tensorflow 使用数据集(tf.data)的方法对数据集进行操纵。
1. 对 数组(内存向量) 进行操纵 :
import tensorflow as tf input_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] #从数组生成数据集 dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(input_data) #dataset = dataset.shuffle(3) #dataset = dataset.repeat(10) #dataset = dataset.batch(2) dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(10).batch(2) # 定义迭代器。 iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # get_next() 返回代表一个输入数据的张量(batch)。 x = iterator.get_next() y = x * x coord=tf.train.Coordinator() with tf.Session() as sess: for i in range(25): print(sess.run(y))
2. 读取文本文件里的数据 ( tf.data.TextLineDataset )
import tensorflow as tf # 创建文本文件作为本例的输入。 with open("./test1.txt", "w") as file: file.write("File1, line1. ") file.write("File1, line2. ") file.write("File1, line3. ") file.write("File1, line4. ") file.write("File1, line5. ") with open("./test2.txt", "w") as file: file.write("File2, line1. ") file.write("File2, line2. ") file.write("File2, line3. ") file.write("File2, line4. ") file.write("File2, line5. ") # 从文本文件创建数据集。这里可以提供多个文件。 input_files = ["./test1.txt", "./test2.txt"] dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset(input_files) #dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2) # 定义迭代器。 iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # 这里get_next()返回一个字符串类型的张量,代表文件中的一行。 x = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess: for i in range(10): print(sess.run(x))
3. 解析TFRecord文件里的数据
准备工作:(mnist数据集的tfrecord格式的保存)
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import numpy as np def _float32_feature(value): return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[value])) def _int64_feature(value): return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) def _bytes_feature(value): return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value])) mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('./data', dtype=tf.uint8, one_hot=True) """ print(mnist.train.images) print(mnist.train.labels) print(mnist.test.images) print(mnist.test.labels) """ train_images=mnist.train.images train_labels=mnist.train.labels #test_images=mnist.test.images #test_labels=mnist.test.labels train_num=mnist.train.num_examples #test_num=mnist.test.num_examples pixels=train_images.shape[1] # 784 = 28*28 file_out='./data/output.tfrecords' writer=tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(file_out) for index in range(train_num): image_raw=train_images[index].tostring() #转换为bytes序列 example=tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={ 'pixels': _int64_feature(pixels), 'label':_int64_feature(np.argmax(train_labels[index])), 'x':_float32_feature(0.1), 'y':_bytes_feature(bytes('abcde', 'utf-8')), 'image_raw':_bytes_feature(image_raw)})) writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) writer.close()
准备工作:(mnist数据集的tfrecord格式的读取)
import tensorflow as tf reader=tf.TFRecordReader() files=tf.train.match_filenames_once('./data/output.*') #filename_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(['./data/output.tfrecords']) filename_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(files) _, serialized_example=reader.read(filename_queue) features=tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example, features={ 'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), 'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32), 'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string) }) #print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor) # necessary operation # bytes_list to uint8_list image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8) #print(image) # tensor uint8 x=features['x'] #y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string) y=features['y'] label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32) pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32) #image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5]) image.set_shape([784]) batch_size=2 image_batch, label_batch, pixels_batch, x_batch, y_batch=tf.train.batch([image, label, pixels,x,y], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=1000+3*batch_size) coord=tf.train.Coordinator() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) threads=tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord) for i in range(1): print(sess.run([image_batch, label_batch, pixels_batch, x_batch, y_batch])) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads)
正式工作:(mnist数据集的tfrecord格式 使用 TFRecordDataset 数据集读取)
import tensorflow as tf files=tf.gfile.Glob('./data/output.*') dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files) def parser(record): features=tf.parse_single_example(record, features={ 'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), 'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32), 'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string) }) #print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor) # necessary operation # bytes_list to uint8_list image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8) #print(image) # tensor uint8 x=features['x'] #y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string) y=features['y'] label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32) pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32) #image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5]) image.set_shape([784]) return image, label, pixels, x, y # map()函数表示对数据集中的每一条数据进行调用解析方法。 dataset = dataset.map(parser) # dataset 数据集操纵 dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2) # 定义遍历数据集的迭代器。 iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # 读取数据,可用于进一步计算 image, label, pixels, x, y = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess: for i in range(1): print(sess.run([image, label, pixels, x, y]))

4. 使用 initializable_iterator 来动态初始化数据集
# 从TFRecord文件创建数据集,具体文件路径是一个placeholder,稍后再提供具体路径。 input_files = tf.placeholder(tf.string) dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(input_files) dataset = dataset.map(parser) # 定义遍历dataset的initializable_iterator。 iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator() image, label = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess: # 首先初始化iterator,并给出input_files的值。 sess.run(iterator.initializer, feed_dict={input_files: ["output.tfrecords"]}) # 遍历所有数据一个epoch。当遍历结束时,程序会抛出OutOfRangeError。 while True: try: x, y = sess.run([image, label]) except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError: break
详细例子:
import tensorflow as tf files=tf.placeholder(tf.string) dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files) def parser(record): features=tf.parse_single_example(record, features={ 'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), 'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32), 'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string) }) #print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor) # necessary operation # bytes_list to uint8_list image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8) #print(image) # tensor uint8 x=features['x'] #y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string) y=features['y'] label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32) pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32) #image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5]) image.set_shape([784]) return image, label, pixels, x, y # map()函数表示对数据集中的每一条数据进行调用解析方法。 dataset = dataset.map(parser) # dataset 数据集操纵 dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2) # 定义遍历数据集的迭代器。 #iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # 定义遍历dataset的initializable_iterator。 iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator() # 读取数据,可用于进一步计算 image, label, pixels, x, y = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess: # 首先初始化iterator,并给出input_files的值。 sess.run(iterator.initializer, feed_dict={files: ["data/output.tfrecords"]}) for i in range(1): print(sess.run([image, label, pixels, x, y]))
或(修改版):
import tensorflow as tf files=tf.train.match_filenames_once('./data/output.*') dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files) def parser(record): features=tf.parse_single_example(record, features={ 'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), 'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32), 'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string) }) #print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor) # necessary operation # bytes_list to uint8_list image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8) #print(image) # tensor uint8 x=features['x'] #y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string) y=features['y'] label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32) pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32) #image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5]) image.set_shape([784]) return image, label, pixels, x, y # map()函数表示对数据集中的每一条数据进行调用解析方法。 dataset = dataset.map(parser) # dataset 数据集操纵 dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2) # 定义遍历数据集的迭代器。 #iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # 定义遍历dataset的initializable_iterator。 iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator() # 读取数据,可用于进一步计算 image, label, pixels, x, y = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess: # 初始化变量。 sess.run((tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())) # 首先初始化iterator,并给出input_files的值。 sess.run(iterator.initializer) while True: try: print(sess.run([image, label, pixels, x, y])) except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError: break
==========================================================
注:
迭代器:
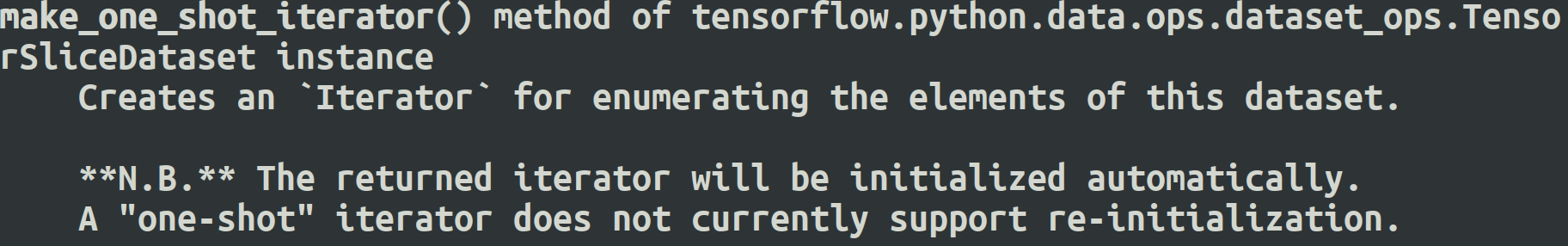
make_one_shot_iterator 方法不能重复初始化,即one-shot(一次性),但是可以自动初始化。
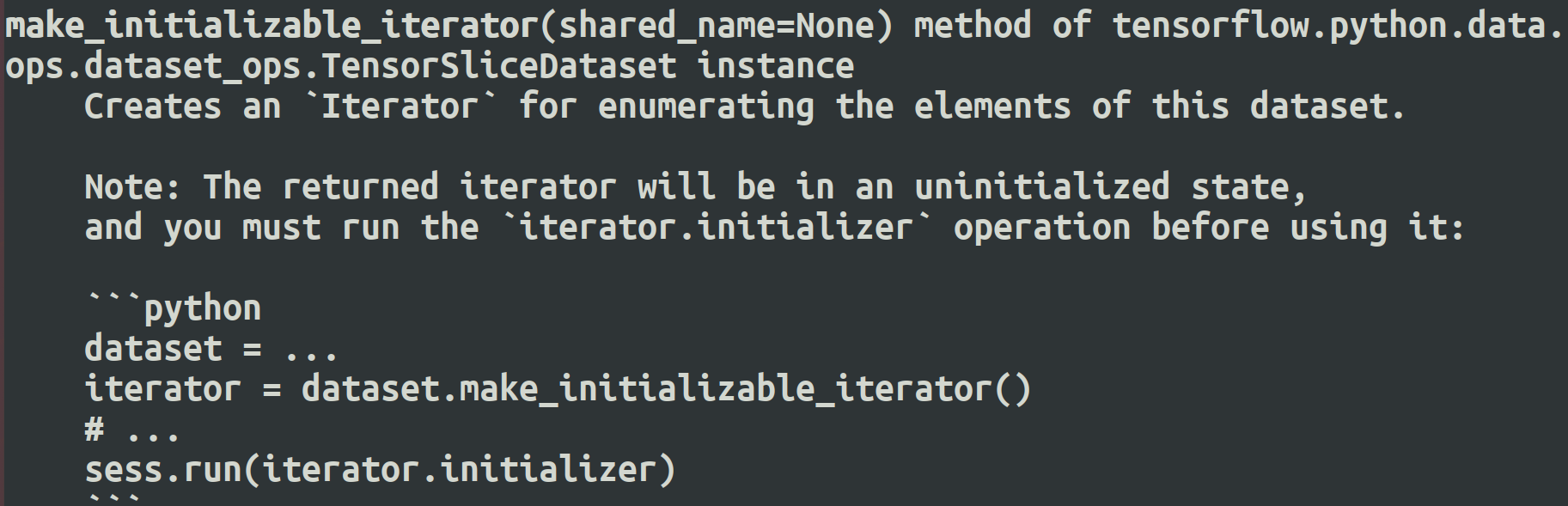
make_initializable_iterator 必须手动初始化,但是可以重复初始化。