1.找到bin目录,下面有elasticSearch的sh文件,查看执行过程
exec "$JAVA" $ES_JAVA_OPTS -Des.path.home="$ES_HOME" -Des.path.conf="$ES_PATH_CONF" -Des.distribution.flavor="$ES_DISTRIBUTION_FLAVOR" -Des.distribution.type="$ES_DISTRIBUTION_TYPE" -cp "$ES_CLASSPATH" org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch "$@"
可以看到主类的名称为:
Elasticsearch
2.主类Elasticsearch
找到main方法,父类
Command的execute()方法,ElasticSearch重写了该方法
@Override protected void execute(Terminal terminal, OptionSet options, Environment env) throws UserException { if (options.nonOptionArguments().isEmpty() == false) { throw new UserException(ExitCodes.USAGE, "Positional arguments not allowed, found " + options.nonOptionArguments()); } if (options.has(versionOption)) { final String versionOutput = String.format( Locale.ROOT, "Version: %s, Build: %s/%s/%s/%s, JVM: %s", Version.displayVersion(Version.CURRENT, Build.CURRENT.isSnapshot()), Build.CURRENT.flavor().displayName(), Build.CURRENT.type().displayName(), Build.CURRENT.shortHash(), Build.CURRENT.date(), JvmInfo.jvmInfo().version()); terminal.println(versionOutput); return; } final boolean daemonize = options.has(daemonizeOption); final Path pidFile = pidfileOption.value(options); final boolean quiet = options.has(quietOption); // a misconfigured java.io.tmpdir can cause hard-to-diagnose problems later, so reject it immediately try { env.validateTmpFile(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new UserException(ExitCodes.CONFIG, e.getMessage()); } try { init(daemonize, pidFile, quiet, env); } catch (NodeValidationException e) { throw new UserException(ExitCodes.CONFIG, e.getMessage()); } } void init(final boolean daemonize, final Path pidFile, final boolean quiet, Environment initialEnv) throws NodeValidationException, UserException { try { Bootstrap.init(!daemonize, pidFile, quiet, initialEnv); } catch (BootstrapException | RuntimeException e) { // format exceptions to the console in a special way // to avoid 2MB stacktraces from guice, etc. throw new StartupException(e); } }
2.启动类Bootstrap
init方法
/** * This method is invoked by {@link Elasticsearch#main(String[])} to startup elasticsearch. */ static void init( final boolean foreground, final Path pidFile, final boolean quiet, final Environment initialEnv) throws BootstrapException, NodeValidationException, UserException { // force the class initializer for BootstrapInfo to run before // the security manager is installed BootstrapInfo.init(); INSTANCE = new Bootstrap(); final SecureSettings keystore = loadSecureSettings(initialEnv); final Environment environment = createEnvironment(pidFile, keystore, initialEnv.settings(), initialEnv.configFile()); LogConfigurator.setNodeName(Node.NODE_NAME_SETTING.get(environment.settings())); try { LogConfigurator.configure(environment); } catch (IOException e) { throw new BootstrapException(e); } if (environment.pidFile() != null) { try { PidFile.create(environment.pidFile(), true); } catch (IOException e) { throw new BootstrapException(e); } } final boolean closeStandardStreams = (foreground == false) || quiet; try { if (closeStandardStreams) { final Logger rootLogger = LogManager.getRootLogger(); final Appender maybeConsoleAppender = Loggers.findAppender(rootLogger, ConsoleAppender.class); if (maybeConsoleAppender != null) { Loggers.removeAppender(rootLogger, maybeConsoleAppender); } closeSystOut(); } // fail if somebody replaced the lucene jars checkLucene(); // install the default uncaught exception handler; must be done before security is // initialized as we do not want to grant the runtime permission // setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new ElasticsearchUncaughtExceptionHandler()); INSTANCE.setup(true, environment); try { // any secure settings must be read during node construction IOUtils.close(keystore); } catch (IOException e) { throw new BootstrapException(e); } INSTANCE.start(); if (closeStandardStreams) { closeSysError(); } } catch (NodeValidationException | RuntimeException e) { // disable console logging, so user does not see the exception twice (jvm will show it already) final Logger rootLogger = LogManager.getRootLogger(); final Appender maybeConsoleAppender = Loggers.findAppender(rootLogger, ConsoleAppender.class); if (foreground && maybeConsoleAppender != null) { Loggers.removeAppender(rootLogger, maybeConsoleAppender); } Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(Bootstrap.class); // HACK, it sucks to do this, but we will run users out of disk space otherwise if (e instanceof CreationException) { // guice: log the shortened exc to the log file ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); PrintStream ps = null; try { ps = new PrintStream(os, false, "UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) { assert false; e.addSuppressed(uee); } new StartupException(e).printStackTrace(ps); ps.flush(); try { logger.error("Guice Exception: {}", os.toString("UTF-8")); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) { assert false; e.addSuppressed(uee); } } else if (e instanceof NodeValidationException) { logger.error("node validation exception {}", e.getMessage()); } else { // full exception logger.error("Exception", e); } // re-enable it if appropriate, so they can see any logging during the shutdown process if (foreground && maybeConsoleAppender != null) { Loggers.addAppender(rootLogger, maybeConsoleAppender); } throw e; } }
找到红色的启动方法start,进去看,是Node的start方法
private void start() throws NodeValidationException { node.start(); keepAliveThread.start(); }
3.节点启动Node
start方法
/** * Start the node. If the node is already started, this method is no-op. */ public Node start() throws NodeValidationException { if (!lifecycle.moveToStarted()) { return this; } logger.info("starting ..."); pluginLifecycleComponents.forEach(LifecycleComponent::start); injector.getInstance(MappingUpdatedAction.class).setClient(client); injector.getInstance(IndicesService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(IndicesClusterStateService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(SnapshotsService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(SnapshotShardsService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(RoutingService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(SearchService.class).start(); nodeService.getMonitorService().start(); final ClusterService clusterService = injector.getInstance(ClusterService.class); final NodeConnectionsService nodeConnectionsService = injector.getInstance(NodeConnectionsService.class); nodeConnectionsService.start(); clusterService.setNodeConnectionsService(nodeConnectionsService); injector.getInstance(ResourceWatcherService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(GatewayService.class).start(); Discovery discovery = injector.getInstance(Discovery.class); clusterService.getMasterService().setClusterStatePublisher(discovery::publish); // Start the transport service now so the publish address will be added to the local disco node in ClusterService TransportService transportService = injector.getInstance(TransportService.class); transportService.getTaskManager().setTaskResultsService(injector.getInstance(TaskResultsService.class)); transportService.start(); assert localNodeFactory.getNode() != null; assert transportService.getLocalNode().equals(localNodeFactory.getNode()) : "transportService has a different local node than the factory provided"; final MetaData onDiskMetadata; try { // we load the global state here (the persistent part of the cluster state stored on disk) to // pass it to the bootstrap checks to allow plugins to enforce certain preconditions based on the recovered state. if (DiscoveryNode.isMasterNode(settings) || DiscoveryNode.isDataNode(settings)) { onDiskMetadata = injector.getInstance(GatewayMetaState.class).loadMetaState(); } else { onDiskMetadata = MetaData.EMPTY_META_DATA; } assert onDiskMetadata != null : "metadata is null but shouldn't"; // this is never null } catch (IOException e) { throw new UncheckedIOException(e); } validateNodeBeforeAcceptingRequests(new BootstrapContext(settings, onDiskMetadata), transportService.boundAddress(), pluginsService .filterPlugins(Plugin .class) .stream() .flatMap(p -> p.getBootstrapChecks().stream()).collect(Collectors.toList())); clusterService.addStateApplier(transportService.getTaskManager()); // start after transport service so the local disco is known discovery.start(); // start before cluster service so that it can set initial state on ClusterApplierService clusterService.start(); assert clusterService.localNode().equals(localNodeFactory.getNode()) : "clusterService has a different local node than the factory provided"; transportService.acceptIncomingRequests(); discovery.startInitialJoin(); final TimeValue initialStateTimeout = DiscoverySettings.INITIAL_STATE_TIMEOUT_SETTING.get(settings); if (initialStateTimeout.millis() > 0) { final ThreadPool thread = injector.getInstance(ThreadPool.class); ClusterState clusterState = clusterService.state(); ClusterStateObserver observer = new ClusterStateObserver(clusterState, clusterService, null, logger, thread.getThreadContext()); if (clusterState.nodes().getMasterNodeId() == null) { logger.debug("waiting to join the cluster. timeout [{}]", initialStateTimeout); final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); observer.waitForNextChange(new ClusterStateObserver.Listener() { @Override public void onNewClusterState(ClusterState state) { latch.countDown(); } @Override public void onClusterServiceClose() { latch.countDown(); } @Override public void onTimeout(TimeValue timeout) { logger.warn("timed out while waiting for initial discovery state - timeout: {}", initialStateTimeout); latch.countDown(); } }, state -> state.nodes().getMasterNodeId() != null, initialStateTimeout); try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new ElasticsearchTimeoutException("Interrupted while waiting for initial discovery state"); } } } injector.getInstance(HttpServerTransport.class).start(); if (WRITE_PORTS_FILE_SETTING.get(settings)) { TransportService transport = injector.getInstance(TransportService.class); writePortsFile("transport", transport.boundAddress()); HttpServerTransport http = injector.getInstance(HttpServerTransport.class); writePortsFile("http", http.boundAddress()); } logger.info("started"); pluginsService.filterPlugins(ClusterPlugin.class).forEach(ClusterPlugin::onNodeStarted); return this; }
里面一个非常重要的对象Injector,我们看看它的定义:
/** * Builds the graphs of objects that make up your application. The injector tracks the dependencies * for each type and uses bindings to inject them. This is the core of Guice, although you rarely * interact with it directly. This "behind-the-scenes" operation is what distinguishes dependency * injection from its cousin, the service locator pattern. * <p> * Contains several default bindings: * <ul> * <li>This {@link Injector} instance itself * <li>A {@code Provider<T>} for each binding of type {@code T} * <li>The {@link java.util.logging.Logger} for the class being injected * <li>The {@link Stage} in which the Injector was created * </ul> * <p> * Injectors are created using the facade class {@link Guice}. * <p> * An injector can also {@link #injectMembers(Object) inject the dependencies} of * already-constructed instances. This can be used to interoperate with objects created by other * frameworks or services. * * @author crazybob@google.com (Bob Lee) * @author jessewilson@google.com (Jesse Wilson) */
简单的说,Injector是一个实例管理器,和spring中IOC的beanfactory功能相当。
需要启动的服务如下:
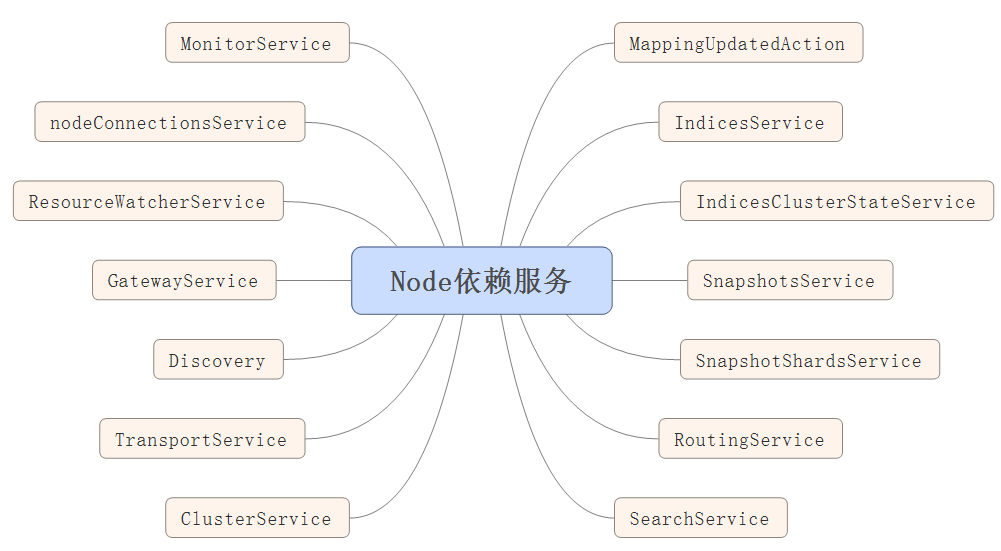
后续会针对每个服务做单独的分析