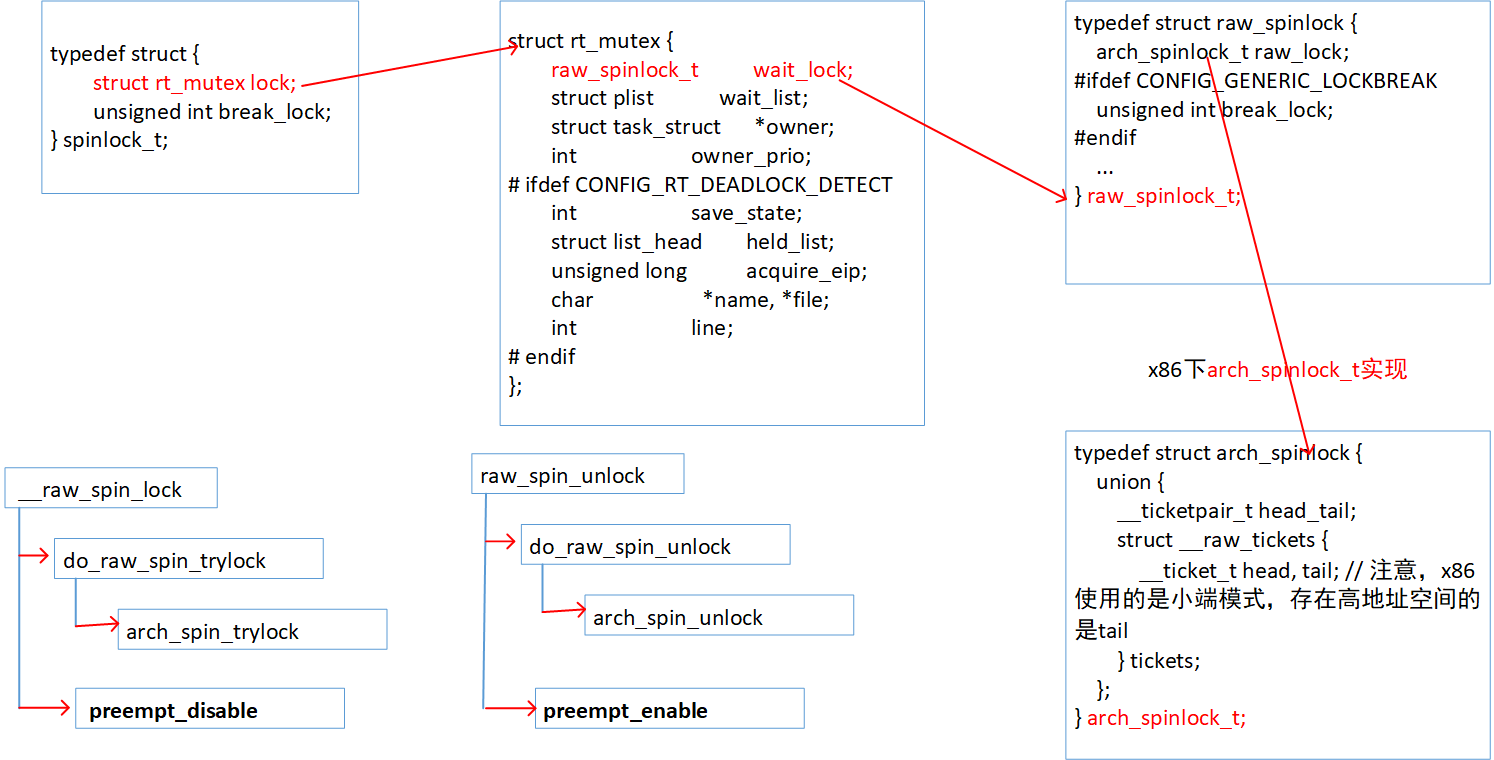
(1)自旋锁适用于SMP系统,UP系统用spinlock是作死。
(2)保护模式下禁止内核抢占的方法:1、运行终端服务例程时2、运行软中断和tasklet时3、设置本地CPU计数器preempt_count
(3)自旋锁的忙等待的实际意义是:尝试获取自旋锁的还有一个进程不断尝试获取被占用的自旋锁,中间仅仅pause一下!
(4)在抢占式内核的spin_lock宏中,第一次关抢占,目的是防止死锁(防止一个已经获取自旋锁而未释放的进程被抢占!
为什么要关闭抢占?
static inline unsigned long __raw_spin_lock_irqsave(raw_spinlock_t *lock) { unsigned long flags; local_irq_save(flags); preempt_disable(); spin_acquire(&lock->dep_map, 0, 0, _RET_IP_);
关闭抢占是在所有spin_lock中都会做的,下面阐述禁止抢占的原因:
如果不禁止内核抢断(或者不禁止中断),可能会有以下的情况发生(假设进程B比进程A具有更高的优先级):
进程A获得spinlock lock
进程B运行(抢占进程A)
进程B获取spinlock lock
由于进程B比进程A优先级高,所以进程B在进程A之前运行,而进程B需要进程A释放lock之后才能运行,于是,死锁
关于preempt_enable 和 preempt_disable
允许抢占和禁止抢占。
例如:内核态程序 和 中断处理程序的互斥
因为中断是异步的(不只要何时发生中断,也即随时可能发生中断),因此如果内核态的程序使用了和中断处理程序中相同的数据结构,那么必须进行互斥访问。
|
load %r0, counter add %r0,1 //发生中断 store %r0,conter |
如果在第二条指令执行时发生中断,而中断处理程序也需要将counter加1等操作,那么counter变量的值就会变得紊乱。
因此,只要非中断处理代码要更新一个与中断处理程序共享的数据结构,那么它就首先禁止中断,执行临界段,然后再重新允许中断。在linux中,如下
preempt_disable(); load %r0, counter add %r0,1 //发生中断 store %r0,conter preempt_enable();
禁用/使能可抢占条件的函数
#if defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_PREEMPT) || defined(CONFIG_PREEMPT_TRACER) extern void add_preempt_count(int val); extern void sub_preempt_count(int val); #else # define add_preempt_count(val) do { preempt_count() += (val); } while (0) # define sub_preempt_count(val) do { preempt_count() -= (val); } while (0) #endif #define inc_preempt_count() add_preempt_count(1) #define dec_preempt_count() sub_preempt_count(1) #define preempt_count() (current_thread_info()->preempt_count) #define preempt_disable() \ do { \ inc_preempt_count(); \ barrier(); \ } while (0) #define preempt_enable_no_resched() \ do { \ barrier(); \ dec_preempt_count(); \ } while (0) #define preempt_check_resched() \ do { \ if (unlikely(test_thread_flag(TIF_NEED_RESCHED))) \ preempt_schedule(); \ } while (0) #define preempt_enable() \ do { \ preempt_enable_no_resched(); \ barrier(); \ preempt_check_resched(); \ } while (0) //检查可抢占条件 # define preemptible() (preempt_count() == 0 && !irqs_disabled()) //自旋锁的加锁与解锁 void __lockfunc _spin_lock(spinlock_t *lock) { preempt_disable(); spin_acquire(&lock->dep_map, 0, 0, _RET_IP_); LOCK_CONTENDED(lock, _raw_spin_trylock, _raw_spin_lock); } void __lockfunc _spin_unlock(spinlock_t *lock) { spin_release(&lock->dep_map, 1, _RET_IP_); _raw_spin_unlock(lock); preempt_enable(); } //设置need_resched标志的函数 static inline void set_tsk_need_resched(struct task_struct *tsk) { set_tsk_thread_flag(tsk,TIF_NEED_RESCHED); } static inline void clear_tsk_need_resched(struct task_struct *tsk) { clear_tsk_thread_flag(tsk,TIF_NEED_RESCHED); } static inline int test_tsk_need_resched(struct task_struct *tsk) { return unlikely(test_tsk_thread_flag(tsk,TIF_NEED_RESCHED)); } //时钟中断时调用的task_tick()函数,当时间片消耗完之后,设置need_resched标志 static void task_tick_rt(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int queued) { update_curr_rt(rq); watchdog(rq, p); /* * RR tasks need a special form of timeslice management. * FIFO tasks have no timeslices. */ if (p->policy != SCHED_RR) return; if (--p->rt.time_slice) return; p->rt.time_slice = DEF_TIMESLICE; /* * Requeue to the end of queue if we are not the only element * on the queue: */ if (p->rt.run_list.prev != p->rt.run_list.next) { requeue_task_rt(rq, p, 0); set_tsk_need_resched(p); } } //设置任务的need_resched标志,并触发任务所在CPU的调度器。 static void resched_task(struct task_struct *p) { int cpu; assert_spin_locked(&task_rq(p)->lock); if (unlikely(test_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_NEED_RESCHED))) return; set_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_NEED_RESCHED); cpu = task_cpu(p); if (cpu == smp_processor_id()) return; /* NEED_RESCHED must be visible before we test polling */ smp_mb(); if (!tsk_is_polling(p)) smp_send_reschedule(cpu); }