1、传统方式
一、src目录下

二、
//普通的增,改,删 查 public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args)throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //加载驱动类 Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection( //建立连接 "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shujuku", "root","123"); System.out.println(con); //得到语句发送器 Statement statement = con.createStatement(); //导Java.sql.statement //String s1 = "insert into sp(bianhao,mingcheng,danjia,geshu)values('05','huotuichang','5.5','30')";//增加 //String s1 = "update sp set mingcheng='huotui' where bianhao='05'";//改变 //String s1 = "delete from sp where bianhao='05'"; //删除 //int a = statement.executeUpdate(s1); //System.out.println(a); String s2 = "select * from sp"; ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(s2); while(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getString(1)+" "+rs.getString(2)+" "+rs.getString(3)+" "+rs.getString(4)); } rs.close(); statement.close(); con.close(); } }
/** *得到语句发送器Statement发送查询语句,获得 结果集 和行光标(操纵行光标看有多少行,得到每行有多少列进行遍历), *creatstatement();(重载形式传参)创建什么样的语句发送器就注定了会得到什么样的结果集(结果集的特性) */ public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { Connection con = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shujuku", "root", "123"); System.out.println(con); stmt = con.createStatement(); //生成的结果集不滚动 String s1 = "select * from sp"; //查询语句 rs = stmt.executeQuery(s1); //操作结果集要学习移动ResultSet内部的“行光标”,以及获取当前行上的每一列上的数据: Boolean b = rs.last(); //把行光标放在最后一行 int a = rs.getRow(); //得到当前多少行 System.out.println("一共有"+a+"行"); rs.beforeFirst(); //挪到第一行上面 int count = rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount();//得到查询结果有多少列 while(rs.next()){ for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) { if(i==count){ System.out.println(rs.getString(i)); }else{ System.out.print(rs.getString(i)+", "); } } } }catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(); }finally{ if(rs!=null)rs.close(); if(stmt!=null)stmt.close(); if(con!=null)con.close(); } } }
/** * 演示不安全的statement */ public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Boolean b1 = Demo3.fun("张三","123"); Boolean b2 = Demo3.fun("李四", "123"); //Boolean b3 = Demo3.fun("a' or 'a' = 'a","a' or 'a' ='a "); System.out.println(b1); System.out.println(b2); //System.out.println(b3); } public static boolean fun(String username,String password) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException{ String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; String mysqlusername = "root"; String mysqlpassword = "123"; String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shujuku"; Class.forName(driverClassName); Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, mysqlusername, mysqlpassword); System.out.println(con); Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); String sql = "select * from login where username = ' "+username+" ' and password = ' "+password+" '"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); return rs.next(); } }
/** * 防sql攻击的语句发送器,PreparedStatement,一出生就和sql语句绑定在一起,想赋值调用一系列setXXX()方法 */ public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Boolean b1 = Demo4.fun("李四","123"); Boolean b2 = Demo4.fun("a' or 'a' = 'a", "a' or 'a'='a"); Boolean b3 = Demo4.fun("a' or 'a' = 'a", "a' or 'a'='a"); System.out.println(b1); System.out.println(b2); System.out.println(b3); } public static boolean fun(String username,String password) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException{ String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shujuku"; String mysqlusername = "root"; String mysqlpassword = "123"; Class.forName(driverClassName); Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, mysqlusername, mysqlpassword); String sql = "select * from login where username =? and password =?"; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);//语句发送器一出生就和模板绑定在一起,sql语句必须遵循这个模板 pstmt.setString(1, username); pstmt.setString(2, password); ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); /*rs.last();int a = rs.getRow();//先到最后一行然后获取一共有多少行 rs.beforeFirst(); int cols = rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); while(rs.next()){ for (int i = 1; i <=cols; i++) { if (i==cols) { System.out.println(rs.getString(i)); } System.out.print(rs.getString(i)+", "); } }*/ /*rs.close(); pstmt.close(); con.close();*/ return rs.next(); } }
java中虽然没有提供连接池,但是提供了连接池的接口DataSource,所有的连接池必须要实现这一接口
2、dbcp连接池
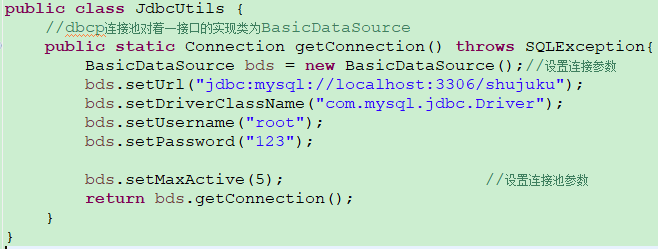
3、c3p0连接池
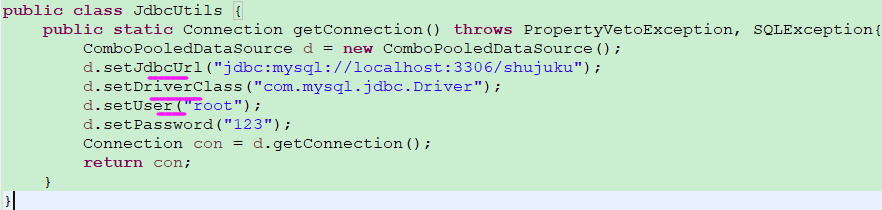
或者准备一个必须取名为c3p0-config.xml的配置文件,必须放在src下,然后可根据传入的参数不同,随意切换数据库
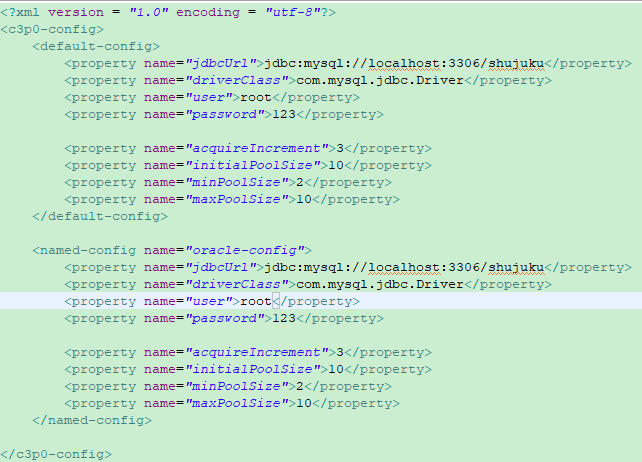

-------------------------------------------------------------
以上操作需要的jar包

大数据
一、图片存入数据库,当然实际将图片的路径存入数据库
public class DemoBlobTu { @Test public void fun1() throws Exception{ //将图片存入数据库中 Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into dashuju (id,filename,data) values(?,?,?)"; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); //语句发送器 pstmt.setInt(1, 1); pstmt.setString(2,"link.jpg"); InputStream is = new FileInputStream("F:\link.jpg"); pstmt.setBinaryStream(3,is); int a = pstmt.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(a); } public void funn2() throws Exception{ Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select filename,data from dashuju where id=?"; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1, 1); ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); rs.next(); String filename = rs.getString("filename"); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("E:\" + filename); InputStream in = rs.getBinaryStream("data"); IOUtils.copy(in, out); } }
二、音乐存入数据库
public class DemoBlobYing { public void fun1() throws Exception{ //把音乐保存到数据库 Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); System.out.println(con); String sql = "insert into dashuju (id,filename,data) values(?,?,?)"; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1, 4); pstmt.setString(2, "李琦 - 金玉良缘.mp3"); InputStream os = new FileInputStream("F://李琦 - 金玉良缘.mp3"); pstmt.setBinaryStream(3, os,1024500); int a = pstmt.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(a); } @Test public void fun2() throws Exception{ Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from dashuju where id='4'"; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); rs.next(); String filename=rs.getString("filename"); OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E://"+filename); InputStream is = rs.getBinaryStream("data"); IOUtils.copy(is,os); os.close(); is.close(); /* rs.next(); String filename = rs.getString("filename"); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("E:\" + filename); InputStream in = rs.getBinaryStream("data"); IOUtils.copy(in, out);*/ } }
批处理
public class Demo { public void fun1() throws Exception{ Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); for (int i = 0; i <10000; i++) { String name = "stu_name"+i; int age = 10+i; String number = "stu"+i; String gender = i%2==0 ? "男":"女"; String sql = "insert into student values('"+name+"','"+number+"','"+gender+"','"+age+"')"; stmt.addBatch(sql); } stmt.executeBatch(); } @Test public void fun2() throws Exception{ Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into student values(?,?,?,?)"; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { pstmt.setString(1, "stu_name"+i); pstmt.setString(2, "PreparedStatement_number"+i); pstmt.setString(3, i%2==0 ? "男":"女"); pstmt.setInt(4, i); pstmt.addBatch(); } pstmt.executeBatch(); } }
事务
首先准备一个账户直接操作数据库

public class JdbcUtils { // 配置文件的默认配置!要求你必须给出c3p0-config.xml!!! private static ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); // 它是事务专用连接! private static ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>(); //使用连接池返回一个连接对象 public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get(); // 当con不等于null,说明已经调用过beginTransaction(),表示开启了事务! if(con != null) return con; return dataSource.getConnection(); } //返回连接池对象! public static DataSource getDataSource() { return dataSource; } /** * 开启事务 * 1. 获取一个Connection,设置它的setAutoComnmit(false) * 2. 还要保证dao中使用的连接是我们刚刚创建的! * -------------- * 1. 创建一个Connection,设置为手动提交 * 2. 把这个Connection给dao用! * 3. 还要让commitTransaction或rollbackTransaction可以获取到! * @throws SQLException */ public static void beginTransaction() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get(); if(con != null) throw new SQLException("已经开启了事务,就不要重复开启了!"); /* * 1. 给con赋值! * 2. 给con设置为手动提交! */ con = getConnection();//给con赋值,表示事务已经开始了 con.setAutoCommit(false); tl.set(con);//把当前线程的连接保存起来! } //提交事务 //1. 获取beginTransaction提供的Connection,然后调用commit方法 public static void commitTransaction() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get();//获取当前线程的专用连接 if(con == null) throw new SQLException("还没有开启事务,不能提交!"); /* * 1. 直接使用con.commit() */ con.commit(); con.close(); // 把它设置为null,表示事务已经结束了!下次再去调用getConnection()返回的就不是con了 tl.remove();//从tl中移除连接 } //提交事务 //1. 获取beginTransaction提供的Connection,然后调用rollback方法 public static void rollbackTransaction() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get(); if(con == null) throw new SQLException("还没有开启事务,不能回滚!"); /* * 1. 直接使用con.rollback() */ con.rollback(); con.close(); tl.remove(); } //释放连接 public static void releaseConnection(Connection connection) throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get(); /* * 判断它是不是事务专用,如果是,就不关闭! * 如果不是事务专用,那么就要关闭! */ // 如果con == null,说明现在没有事务,那么connection一定不是事务专用的! if(con == null) connection.close(); // 如果con != null,说明有事务,那么需要判断参数连接是否与con相等,若不等,说明参数连接不是事务专用连接 if(con != connection) connection.close(); } }

judi略