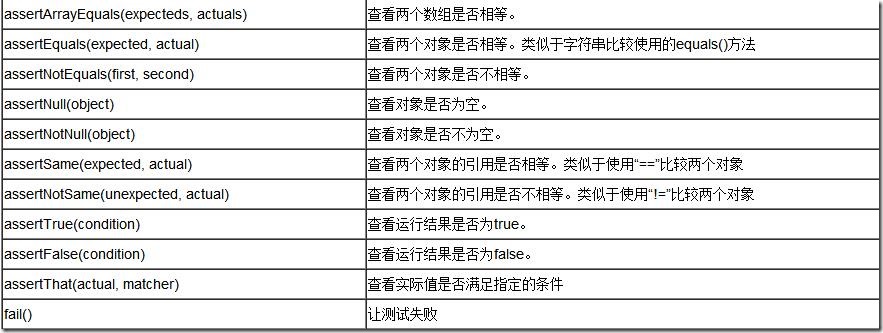
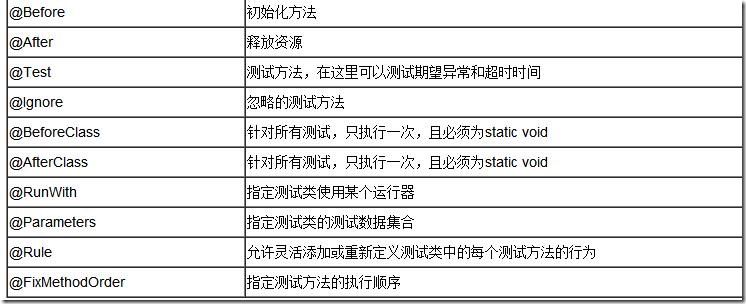
一. 断言核心方法
示例代码:
package com.test; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; /** * @Title: testAssert.java * @Package com.test * @Description: junit中常见的断言 * @author lky * @date 2015年10月17日 上午9:15:59 * @version V1.0 */ public class testAssert { /** * @Title: testAssertByteArrayEqual * @Description: 判断字节数组是否相等 */ @Test public void testAssertByteArrayEqual(){ Assert.assertArrayEquals("byteArray fail to equal ", "lky".getBytes(),"lky".getBytes()); } /** * @Title: testAssertEqual * @Description: 判断两个对象是否相等,只比较值,不比较它们的地址,类似于java中的equal的比较 */ @Test public void testAssertEqual(){ Assert.assertEquals("fail to equql", 50,50); } @Test public void testAssertNotEqual(){ Assert.assertNotEquals("should be not equal",50,49); } /** * @Title: testAssertNotNull * @Description: 判断一个对象是否为空 */ @Test public void testAssertNotNull(){ Assert.assertNotNull("should be not null", new Object()); } @Test public void testAssertNull(){ Assert.assertNull("should be null", null); } /** * @Title: testAssertSame * @Description: 判断两个对象是否相等,包括值和地址,类似于java中的= */ @Test public void testAssertSame(){ Integer number=Integer.valueOf(10); Assert.assertSame("should be same",number ,number); } @Test public void testAssertNotSame(){ Assert.assertNotSame("should be not same", new Object(), new Object()); } }
二.注解核心方法
- 执行顺序
一个测试类单元测试的执行顺序为:
@BeforeClass –> @Before –> @Test –> @After –> @AfterClass
- 每一个测试方法的调用顺序为:
@Before –> @Test –> @After
示例代码:
package com.test; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.AfterClass; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.BeforeClass; import org.junit.Ignore; import org.junit.Test; /** * @Title: testAnnotation.java * @Package com.test * @Description: junit测试中注解测试 * @author lky * @date 2015年10月17日 上午9:36:39 * @version V1.0 */ public class testAnnotation { private static Demo demo=null; /** * @Title: testBeforeClass * @Description: 在该类加载时运行,有且仅仅执行一次 */ @BeforeClass public static void testBeforeClass(){ demo=new Demo(); System.out.println("Test --------->testBeforeClass"); } /** * @Title: testBefore * @Description: 在每一个测试执行前,自动被调用 */ @Before public void testBefore(){ System.out.println("Test---------->testBefore"); } /** * @Title: testAdd * @Description: 真正去做测试的代码 */ @Test public void testAdd(){ Assert.assertEquals(5, demo.add(2, 3)); } /** * @Title: testAdd1 * @Description: ignore表示忽略该测试 */ @Ignore @Test public void testAdd1(){ Assert.assertEquals(4, demo.add(2, 2)); } /** * @Title: testAfter * @Description: 每一个测试执行结束后会被调用 */ @After public void testAfter(){ System.out.println("Test----------->testAfter"); } /** * @Title: testAfterClass * @Description: 所有测试执行结束以后,执行(有且执行一次) */ @AfterClass public static void testAfterClass(){ System.out.println("Test------------>testAfterClass"); } }
三.参数化测试
有时一个测试方法,不同的参数值会产生不同的结果,那么我们为了测试全面,会把多个参数值都写出来并一一断言测试,这样有时难免费时费力,这是我们便可以采用参数化测试来解决这个问题。参数化测试就好比把一个“输入值,期望值”的集合传入给测试方法,达到一次性测试的目的。
示例代码:
package com.test; public class Demo { public int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; } }
package com.test; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.BeforeClass; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.junit.runners.Parameterized; import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters; /** * @Title: testParam.java * @Package com.test * @Description: 多组数据的单元测试(参数化测试) * @author lky * @date 2015年10月17日 上午9:20:54 * @version V1.0 */ //不使用junit默认的运行器,指定特定的运行器 @RunWith(Parameterized.class) public class testParam { private int expected; private int input1; private int input2; private static Demo demo; public testParam(int expected,int input1,int input2) { this.expected=expected; this.input1=input1; this.input2=input2; } /** * @Title: initData * @Description: 测试数据初始化 * @param @return 设定文件 * @return Collection<? extends Object> 返回类型 * @throws */ @Parameters(name="第 {index} 组:-------> {1} + {2} = {0}") public static Collection<?extends Object> initData(){ return Arrays.asList(new Object [][]{{3,2,1},{5,-1,6},{-7,-3,-4},{7,3,4}}); } @BeforeClass public static void loadUp(){ demo=new Demo(); } @Test public void testAdd(){ Assert.assertEquals("should be equal", this.expected, demo.add(this.input1, this.input2)); } }
四.异常测试
示例代码:
package com.test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Rule; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.rules.ExpectedException; /** * * @Title: testException.java * @Package com.test * @Description: 异常测试(两种方法) * @author lky * @date 2015年10月17日 上午10:00:32 * @version V1.0 */ public class testException { @Test(expected=IndexOutOfBoundsException.class) public void empty(){ new ArrayList<Object>().get(0); } @Rule public ExpectedException thrown=ExpectedException.none(); @Test public void shouldTestExceptionMessage() throws IndexOutOfBoundsException { List<?extends Object> list=new ArrayList<Object>(); thrown.expectMessage("Index: 0, Size: 0"); thrown.expect(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class); list.get(0); Assert.assertEquals(1, list.get(0)); } }
五.超时测试
有时为了防止出现死循环或者方法执行过长(或检查方法效率),而需要使用到限时测试。顾名思义,就是超出设定时间即视为测试失败。共有两种写法
示例代码:
package com.test; import org.junit.Rule; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.rules.Timeout; /** * @Title: testTimeOut.java * @Package com.test * @Description: 超时测试 * @author lky * @date 2015年10月17日 上午9:58:18 * @version V1.0 */ public class testTimeOut { //定义被测试方法的时间参数, @Rule public Timeout timeout=new Timeout(10000); @Test public void test(){ } @Test(timeout=10000) public void test1(){ } }
六.打包测试
如果一个项目中有很多个测试用例,如果一个个测试也很麻烦,因此打包测试就是一次性测试完成包中含有的所有测试用例。
示例代码:
package com.test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.junit.runners.Suite; import org.junit.runners.Suite.SuiteClasses; /** * @Title: testSuite.java * @Package com.test * @Description: 打包测试 * @author lky * @date 2015年10月17日 上午10:05:25 * @version V1.0 */ @RunWith(Suite.class) @SuiteClasses({testAnnotation.class,testAssert.class,testParam.class,testException.class,testTimeOut.class}) public class testSuite { }