什么是AC自动机?
AC自动机并不是自动AC机(●’◡’●),Aho–Corasick算法是由Alfred V. Aho和Margaret J.Corasick 发明的字符串搜索算法.
他能做什么?
在文本串上匹配多模式串,常用的用于计算文本串上出现了多少个模式串。
他是怎么做的?
与KMP算法相似,用fail指针指向失配时的下一个匹配位置。不同的是KMP只适用于单模式串,AC自动机可以匹配多个模式串. AC自动机的基础知识有字典树,KMP(希望把KMP真正理解懂再来搞这个东西)
fail指针是怎么做的?
在KMP算法中next指针(fail指针)实际是找出该字串的最长后缀匹配,在AC自动机中每个节点的fail指针指向该节点对应字符串的最长后缀节点(这个节点不能为本身,意思与Kmp的next指针相似)
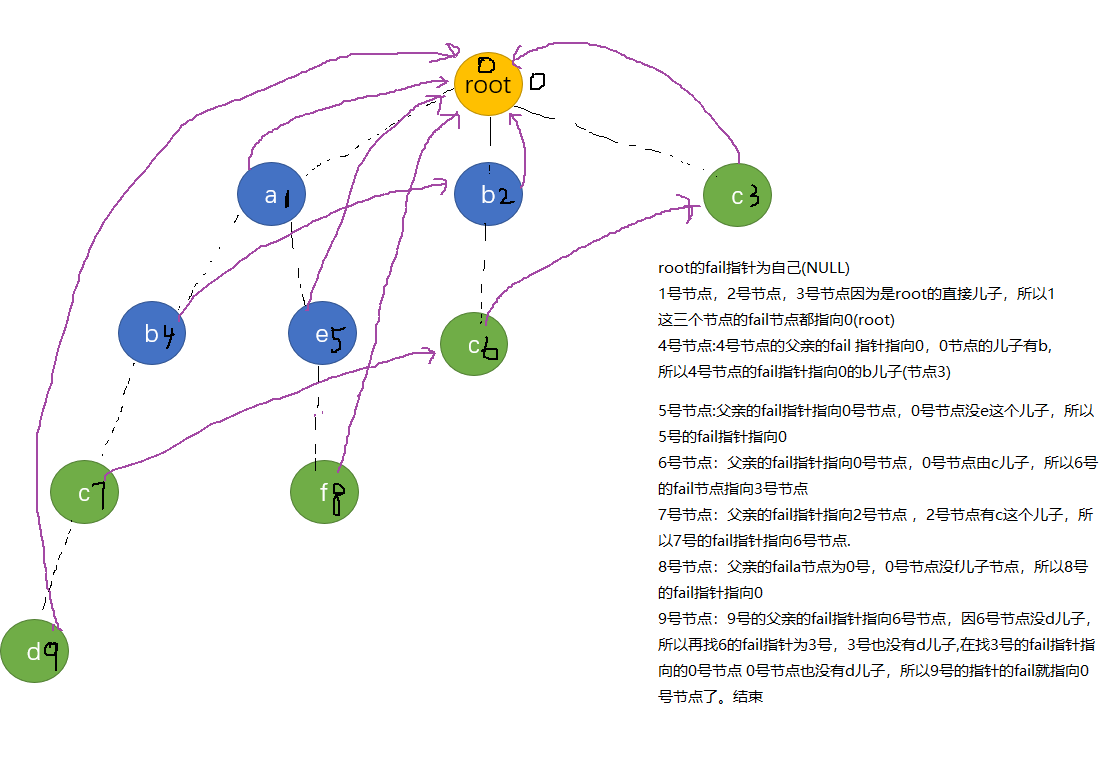
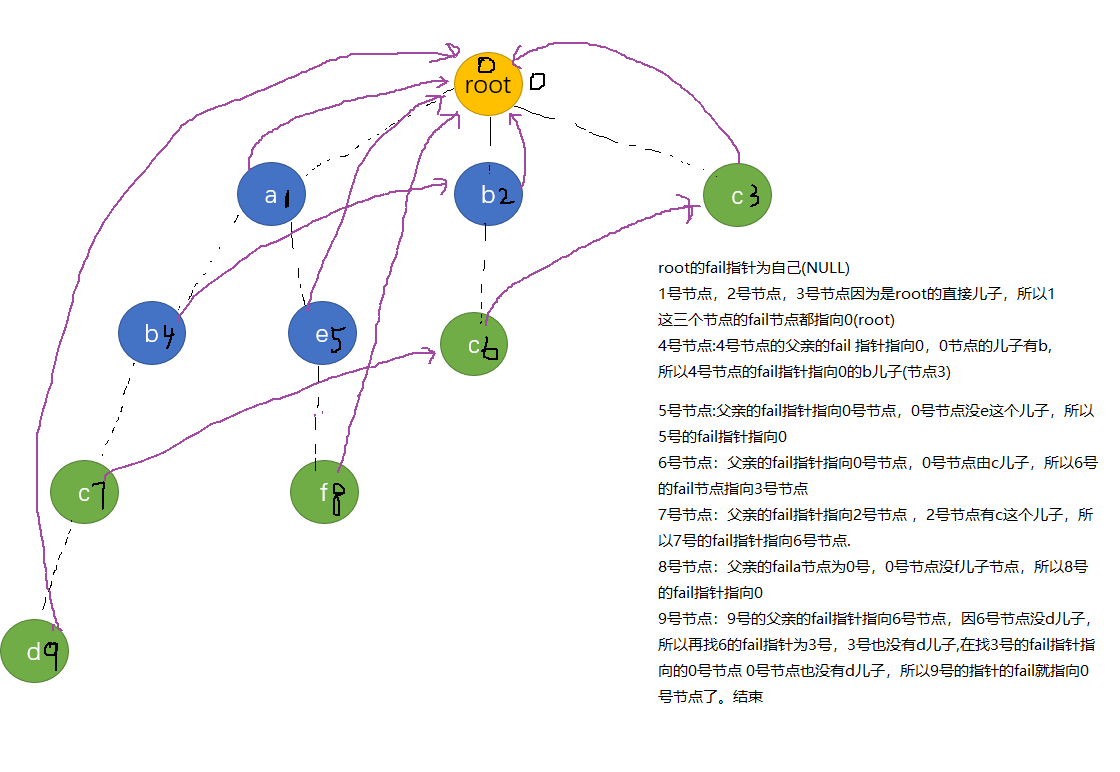
下面是一些单词 ,对这些单词创建字典树
接下里就创建fail指针,首先fail的意义跟Kmp算法中next的意义相同,都指向该字串的最长后缀。
怎么创建fail指针呢?
首先按照fail指针的意义,root的所有直接儿子的fail指针都指向root, Why? 因为root直接儿子的节点代表的字符长度都为1,且字符不重复,又因为fail指针的意义为指向最长后缀字符串的节点(非本身),所以这一步也就合情合理了吧。
接下来,对于每个节点,要找该节点的fail指针(最长匹配)怎么找呢?
是不找是这个节点的父亲的fail所代表节点**的儿子有没有这个字符?,如果没有,再找它爸爸的fail的fail的儿子有没有这个字符,(这句话可能有点绕,结合kmp的意思理解一下)直至找到匹配的节点或者根节点。
我们习惯上用用队列作为工具来计算fail指针
void bulid_fail()
{
int now=0;
int to;
/*
保证队列里的fail指针全部OK
从队列中取一个 把其下面的fail指针OK 并且加入队列
*/
queue<int> mmp;
for(int i=0;i<26;++i)//将根节点的所有儿子加入队列
{
if(node[0].next[i]!=-1)
mmp.push(node[0].next[i]);
}
while(!mmp.empty())//
{
now=mmp.front();
mmp.pop();
for(int i=0;i<26;++i)//将此节点的儿子的 fail指针计算出来并加入队列
{
if(node[now].next[i]!=-1)
{
mmp.push(node[now].next[i]);
/* 计算now的 第i个儿子的fail指针 */
to=node[now].fail;
while(to>0&&node[to].next[i]==-1)
to=node[to].fail;
/* 直至根节点 或者fail的父节点*/
if(node[to].next[i]!=-1)//否则没有最大匹配 即为空
node[node[now].next[i]].fail=node[to].next[i];
}
}
}
}
fail指针建好之后 就是文本串在AC自动机上的匹配了
int Find_words(char *tx)
{
int ans=0;
int now=0;//当前最大匹配下标
int to,i;
while(*tx)
{
i=hash_letter(*tx);
//没有下面的匹配,则找跟此字符的最大匹配
while(now>0&&node[now].next[i]==-1)
now=node[now].fail;
if(node[now].next[i]!=-1)
now=node[now].next[i];
/* 开始计算以now为后缀的单词出现数*/
to=now;
while(to&&node[to].cnt!=-1)/*精髓之处,匹配过后设为-1代表该后缀对应所有的字符串都匹配过了,避免后来重复匹配已经匹配过的单词*/
{
ans+=node[to].cnt;
node[to].cnt=-1;//标记该单词已经加过了 就算这个单词没出现 标记为-1代表这个字符串的后缀节点全扫描过了
to=node[to].fail;
}
++tx;
}
return ans;
}
AC自动机模板题
hdu2222http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2222
模板代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e5+7;
struct AcTireNode
{
int next[26];
int fail,cnt;//要保证fail指针不能为自己
void clear()
{
memset(next,-1,sizeof(next));
fail=cnt=0;//初始化
}
};
class AcTire{
/*
AC 自动机
1.输入模式串 构建字典树
2.构建fail指针
3.匹配文本串
4.初始化树
*/
public:
AcTireNode *node;
int top;//使用了多少个节点
AcTire()
{
top=0;
node=new AcTireNode[maxn];
node[0].clear();
}
inline int hash_letter(char c)
{
return c-'a';
}
void insert(char *p)
{
int now=0;
while(*p)
{
if(node[now].next[hash_letter(*p)]==-1)
{
node[now].next[hash_letter(*p)]=++top;
node[top].clear();//初始化该节点的信息
}
now=node[now].next[hash_letter(*p)];
++p;
}
node[now].cnt++;
}
void bulid_fail()
{
int now=0;
int to;
/*
保证队列里的fail指针全部OK
从队列中取一个 把其下面的fail指针OK 并且加入队列
*/
queue<int> mmp;
for(int i=0;i<26;++i)//将根节点的所有儿子加入队列
{
if(node[0].next[i]!=-1)
mmp.push(node[0].next[i]);
}
while(!mmp.empty())//
{
now=mmp.front();
mmp.pop();
for(int i=0;i<26;++i)//将此节点的儿子的 fail指针计算出来并加入队列
{
if(node[now].next[i]!=-1)
{
mmp.push(node[now].next[i]);
/* 计算now的 第i个儿子的fail指针 */
to=node[now].fail;
while(to>0&&node[to].next[i]==-1)
to=node[to].fail;
/* 直至根节点 或者fail的父节点*/
if(node[to].next[i]!=-1)//否则没有最大匹配 即为空
node[node[now].next[i]].fail=node[to].next[i];
}
}
}
}
int Find_words(char *tx)
{
int ans=0;
int now=0;//当前最大匹配下标
int to,i;
while(*tx)
{
i=hash_letter(*tx);
//没有下面的匹配,则找跟此字符的最大匹配
while(now>0&&node[now].next[i]==-1)
now=node[now].fail;
if(node[now].next[i]!=-1)
now=node[now].next[i];
/* 开始计算以now为后缀的单词出现数*/
to=now;
while(to&&node[to].cnt!=-1)/*精髓之处,匹配过后设为-1代表该后缀对应所有的字符串都匹配过了,避免后来重复匹配已经匹配过的单词*/
{
ans+=node[to].cnt;
node[to].cnt=-1;//标记该单词已经加过了 就算这个单词没出现 标记为-1代表这个字符串的后缀节点全扫描过了
to=node[to].fail;
}
++tx;
}
return ans;
}
void clear()
{
node[0].clear();
top=0;
}
~AcTire()
{
delete []node;
}
};
char tx[1000007],words[55];
int main()
{
AcTire dch;
int t;
int n;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
dch.clear();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
scanf("%s",words);
dch.insert(words);
}
dch.bulid_fail();
scanf("%s",tx);
printf("%d
",dch.Find_words(tx));
}
}