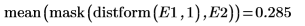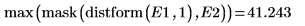Use the distform function for calculating the Euclidean distance transform of matrix M, considering pixels with value fg to be foreground pixels.
For information on using this example, refer to About Image Processing Examples.
Image Matrix
1. Define an image matrix and apply distform to it.
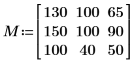
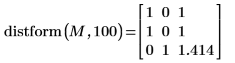
The value of each output pixel is the distance to the closest input foreground (value 100) pixel:
◦ For input foreground pixels, the output distance is zero
◦ For horizontal and vertical neighbors, the distance is 1
◦ For diagonal neighbors, the distance is the square root of 2 or 1.414
Image with a Single Nonzero Pixel
1. Define an image with a single, nonzero pixel.
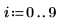
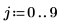
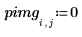
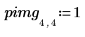

2. Apply distform to the image:
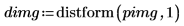
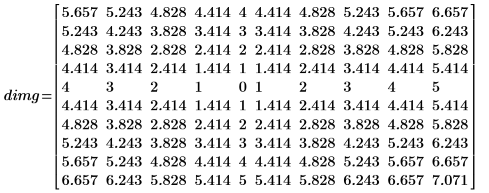
The distance increases monotonically as we move away from the foreground pixel (the center pixel) in the input image.
The distance transform produces an approximately Euclidean distance. In the above example, you can see that the exact Euclidean distance transform output for matrix location (0,1) should be:
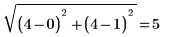
whereas in our output image the value is 5.243.
Image of a Circular Object
1. Define an image of a circle:
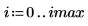
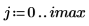
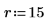
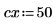
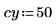
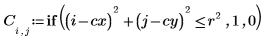
2. Use the scale function to scale the circle.
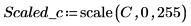
3. Use the WRITEBMP function to write the scaled circle to a file.
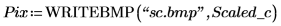
4. Apply the distform function to the circle, scale it and save the results to a new file.
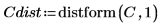
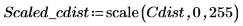
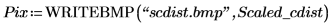
5. Insert the images from the two files and compare the result.
 |
 |
|
(sc.bmp)
|
(scdist.bmp)
|
The distance values are zero for all points within the circle and increase monotonically as we move outward, but they are not exactly equal to the Euclidean distance, or the output would be radially symmetric.
Two Binary Images of a Single Object
1. Read in an image.
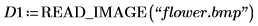
2. Use the translate function to create translated versions of the image and write the translated images to files.
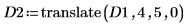
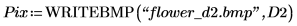
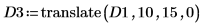
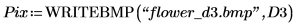
3. Insert the images from the three files and compare the result.
 |
 |
 |
|
(flower.bmp)
|
(flower_d2.bmp)
|
(flower_d3.bmp)
|
4. Use the distform function to calculate the distance transform of D1.
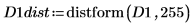
5. Use functions mask and mean to mask the distance transform image with images D2 and D3 and compute the mean of the entire image. This represents a measure of the distance between the two images.
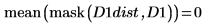
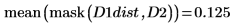
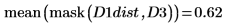
The distance between D1 and D1 is zero, and the distance between D1 and the other images increases with the degree of translation.
6. Compute the Hausdorff distance
The Hausdorff distance is defined as the maximum of the closest distance between points in two sets. To compute the Hausdorff distance between the two images, use the max function instead of function mean.
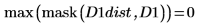
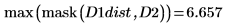
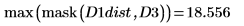
Two Edge Images
You can compare the performance of edge detectors by computing the distance between two edge images. Use either the mean or the maximum of the masked distances as a measure of the edge distance.
1. Use the READ_IMAGE function to read an image file.
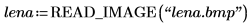
2. Apply the two edge detectors canny and binarize to the image and write the results to external files.
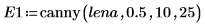
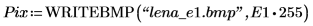
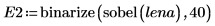
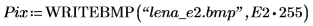
3. Insert, and visually compare, the two images.
 |
 |
|
(lena_e1.bmp)
|
(lena_e2.bmp)
|
4. Calculate the overall distance between the edges.