<1>if-else的使用格式

1 if 条件: 2 满足条件时要做的事情1 3 满足条件时要做的事情2 4 满足条件时要做的事情3 5 ...(省略)... 6 else: 7 不满足条件时要做的事情1 8 不满足条件时要做的事情2 9 不满足条件时要做的事情3 10 ...(省略)...
看一下下面的例子

1 menpiao= 1 # 用1代表有门票,0代表没有门票 2 if menpiao == 1: 3 print('有门票,可以陪女朋友看电影!~~') 4 else: 5 print("亲爱的,那就下次见了,一票难求啊~~~~(>_<)~~~~")
<1> elif的功能
elif的使用格式如下:

1 if xxx1: 2 事情1 3 elif xxx2: 4 事情2 5 elif xxx3: 6 事情3
说明:
- 当xxx1满足时,执行事情1,然后整个if结束
- 当xxx1不满足时,那么判断xxx2,如果xxx2满足,则执行事情2,然后整个if结束
- 当xxx1不满足时,xxx2也不满足,如果xxx3满足,则执行事情3,然后整个if结束
demo:

score = 77
if score>=90 and score<=100:
print('本次考试,等级为A')
elif score>=80 and score<90:
print('本次考试,等级为B')
elif score>=70 and score<80:
print('本次考试,等级为C')
elif score>=60 and score<70:
print('本次考试,等级为D')
elif score>=0 and score<60:
print('本次考试,等级为E')
<2> 注意点
可以和else一起使用

if 性别为男性: 输出男性的特征 ... elif 性别为女性: 输出女性的特征 ... else: 第三种性别的特征 ...
-
说明:
- 当 “性别为男性” 满足时,执行 “输出男性的特征”的相关代码
- 当 “性别为男性” 不满足时,如果 “性别为女性”满足,则执行 “输出女性的特征”的相关代码
- 当 “性别为男性” 不满足,“性别为女性”也不满足,那么久默认执行else后面的代码,即 “第三种性别的特征”相关代码
- elif必须和if一起使用,否则出错
-
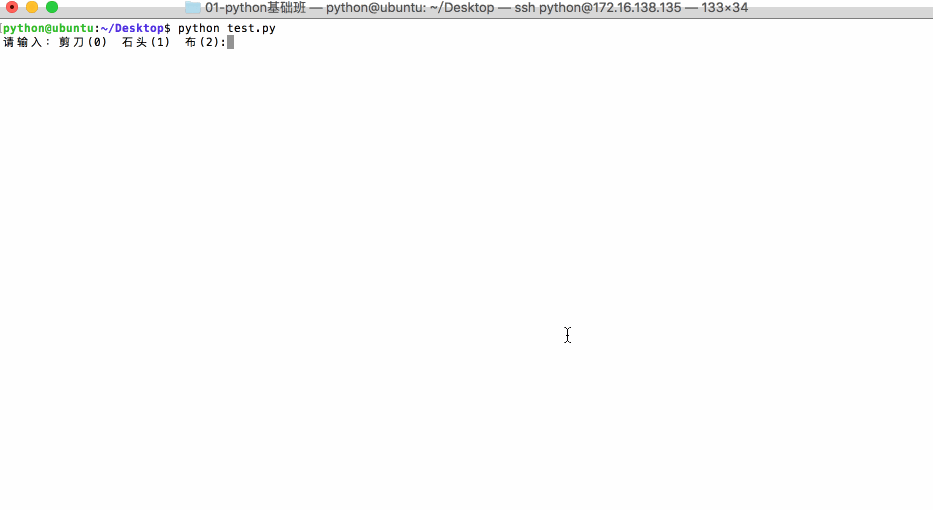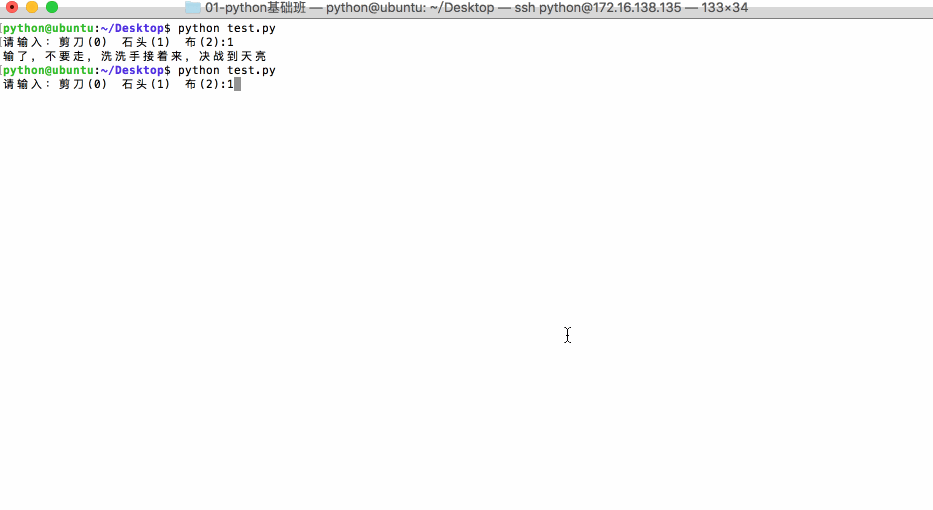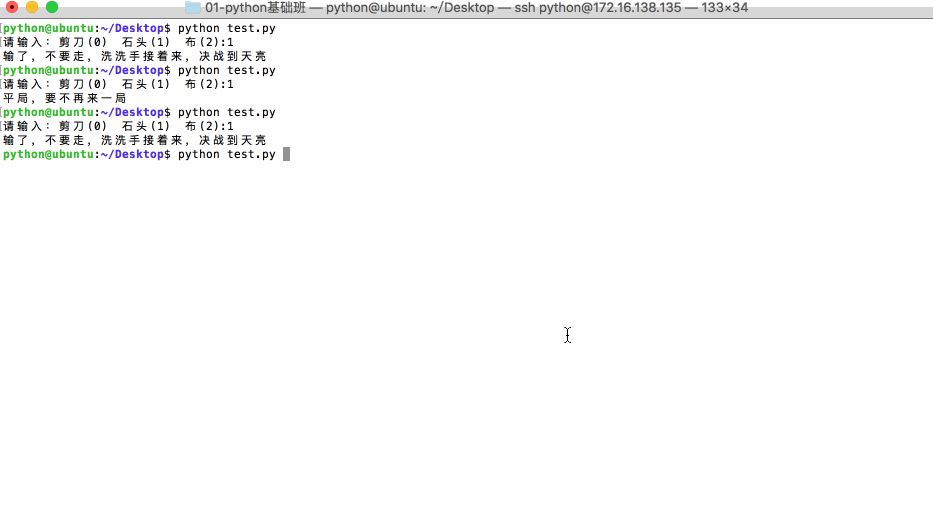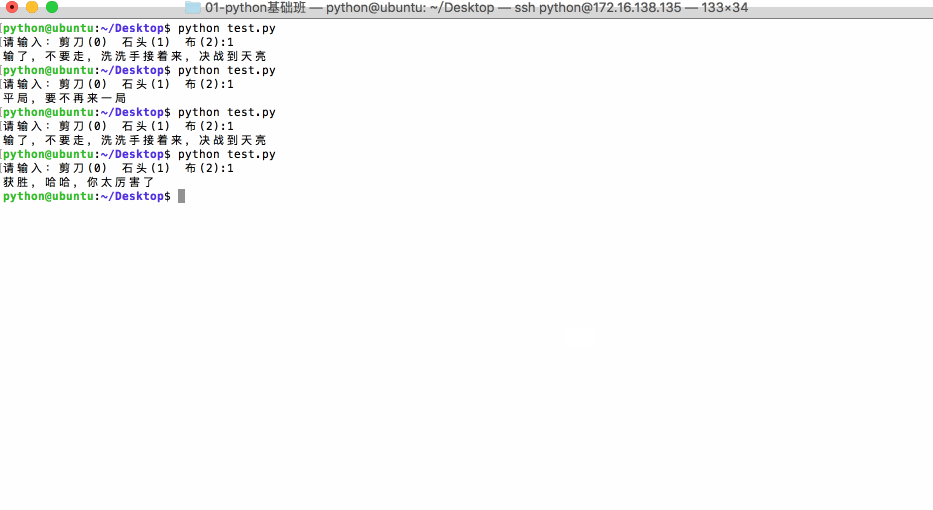
应用:猜拳游戏
-
<2>参考代码:
-
 View Code
View Codeimport random player = input('请输入:剪刀(0) 石头(1) 布(2):') player = int(player) computer = random.randint(0,2) # 用来进行测试 #print('player=%d,computer=%d',(player,computer)) if ((player == 0) and (computer == 2)) or ((player ==1) and (computer == 0)) or ((player == 2) and (computer == 1)): print('获胜,哈哈,你太厉害了') elif player == computer: print('平局,要不再来一局') else: print('输了,不要走,洗洗手接着来,决战到天亮')
-
while循环应用
- 打印1到100的和
-
 View Code
View Code#encoding=utf-8 i = 1 sum = 0 while i<=100: sum = sum + i i += 1 print("1~100的累积和为:%d"%sum)
注意:其实sum(range(1,101))就可以实现此处只是练习while循环
break和continue的使用

# n = 0 # while n < 10: # if n > 3: # break # print(n) # n += 1 # break为终止循环,不在循环 # for i in range(1,20): # if i %2 ==0: # continue #只是终止本次循环,下面代码不会执行,进入下一次循环 # print(i)
for循环及range简单介绍
# range的使用 # for i in range(1,20,2): #第三个参数为步长 # print(i) # 判断是否是迭代器 # Iterable(可迭代对象) # Iterator(迭代器) from collections import Iterable, Iterator print(isinstance(range(9), Iterator)) # False 并不是迭代器 print(isinstance(range(9), Iterable)) # True 是迭代对象
