______________________每逢七夕,小雨淅淅沥沥天降,音乐雷声,我今天就呆在宿舍啦嘞。嘻嘻。




且看这道训练的试题:





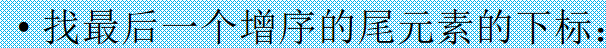


一个比较投巧的方案是:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a;
while(cin>>a && a!="#")
{
if(next_permutation(a.begin(),a.end())) cout<<a<<endl;
//在algorithm.h文件里,有直接能够使用的字典顺序的函数next_permutation(),
else cout<<"No Successor"<<endl;
}
return 0;
} 可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/lcchuguo/p/5047051.html



STL提供了两个用来计算排列组合关系的算法,分别是next_permutation和prev_permutation。
组合数学中经常用到排列,这里介绍一个计算序列全排列的函数:next_permutation(start,end),和prev_permutation(start,end)。这两个函数作用是一样的,区别就在于前者求的是当前排列的下一个排列,后一个求的是当前排列的上一个排列。至于这里的“前一个”和“后一个”,我们可以把它理解为序列的字典序的前后,严格来讲,就是对于当前序列pn,他的下一个序列pn+1满足:不存在另外的序列pm,使pn<pm<pn+1.
牛刀小试:
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int main() { int ans[4]={1,2,3,4}; sort(ans,ans+4); do { for(int i=0;i<4;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; }while(next_permutation(ans,ans+4)); return 0; }
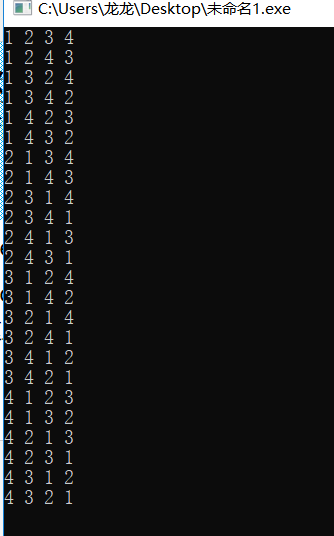
另外,需要强调的是,next_permutation()在使用前需要对欲排列数组按升序排序,否则只能找出该序列之后的全排列数。
题目:https://vjudge.net/contest/317909?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg#problem/C
codes:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char s[12];
int n;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
cin>>s;
int len=strlen(s);//求字符数组的长度的函数strlen()
sort(s,s+len);
do
{
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) cout<<s[i];
cout<<endl;
}while(next_permutation(s,s+len));
cout<<"
";
}
return 0;
}





_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________>这个问题的解决放在我的另一篇blog上啦!