基本概念
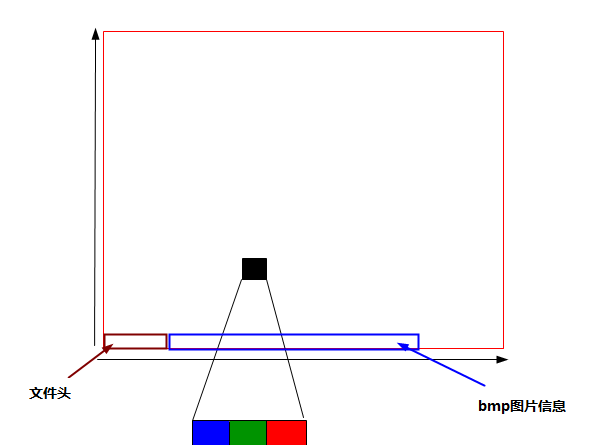
BMP是英文Bitmap的缩写,由称作像素(图片元素)的单个点组成的,每个像素点由三个字节(用char型定义)组成,按照蓝绿红排列。这些点可以进行不同的排列和染色以构成图样。如下图所示,当读取图片信息时,文件指针由左下角开始增长。如下图所示,BMP图片包含了14个字节的文件头信息,和40和字节的BMP图片信息,读取BMP数据的时候注意主要跳过。
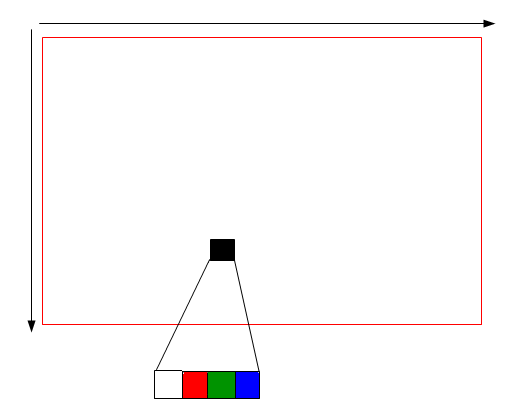
下图为LCD显示屏,它的数据从上角开始增长的,而且是由四个字节(用int型定义)组成一个像素点,而且原色排列也与BMP排序不同,编程时注意。
下图为BMP转换为LCD显示的过程。

使用LCD显示位图
该程序的文件结构如下:

需要注意的是,BMP图片大小应该与LCD分辨率一致,不然将会错位。
main.c
#include "main.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
lcd_info lcd;
BITMAPFILEHEADER file_head; //存放文件头的结构体
BITMAPINFOHEADER bmp_info; //存放bmp数据的结构体
int bmp_size;
int x;
int y;
int color;
char bmp_buf[LCD_W*LCD_H*3]; //存放bmp数据
lcd = init_lcd(LCD_PATH);
int fd_bmp = init_bmp(BMP_PATH);
file_head = read_file_head(fd_bmp, file_head); //获得文件头,并且移动文件指针
bmp_info = read_file_bmp_info(fd_bmp, bmp_info); //获得bmp图片信息,并且将文件指针移动到了bmp图片的数据部分
int ret = read(fd_bmp, &bmp_buf, LCD_W*LCD_H*3); //获得文件数据,并且将用char类型来存放
if (-1 == ret)
{
printf("read bmp_data msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
}
printf("read bmp_data %d
", ret);
for (y = 0; y < LCD_H; y++)
{
for ( x = 0; x < LCD_W; x++)
{
/* 将BMP的3个元素组成一个能在LCD上正确显示的像素 */
color = bmp_buf[(x+y*800)*3+0] << 0 |
bmp_buf[(x+y*800)*3+1] << 8 |
bmp_buf[(x+y*800)*3+2] << 16;
draw_point(lcd.p_lcd, color, x, LCD_H - 1 - y); //每获得一个像素就根据坐标去打印它,注意纵轴方向需要倒着打印,因为LCD与位图的显示与存放的方式不同
}
}
return 0;
}
lcd.c
#include "lcd.h"
#include "main.h"
lcd_info init_lcd(const char *path)
{
lcd_info lcd = {
.fd_lcd = -1,
.p_lcd = NULL
};
lcd.fd_lcd = open(LCD_PATH , O_RDWR);
if (-1 == lcd.fd_lcd)
{
printf("open lcd.fd_lcd msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
return lcd;
}
lcd.p_lcd = mmap(NULL, LCD_SIZE, PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ , MAP_SHARED, lcd.fd_lcd , 0);
if (MAP_FAILED == lcd.p_lcd)
{
printf("mmap msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
return lcd;
}
return lcd;
}
/* 画点函数
**/
bool draw_point(int *address, int color, int x, int y)
{
if (NULL == address)
{
printf("draw_point msg:%s
", strerror(errno));
return false;
}
*(address + (x + (y*800))) = color;
return true;
}
bmp.c
#include "bmp.h"
/* 初始化图片获得图片句柄
**/
int init_bmp(const char *bmp_path)
{
int fd_bmp = open(bmp_path, O_RDONLY);
if (-1 == fd_bmp)
{
printf("open fd_bmp msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return fd_bmp;
}
BITMAPFILEHEADER read_file_head(int fd_bmp, BITMAPFILEHEADER file_head)
{
int ret = read(fd_bmp, &file_head, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER));
if (-1 == ret)
{
printf("read file_head msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
return file_head;
}
printf("read file_head %d
", ret);
return file_head;
}
BITMAPINFOHEADER read_file_bmp_info(int fd_bmp, BITMAPINFOHEADER bmp_info)
{
int ret = read(fd_bmp, &bmp_info, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER));
if (-1 == ret)
{
printf("read bmp_info msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
return bmp_info;
}
printf("read bmp_info %d
", ret);
return bmp_info;
}
main.h
#define __MAIN__H__
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "lcd.h"
#include "bmp.h"
#define LCD_PATH "/dev/fb0"
#define BMP_PATH "./1.bmp"
#define LCD_W 800
#define LCD_H 480
#define LCD_SIZE LCD_W*LCD_H*4
#endif
lcd.h
#ifndef __LCD__H__
#define __LCD__H__
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
typedef struct Lcd_Info{
int fd_lcd;
int* p_lcd;
}lcd_info;
lcd_info init_lcd(const char *path);
bool draw_point(int *address, int color, int x, int y);
#endif
bmp.h
#ifndef __BMP__H__
#define __BMP__H__
#include "lcd.h"
#include "main.h"
typedef short WORD;
typedef int DWORD;
typedef long LONG;
typedef struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER
{
WORD bfType;//位图文件的类型,必须为BM(1-2字节)
DWORD bfSize;//位图文件的大小,以字节为单位(3-6字节,低位在前)
WORD bfReserved1;//位图文件保留字,必须为0(7-8字节)
WORD bfReserved2;//位图文件保留字,必须为0(9-10字节)
DWORD bfOffBits;//位图数据的起始位置,以相对于位图(11-14字节,低位在前)
//文件头的偏移量表示,以字节为单位
}__attribute__((packed)) BITMAPFILEHEADER;
typedef struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER{
DWORD biSize;//本结构所占用字节数(15-18字节)
LONG biWidth;//位图的宽度,以像素为单位(19-22字节)
LONG biHeight;//位图的高度,以像素为单位(23-26字节)
WORD biPlanes;//目标设备的级别,必须为1(27-28字节)
WORD biBitCount;//每个像素所需的位数,必须是1(双色),(29-30字节)
//4(16色),8(256色)16(高彩色)或24(真彩色)之一
DWORD biCompression;//位图压缩类型,必须是0(不压缩),(31-34字节)
//1(BI_RLE8压缩类型)或2(BI_RLE4压缩类型)之一
DWORD biSizeImage;//位图的大小(其中包含了为了补齐行数是4的倍数而添加的空字节),以字节为单位(35-38字节)
LONG biXPelsPerMeter;//位图水平分辨率,每米像素数(39-42字节)
LONG biYPelsPerMeter;//位图垂直分辨率,每米像素数(43-46字节)
DWORD biClrUsed;//位图实际使用的颜色表中的颜色数(47-50字节)
DWORD biClrImportant;//位图显示过程中重要的颜色数(51-54字节)
}__attribute__((packed)) BITMAPINFOHEADER;
int init_bmp(const char *bmp_path);
BITMAPFILEHEADER read_file_head(int fd_bmp, BITMAPFILEHEADER file_head);
BITMAPINFOHEADER read_file_bmp_info(int fd_bmp, BITMAPINFOHEADER bmp_info);
#endif
Makefile
CC=arm-linux-gcc
TAG=./bin/main
SRC=$(wildcard ./src/*.c)
objs = ./src/main.o ./src/lcd.o ./src/bmp.o
override CONFIG += -I./inc
$(TAG):$(SRC)
$(CC) $^ -o $@ $(CONFIG)
$(SRC):$(OBJ)
$(CC) $^ -o $@ -c $(objs)
使用LCD显示小图
上个程序只能够显示固定大小的图片,因为LCD是顺序存放的,当图片大小和分辨不一样将会错位,如当LCD的一行像素足够存放BMP像素数据的两行,LCD便会将需要分两行显示的数据,显示成一行,从而导致了数据错位。这里只需要更改主程序,其他程序是一样的。
main.c
#include "main.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
lcd_info lcd;
BITMAPFILEHEADER file_head;
BITMAPINFOHEADER bmp_info;
int bmp_size;
int x;
int y;
int color;
lcd = init_lcd(LCD_PATH);
int fd_bmp = init_bmp(BMP_PATH);
file_head = read_file_head(fd_bmp, file_head);
bmp_info = read_file_bmp_info(fd_bmp, bmp_info);
int bmp_w = bmp_info.biWidth; //获得图片宽度,循环时用到
int bmp_h = bmp_info.biHeight;//获得图片高度,循环时用到
char bmp_buf[LCD_W*LCD_H*3];
int ret = read(fd_bmp, &bmp_buf, LCD_W*LCD_H*3);
if (-1 == ret)
{
printf("read bmp_data msg: %s
", strerror(errno));
}
printf("read bmp_data %d
", ret);
// 输出文件的信息
printf("type:%x size:%d offset:%d
" , file_head.bfType , file_head.bfSize,file_head.bfOffBits );
printf("biWidth:%ld biHeight:%ld biBitCount:%d biSizeImage:%d
",
bmp_info.biWidth,
bmp_info.biHeight,
bmp_info.biBitCount,
bmp_info.biSizeImage);
int tmp_y = 0;
//bmp每行像素的所占字节数需要被4整除,但不满足这个条件时需要补充字节
int swallow = 0 ; //定义需要补充的字节数变量
if ((swallow = ((bmp_w*3)%4)) != 0 ) //bmp_w*3求出bmp每行所占的字节数,再取余,得到余数
{
swallow = 4 - swallow; //向上补充
printf("需要补充%d个空字节!!
" , swallow );
}
else
{
printf("不需要补充空字节!!
" );
swallow = 0 ;
}
for (y = 0; y < bmp_h; y++)
{
for ( x = 0; x < bmp_w; x++)
{
/* y*swallow:表示y每增加1需要跳过的字节数,因为是补充字节是没有数据的,而且不跳过会导致LCD显示错位 */
color = bmp_buf[(x + y * bmp_w ) * 3 + 0 + y * swallow] << 0 |
bmp_buf[(x + y * bmp_w ) * 3 + 1 + y * swallow] << 8 |
bmp_buf[(x + y * bmp_w ) * 3 + 2 + y * swallow] << 16;
tmp_y = (y * bmp_w + y * (LCD_W-bmp_w)) / LCD_W; //这里是将BMP的纵轴坐标转换LCD纵轴坐标。横坐标不需要管,因为不会错位。
draw_point(lcd.p_lcd, color, x, bmp_h - 1 - tmp_y);
}
}
return 0;
}