part one
在main中加上try/catch(IOException e1){}) 把两个readline包含进去即可
bug是,当withdraw负数时:

part two
在findAccount函数中new throws然后每个相关函数都要throws,最后到throw到main后catch。
part three
![]()
把题目看仔细,说的是withdraw和deposit都有错的所以两个函数里面都要new BadTransactionException,一直throw到main再catch。
Extra
有两种方法:
方法一:把catch后的readline语句移动到catch前,也就是while里try的最后。
方法二:在catch(BadTransactionException e3){System.err.println(e3);}语句后面加上continue变成
catch(BadTransactionException e3){System.err.println(e3);continue;)
两种方法都可以。但是题目貌似要求moving哈哈。
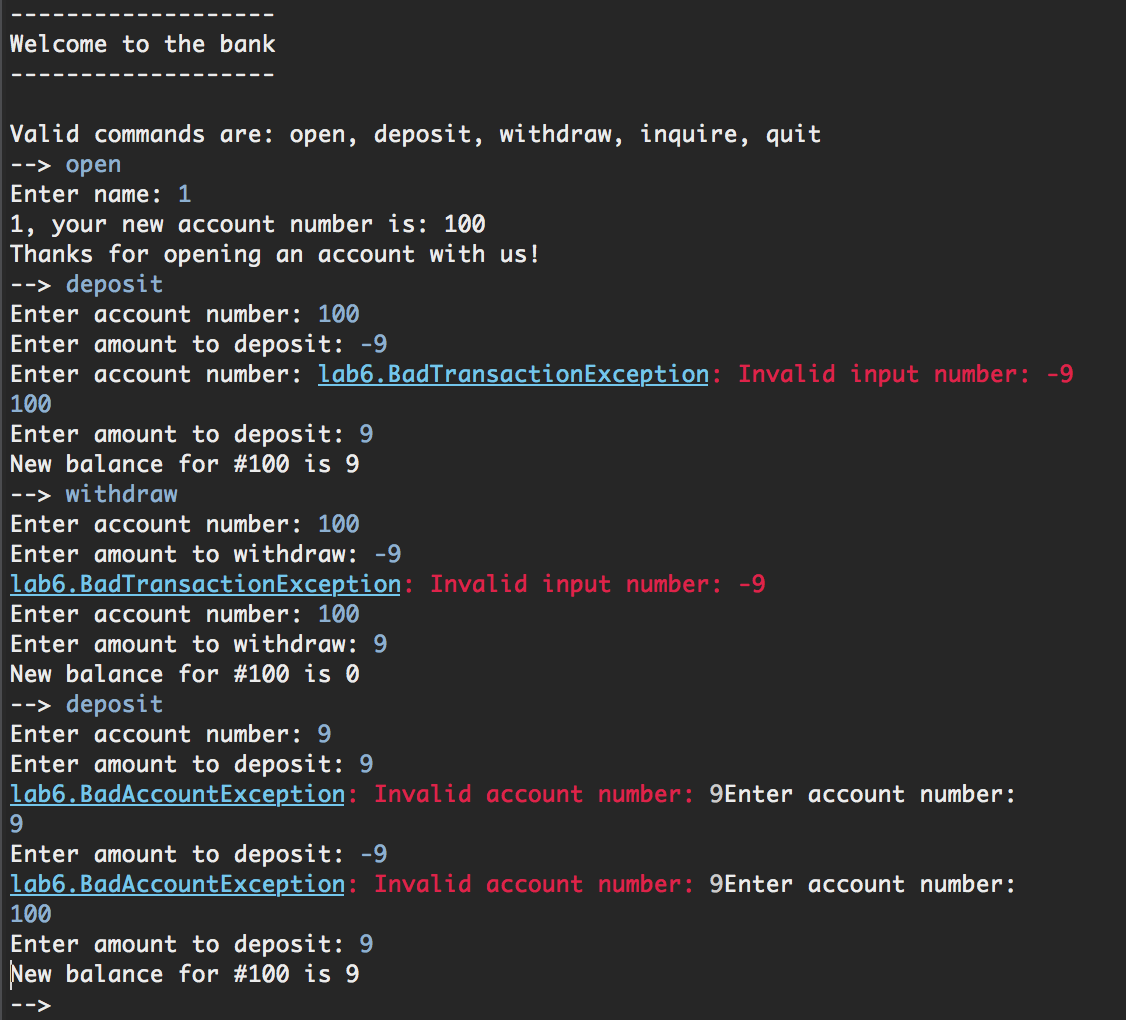
测试图片:(除了格式有点小问题,有时候exception会在repeat command后面或者不换行有时候又是正确的格式。。。并不知道为什么。。。)
放下代码吧,发现和熊孩子的有些不同(accountData里面没有throw,都在main里catch的):

package lab6; /* BankApp.java */ import java.io.*; import sortedlist.*; /** * A bank application. Allows a user to create and manipulate * banking accounts, using an ATM that is shared by all banking applications. */ public class BankApp { private BufferedReader bReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); private VirtualTeller ATM = new VirtualTeller(); public static void main(String[] args) { greeting(); usage(); BankApp bankApp = new BankApp(); try{ String command = bankApp.readLine("--> "); while (!command.equals("quit")) { try{ if (command.equals("open")) { bankApp.open(); } else if (command.equals("deposit")) { bankApp.doDeposit(); } else if (command.equals("withdraw")) { bankApp.doWithdraw(); } else if (command.equals("inquire")) { bankApp.doInquire(); } else { System.err.println("Invalid command: " + command); usage(); } command = bankApp.readLine("--> "); } catch(IOException e) { System.err.println(e); } catch(BadAccountException e2){System.err.println(e2);} catch(BadTransactionException e3){System.err.println(e3);} // command = bankApp.readLine("--> "); 另一种方法:在catch后面加上continue } }catch(IOException e1){} } public BankApp() { // The field declarations have initializers; // no initialization is needed here. } /** * open() prompts the user to create an account and creates one in the ATM. * @exception IOException if there are problems reading user input. */ private void open() throws IOException { String name = readLine("Enter name: "); int newNum = ATM.openAccount(name); System.out.println(name + ", your new account number is: " + newNum); System.out.println("Thanks for opening an account with us!"); } /** * doDeposit() prompts the user for an account number and tries to perform a * deposit transaction on that account. * @exception IOException if there are problems reading user input. */ private void doDeposit() throws IOException,BadAccountException,BadTransactionException{ // Get account number. int acctNumber = readInt("Enter account number: "); int amount = readInt("Enter amount to deposit: "); ATM.deposit(acctNumber, amount); System.out.println("New balance for #" + acctNumber + " is " + ATM.balanceInquiry(acctNumber)); } /** * doWithdraw() prompts the user for an account number and tries * to perform a withdrawal transaction from that account. * @exception IOException if there are problems reading user input. */ private void doWithdraw() throws IOException,BadAccountException,BadTransactionException{ // Get account number. int acctNumber = readInt("Enter account number: "); int amount = readInt("Enter amount to withdraw: "); ATM.withdraw(acctNumber, amount); System.out.println("New balance for #" + acctNumber + " is " + ATM.balanceInquiry(acctNumber)); } /** * doInquire() prompts the user for an account number, then attempts to * discover and print that account's balance. * @exception IOException if there are problems reading user input. */ private void doInquire() throws IOException,BadAccountException{ int acctNumber = readInt("Enter account number: "); System.out.println("Balance for #" + acctNumber + " is " + ATM.balanceInquiry(acctNumber)); } /** * greeting() displays a greeting message on the screen. */ private static void greeting() { System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println("Welcome to the bank"); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println(); } /** * usage() displays instructions on using the command line arguments. */ private static void usage() { System.out.println("Valid commands are: " + "open, deposit, withdraw, inquire, quit"); } /** * readLine() prints the given prompt and returns a string from the * input stream. * @param prompt is the string printed to prompt the user. */ private String readLine(String prompt) throws IOException { System.out.print(prompt); System.out.flush(); return bReader.readLine(); } /** * readInt() returns an integer from the input stream after prompting * the user. * @param prompt is the string printed to prompt the user. * @return an int read from the user. */ private int readInt(String prompt) throws IOException { String text = readLine(prompt); return Integer.valueOf(text).intValue(); } }

package lab6; /* VirtualTeller.java */ import sortedlist.*; /** * An implementation of a virtual automated teller machine. **/ public class VirtualTeller { private static int nextAccountID = 100; private SortedList accounts; /** * Constructs a new virtual teller. **/ public VirtualTeller() { accounts = new SortedList(); } /** * openAccount() creates a new account for the customer "name". * @param name the customer's name. * @return the new account's ID number. **/ public int openAccount(String name) { AccountData newData = new AccountData(name, nextAccountID); accounts.insert(newData); nextAccountID++; return newData.getNumber(); } /** * withdraw() withdraws "amount" dollars from the account whose number is * "acct". Assumes that amount >= 0. If "acct" is invalid, no action is * taken. * @param acct is an account number. * @param amount an amount of money. */ public void withdraw(int acct, int amount) throws BadAccountException,BadTransactionException{ AccountData account = findAccount(acct); if (account == null) { // Didn't find the account. System.out.println("Error: Couldn't find account number `" + acct + "'" ); } else { if(amount<0){throw new BadTransactionException(amount);} account.withdraw(amount); } } /** * deposit() deposits "amount" dollars into the bank account whose number is * "acct". Assumes that amount >= 0. If "acct" is invalid, no action is * taken. * @param acct is an account number. * @param amount an amount of money. */ public void deposit(int acct, int amount) throws BadAccountException,BadTransactionException{ AccountData account = findAccount(acct); if (account == null) { System.out.println("Error: Couldn't find account number `" + acct + "'"); } else { if(amount<0){throw new BadTransactionException(amount);} account.deposit(amount); } } /** * balanceInquiry() finds the balance on the account whose number is "acct". * If "acct" is an invalid number, returns -1. * @param acct an account number. * @return the balance, or -1 if the account number is invalid. */ public int balanceInquiry(int acct) throws BadAccountException{ AccountData account = findAccount(acct); if (account == null) { System.out.println("Error: Couldn't find account number `" + acct + "'" ); return -1; } else { return account.getBalance(); } } /** * findAccount() gets the AccountData object associated with account number * "acct". If "acct" does not refer to a valid account, returns null. * @param acct is an account number. * @return the AccountData object associated with the account number. */ private AccountData findAccount(int acct) throws BadAccountException{ AccountData account = (AccountData) accounts.find(acct); if(account==null){ throw new BadAccountException(acct); } return account; } }

package lab6; /* BadAccountException.java */ /** * Implements an exception that should be thrown for nonexistent accounts. **/ public class BadTransactionException extends Exception { public int accountNumber; // The invalid account number. /** * Creates an exception object for nonexistent account "badAcctNumber". **/ public BadTransactionException(int badAcctNumber) { super("Invalid input number: " + badAcctNumber); accountNumber = badAcctNumber; } }
