关于C++多线程,写得好的博客太多了,内容丰富,排版又好看,就是难找。
整体看过以后,本人也总结一下,仅作为日后参照。
这里先推荐看过的几篇博文链接,非常值得一看。
https://blog.csdn.net/dingdingdodo/article/details/108477195
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinbiao/p/11190336.html
http://zhangxiaoya.github.io/2015/05/15/multi-thread-of-c-program-language-on-linux/
https://www.cnblogs.com/hesper/p/10738987.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39382769/article/details/96075346
注:本人所用IDE为Dev-C++。
重在简洁啊,而且既能用windows平台下的,也能用linux平台下的多线程机制。
一:C++11规范下的线程库
1.C++11 线程库的基本用法:创建线程、分离线程
#include<iostream>
#include<thread>
#include<windows.h>
using namespace std;
void threadProc()
{
cout<<"this is in threadProc\n";
cout<<"thread1's id is "<<this_thread::get_id()<<endl; //获取所属线程的id
}
void threadProc2(int num)
{
cout<<"thread num = "<<num<<endl;
}
void threadProc3()
{
cout<<"this thread is detached\n";
}
void threadProc4()
{
cout<<"this thread is detached and won't print in the same console.'\n";
}
int main()
{
thread a;//创建线程1,定义线程,后面再分配任务
a = thread(threadProc);
thread b(threadProc2,5);//创建线程2 ,定义线程的时候分配任务,参数类似于printf一样,可以为多个
a.join();
b.join();//采用join,主线程会阻塞等待子线程执行完毕
thread c(threadProc3);
c.detach();//采用detach,主线程不会等,这个线程开启早,还能输出到主线程的控制台
cout<<"main thread exit"<<endl;
thread d(threadProc4);
d.detach();//这个线程太晚了,主线程已经结束,不能输出到主线程的控制台了
}
运行结果:
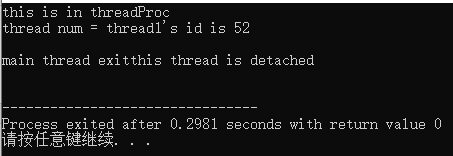
2.基本的互斥锁
上述运行,输出语句显然没有顺序执行,为了达到一行一行输出的效果,可以使用最基本的互斥锁。
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<mutex> using namespace std; mutex mu;//互斥锁 void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { // mu.lock();//锁住 cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; // mu.unlock();//释放 } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { // mu.lock(); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; // mu.unlock(); } } int main() { thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); cout<<"main thread finish."<<endl; }
运行结果1:
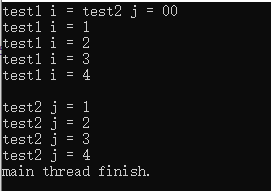
不加锁的话,输出就会混乱。
这里打开4行注释,重新运行。
运行结果2:
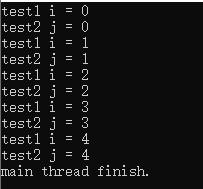
可以简单理解为,test1获得锁以后,test2调用lock(),就会阻塞执行,直到test1()调用unlock()释放锁。
3.lock_guard.
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<mutex> using namespace std; mutex mu;//互斥锁 /* lock_guard<mutex> locka(mu); 作用范围为从这一行开始,到那一次循环结束,还不用自己手动解锁。 */ void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { lock_guard<mutex> locka(mu); cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { lock_guard<mutex> lock(mu); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; } } int main() { thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); cout<<"main thread finish."<<endl; }
运行结果:
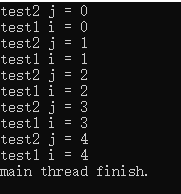
4.unique_lock
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<mutex> using namespace std; mutex mu;//互斥锁 void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { unique_lock<mutex> locka(mu,defer_lock); cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; locka.lock(); cout<<"this is lock1"<<endl; } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { unique_lock<mutex> locka(mu); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; locka.unlock(); locka.lock(); cout<<"this is lock2"<<endl; } } int main() { thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); cout<<"main thread finish."<<endl; }
运行结果:
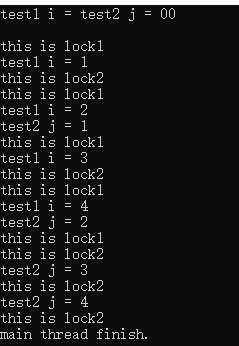
5.condition_variable
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<mutex> #include<condition_variable> using namespace std; mutex mu; condition_variable cv; bool print = false; void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { unique_lock<mutex> l(mu); cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; cv.notify_one(); print = true; } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { unique_lock<mutex> l(mu); if(!print) { cv.wait(l); } cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; print = false; } } int main() { thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); }
运行结果如下:

二:W32API实现线程同步
1.临界区
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<windows.h> using namespace std; CRITICAL_SECTION section;//临界区变量 void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { EnterCriticalSection(§ion);//类似于 mutex.lock() cout<<"this is test1 i = "<<i<<endl;
Sleep(1); LeaveCriticalSection(§ion);//类似于 mutex.unlock() } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { EnterCriticalSection(§ion); cout<<"this is test2 j = "<<j<<endl;
Sleep(1); LeaveCriticalSection(§ion); } } int main() { InitializeCriticalSection(§ion);//初始化临界区对象 thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); DeleteCriticalSection(§ion);//用完了,就删除临界区 }
运行结果:
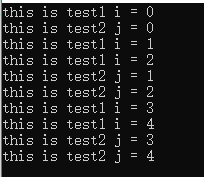
效果类似于mutex,只是都要在执行完循环进行解锁的操作
2.互斥锁。
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<windows.h> using namespace std; HANDLE hmutex; void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { WaitForSingleObject(hmutex,INFINITE);//类似于mutex.lock() 阻塞等待多少时间 cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; ReleaseMutex(hmutex);//类似于mutex.unlock() 释放互斥锁 } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { WaitForSingleObject(hmutex,INFINITE); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; ReleaseMutex(hmutex); } } int main() { hmutex = CreateMutex(NULL,FALSE,"mutex");//创建一个互斥锁 thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); CloseHandle(hmutex);//释放句柄 }
运行结果:
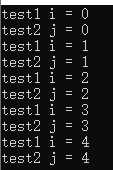
效果基本差不多的,让输出有顺序是绰绰有余了。
3.事件
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<windows.h> using namespace std; HANDLE hevent; void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { WaitForSingleObject(hevent,INFINITE);//类似于mutex.lock() 阻塞等待多少时间 cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; SetEvent(hevent);//类似于mutex.unlock() 释放互斥锁 } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { WaitForSingleObject(hevent,INFINITE); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; SetEvent(hevent); } } int main() { hevent = CreateEvent(NULL,FALSE,TRUE,"event");//创建一个事件 thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); CloseHandle(hevent);//释放句柄 }
运行结果:
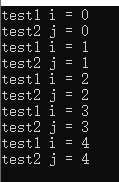
4.信号量
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<windows.h> using namespace std; HANDLE sem; void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { WaitForSingleObject(sem,INFINITE);//类似于mutex.lock() 阻塞等待多少时间 cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; ReleaseSemaphore(sem,1,NULL);//类似于mutex.unlock() 释放互斥锁 } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { WaitForSingleObject(sem,INFINITE); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; ReleaseSemaphore(sem,1,NULL); } } int main() { sem = CreateSemaphore(NULL,1,2,"semaphore"); thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); CloseHandle(sem);//释放句柄 }
运行结果:
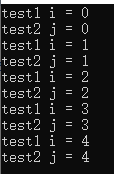
三:linux支持的多线程同步
1.互斥锁
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<pthread.h> using namespace std; pthread_mutex_t mu = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mu);//类似于mutex.lock() 阻塞等待多少时间 cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mu);//类似于mutex.unlock() 释放互斥锁 } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mu); cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mu); } } int main() { thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); }
2.条件变量
#include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<pthread.h> using namespace std; pthread_mutex_t mu = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; bool one = true; void test1() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mu); cout<<"test1 begin()"<<endl; while(one) { pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mu); } cout<<"test1 continue"<<endl; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mu); } void test2() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mu); cout<<"test2 begin()"<<endl; one = false; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mu); cout<<"test2 finish"<<endl; pthread_cond_signal(&cond); } int main() { thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); }
运行结果:
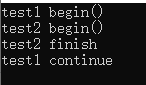
3.信号量
#include<iostream> #include<pthread.h> #include<semaphore.h> #include<thread> using namespace std; sem_t se; void test1() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { sem_wait(&se);//类似于mutex.lock() 阻塞等待多少时间 cout<<"test1 i = "<<i<<endl; sem_post(&se);//类似于mutex.unlock() 释放互斥锁 } } void test2() { for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { sem_wait(&se);; cout<<"test2 j = "<<j<<endl; sem_post(&se); } } int main() { sem_init(&se,0,1);//初始化信号量 thread a(test1); thread b(test2); a.join(); b.join(); sem_destroy(&se);//删除信号量 }
4.读写锁
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> int number = 0; // 读写锁 pthread_rwlock_t lock; void *write_func(void *arg) { while (1) { pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&lock); number++; printf("+++++write: %lu, %d\n", pthread_self(), number); pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock); sleep(1); } return NULL; } void *read_func(void *arg) { while (1) { pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock); printf("======read: %lu, %d\n", pthread_self(), number); pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock); sleep(1); } return NULL; } int main() { int i; pthread_t p[8]; // 初始化读写锁 pthread_rwlock_init(&lock, NULL); // 3个写线程 for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) { pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, write_func, NULL); } // 5个读线程 for (i = 3; i < 8; i++) { pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, read_func, NULL); } // 回收子线程 for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) { pthread_join(p[i], NULL); } pthread_rwlock_destroy(&lock); return 0; }
这一篇直接使用别人的代码了,麻烦,直接作为参考就好了。
5.不使用C++11线程库创建线程
#include<iostream> #include<pthread.h> using namespace std; void* test1(void*) { cout<<"hello world"<<endl; } int main() { pthread_t t1; pthread_create(&t1,NULL,test1,NULL); pthread_join(t1,NULL); }
感觉挺麻烦,都不想多写了。