-- 歌手表 CREATE TABLE `singer` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL, `update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `singer` (`id`, `update_time`, `name`)VALUES(1, '2020-10-28 10:00:00', 'a'),(2, '2020-10-28 11:00:00', 'b'),(3, '2020-10-28 12:00:00', 'c'); -- 专辑表 CREATE TABLE `album` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_name` (`name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `album` (`id`, `name`)VALUES(1, 'album1'),(2, 'album2'),(3, 'album3'),(4, 'album4'); -- 歌手专辑关联表 CREATE TABLE `singer_album` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL, `singer_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `album_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `remark` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_singer_album` (`singer_id`,`album_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `singer_album` (`id`, `singer_id`, `album_id`, `remark`) VALUES(1, 1, 1, NULL),(2, 2, 2, NULL),(3, 3, 3, NULL),(4, 1, 4, NULL);
测试explain效果:
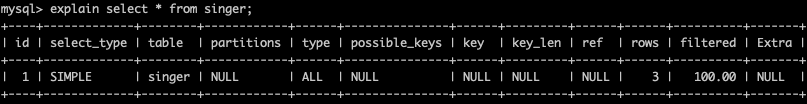
explain select * from singer;
explain extended select * from singer where id = 2;
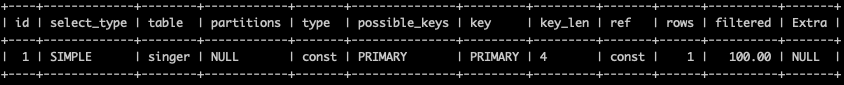
show warnings;

2)explain partitions:相比 explain 多了个 partitions 字段,如果查询是基于分区表的话,会显示查询将访问的分区。
explain partitions select * from singer where id = 2;

下面开始展示explain每一列的信息
1. id列
id列越大执行优先级越高,id相同则从上往下执行,id为NULL最后执行。
2. select_type列
select_type 表示对应行是简单还是复杂的查询。
1)simple:简单查询。查询不包含子查询和union
explain select * from singer where id = 2;

2)primary:复杂查询中最外层的 select
3)subquery:包含在 select 中的子查询(不在 from 子句中)
-- 关闭mysql5.7新特性对衍生表的合并优化 set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; explain select (select 1 from singer where id = 1) from (select * from album where id = 1) abl;
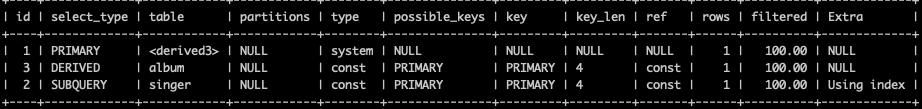
-- 还原默认配置 set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on';
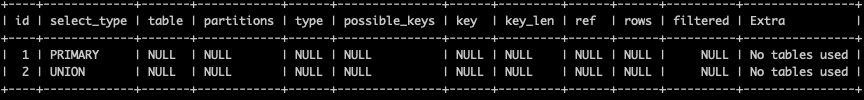
explain select 1 union all select 1;
3. table列
explain select min(id) from singer;

const, system:mysql能对查询的某部分进行优化并将其转化成一个常量(可以看show warnings 的结果)。用于primary key 或 unique key 的所有列与常数比较时,所以表最多有一个匹配行,读取1次,速度比较快。system是const的特例,表里只有一条数据匹配时为system.
explain extended select * from (select * from singer where id = 1) temp;

show warnings;
eq_ref:primary key 或 unique key 索引的所有部分被连接使用 ,最多只会返回一条符合条件的记录。这可能是在const 之外最好的联接类型了,简单的 select 查询不会出现这种 type。
explain select * from singer_album left join singer on singer_album.singer_id = singer.id;

ref:相比 eq_ref,不使用唯一索引,而是使用普通索引或者唯一性索引的部分前缀,索引要和某个值相比较,可能会找到多个符合条件的行。
1.简单的select查询,name是普通索引(非唯一索引)
explain select * from album where name = 'album1';

2.关联表查询,使用了联合索引的左前缀部分
explain select * from singer s join singer_album a on s.id = a.singer_id;

range:范围扫描通常出现在in(),between,>,<等条件中
explain select * from singer where id > 1;

index:扫描全表就能拿到结果,一般是扫描某个二级索引,这种扫描不会从根节点开始快速查找,而是直接对叶子节点遍历,速度还是比较慢的,这种查询一般为使用覆盖索引,二级索引一般比较小,这种通常比ALL快一些
ALL:即全表扫描,扫描聚簇索引上的所有叶子节点,这种情况需要建索引来进行优化
5. possible_keys列
explain select * from singer_album where singer_id = 2;

key_len计算规则如下:
字符串:char(n):n字节长度,varchar(n):如果是utf-8,则存储字节是3n+2,2字节用来存储字符串长度
数值类型:tinyint:1字节,smallint:2字节,int:4字节,bigint:8字节
时间类型:date:3字节,timestamp:4字节,datetime:8字节
如果字段允许为null,需要1字节记录是否为null,索引最大长度是768字节,当字符串过长时,mysql会做一个类似左前缀索引的处理,将前半部分的字符提取出来做索引。
explain select singer_id,id from singer_album where singer_id = 1;

2)Using where:使用 where 语句来处理结果,并且查询的列未被索引覆盖
explain select * from singer where name = 'abc';

3)Using index condition:查询的列不完全被索引覆盖,where条件中是一个使用索引的范围查找
explain select * from singer_album where singer_id > 1;

4)Using temporary:mysql需要创建一张临时表来处理查询。出现这种情况一般是要进行优化的,首先是想到用索引来优化。
1. singer.name没有索引,此时创建了张临时表来distinct
explain select distinct(name) from singer;

2. album.name建立idx_name索引,此时查询时extra是using index,没有用临时表
explain select distinct(name) from album;

5)Using filesort:将用外部排序而不是索引排序,数据较小时从内存排序,否则需要在磁盘完成排序。这种情况下一般也是要考虑使用索引来优化的。
explain select * from singer order by name;

2. album.name建立了idx_name索引,此时查询时extra是using index
mysql> explain select * from album order by name;

6)Select tables optimized away:使用某些聚合函数(比如 max、min)来访问存在索引的某个字段是
explain select min(singer_id) from singer_album;
