
临近年关,不少人蠢蠢欲动,有童鞋问我java后端面试会面试什么?
作为一个java后端老鸟,跌打滚爬多次被面试和面试别人,总结了一些经验,希望对大家有所帮助。
特别说明,仅仅针对工作两年以上的java后端开发。以开放性题目为主。
1.数据结构相关
假设1亿整数存放在一个txt文件中,如何去重和排序?
思路:
1.1.面试者要评估一下一亿整数的大小。一个int占4个字节,1亿呢?
1.2.去重的数据结构有哪些?HashSet--->引申到HashMap--->ConcurrentHashMap
1.3 数据量增大到十亿百亿怎么去重?
布隆过滤器,优点,缺点
1.4.其他方式?
数据库distinct order by,txt怎么导入到数据库?load
redis去重排序,redis的数据结构-->引申到其他数据结构 String,list,hash,set,sorted set,hyperloglog,geo
mongo去重排序,
....
2. 算法相关,主要考察代码能力
斐波那契数列(fabnacci)实现,首先介绍一下该算法的思想
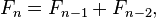
2.1 第一级别实现: 两层递归
public static long fibonacci(int n){ if(n==0) return 0; else if(n==1) return 1; else return fibonacci(n-1)+fibonacci(n-2); }
问算法复杂度及评估一下性能问题,提示可以优化。
2.2 第二级别:减少一层递归
public static void main(String[] args) { long tmp=0; // TODO Auto-generated method stub int n=10; Long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ System.out.print(fibonacci(i)+" "); } System.out.println("-------------------------"); System.out.println("耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)); } public static long fibonacci(int n) { long result = 0; if (n == 0) { result = 0; } else if (n == 1) { result = 1; tmp=result; } else { result = tmp+fibonacci(n - 2); tmp=result; } return result; }
问题,算法复杂度,引导有没有不用递归的?
2.3 无递归
public static long fibonacci(int n){ long before=0,behind=0; long result=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(i==0){ result=0; before=0; behind=0; } else if(i==1){ result=1; before=0; behind=result; }else{ result=before+behind; before=behind; behind=result; } } return result; }
3.并发问题
给出一个普通的spring mvc controller,如下:
@Controller public class WelcomeController { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WelcomeController.class);
@Autowired
private final HelloWorldService helloWorldService; @RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String index(Map<String, Object> model) { logger.debug("index() is executed!"); model.put("title", helloWorldService.getTitle("")); model.put("msg", helloWorldService.getDesc()); return "index"; } }
问题:
3.1.线程模型是什么?单线程
3. 2.如何提升qps?线程池 executor
3.3.在线程池下如何控制并发?信号量Semaphore或者计数器CountDownLatch
引申到:Java中的可重入锁:synchronized 和 java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock
4.数据库相关
场景:一张表 test(a,b,c,e,f,g) 100w记录 常用查询条件 ab abc abe,如何提升查询效率?
4.1.索引,
4.2.复合索引的规则:最左原则。查询条件ae走不走索引?
4.3 1000w,1亿,十亿以上条记录查询是否会有什么不同?
4.4 多线程下如何保证数据一致性?乐观锁/悲观锁,应用场景不同点
5.设计模式相关
public class Test { @Test public void test() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { AsyncTaskExecutor executor = new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor("sys.out"); Future<String> future = executor.submit(new OutThread()); System.out.println(future.get()); System.out.println("Hello, World!"); Thread.sleep(10000 * 1000L); } static class OutThread implements Callable<String> { public void run() { } @Override public String call() throws Exception { String ret = " i test callable"; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000L); System.out.println("i sleep 1s"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } return ret; } } }
5.1 看程序说明
5.2 引申到reactor模型
spring reactor
vert.x
akka
5.3 servlet 3 响应式编程
太累,先写到这里吧。