概念
一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不是标准,只是提供了一组设计原则和约束条件。它主要用于客户端和服务器交互类的软件。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
URL定义
资源:互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源
资源操作:使用POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,使用不同方法对资源进行操作。
分别对应 添加、 删除、修改、查询。
传统方式操作资源
http://127.0.0.1/item/queryUser.action?id=1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item/saveUser.action 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/updateUser.action 更新,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteUser.action?id=1 删除,GET或POST
请求方式
可以通过 GET、 POST、 PUT、 PATCH、 DELETE 等方式对服务端的资源进行操作。其中,GET 用于查询资源,POST 用于创建资源,PUT 用于更新服务端的资源的全部信息,PATCH 用于更新服务端的资源的部分信息,DELETE 用于删除服务端的资源。
这里使用“用户”的案例进行回顾通过 GET、 POST、 PUT、 PATCH、 DELETE 等方式对服务端的资源进行操作。
SpringBoot测试
测试代码:
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUser(){
return "GET-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveUser(){
return "POST-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(){
return "PUT-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(){
return "DELETE-张三";
}
首先html中只能发送GET后者POST,如果要实现REST风格的话,需要把html修改成下面的这种
<form action="/user" method="get">
<input value="REST-GET 提交" type="submit"/>
</form>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input value="REST-POST 提交" type="submit"/>
</form>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input name="_method" type="hidden" value="delete"/>
<input name="_m" type="hidden" value="delete"/>
<input value="REST-DELETE 提交" type="submit"/>
</form>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input name="_method" type="hidden" value="PUT"/>
<input value="REST-PUT 提交" type="submit"/>
</form>
但是光改成这样,不能生效,因为在自动配置类中,默认是关闭的,需要手动开启。
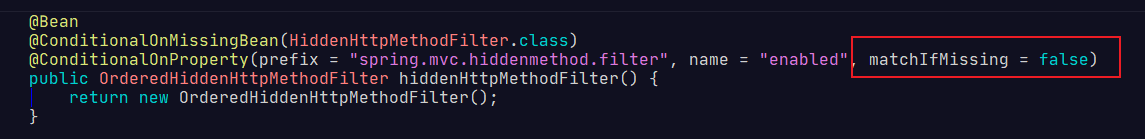
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
//这里先判断请求是否是POST,而且没有异常
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) == null) {
//methodParam 就是_method
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
//兼容以下请求;**PUT**.**DELETE**.**PATCH**
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
//原生request(post),包装模式requesWrapper重写了getMethod方法,返回的是传入的值
//过滤器链放行的时候用wrapper。以后的方法调用getMethod是调用****requesWrapper的。
requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(requestToUse, response);
}
源码
画了一个简易的流程图,方便结合下面的代码一起看。
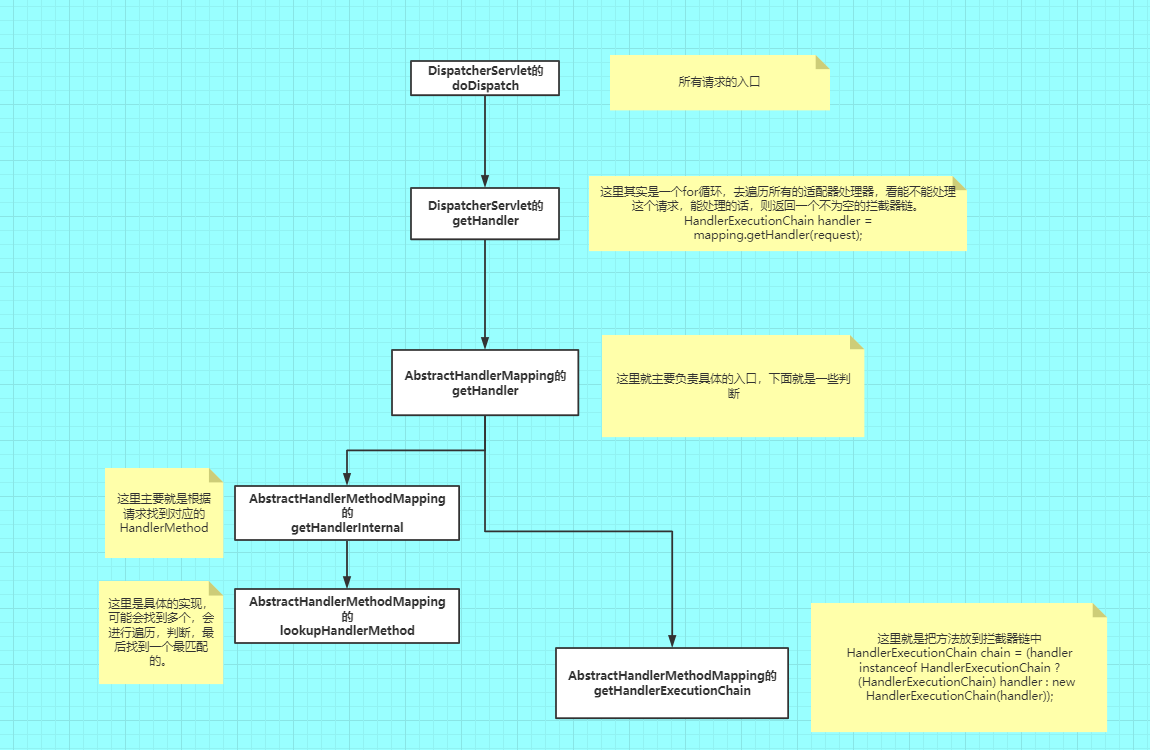
- 首先请求都会经过mvc的DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法。
其中这里的request方法,里面包含了各种请求信息。
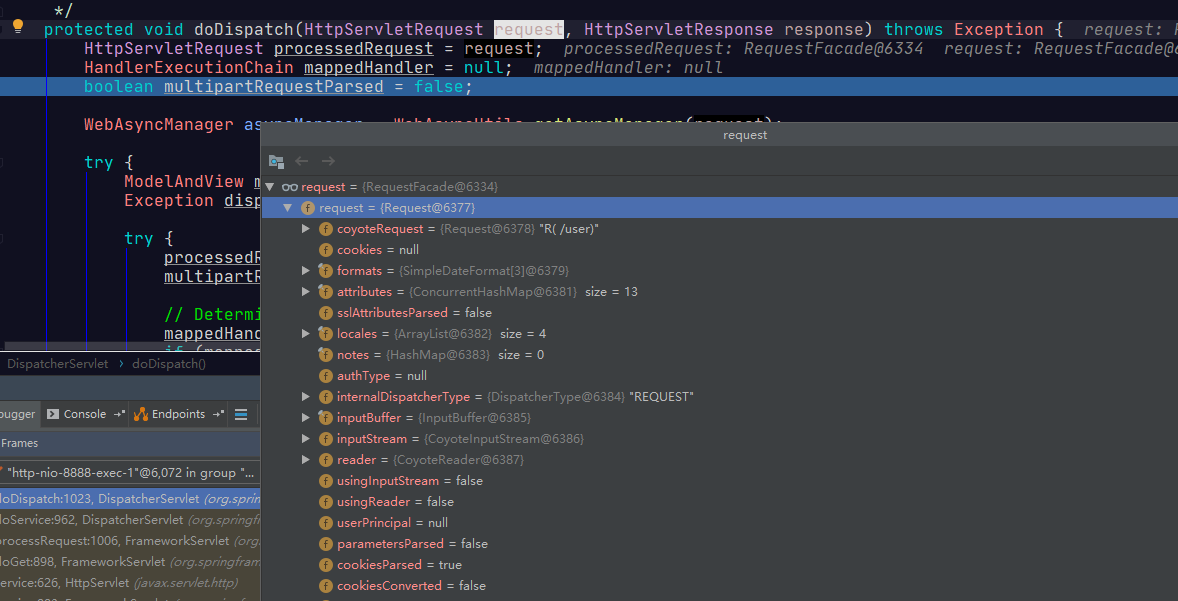
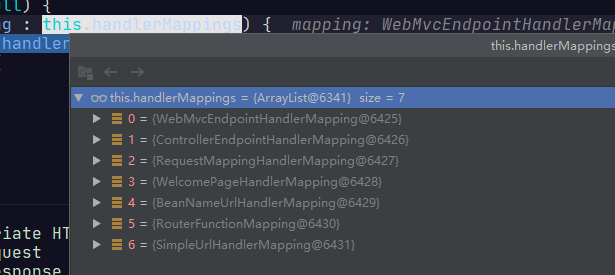
- 然后进去到这个getHandler方法。
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//这里的是,List<HandlerMapping>,具体见下图
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
//这里会for循环变量各个请求映射器,看那个可以处理请求。
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
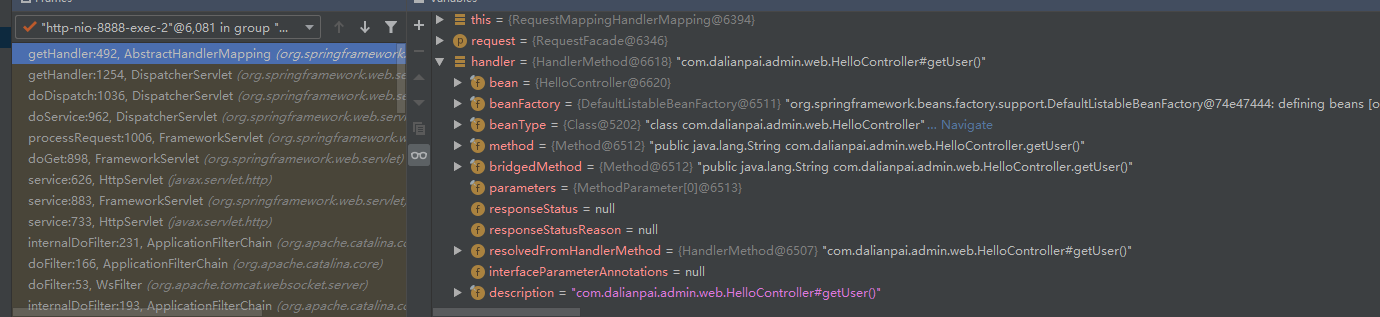
- 然后进去到 AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler方法中。
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 这里就是返回的HandlerMethod,具体信息如下图
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
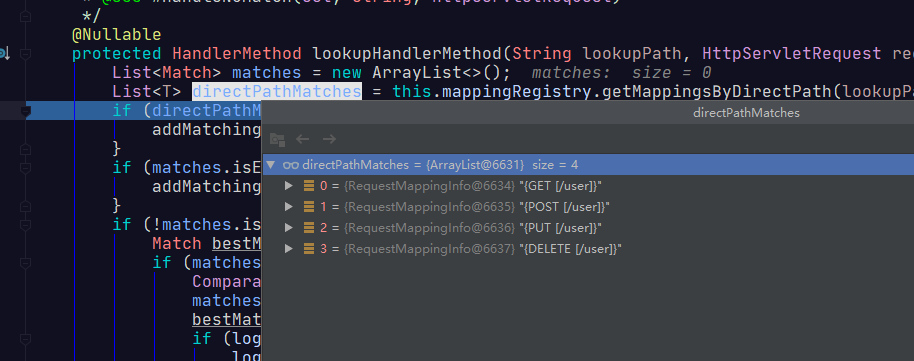
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//lookupPath 就是请求的路径 /user
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
//这里获取一个读锁
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
//释放锁
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//注,这里的Match里面保存了Mapping和HandlerMethod
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
//这里根据请求的路径,找到能匹配的路径,见下图可以找到4个
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
//这里对那4个请求进行判断。
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match,
this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping).getHandlerMethod()));
}
}
}
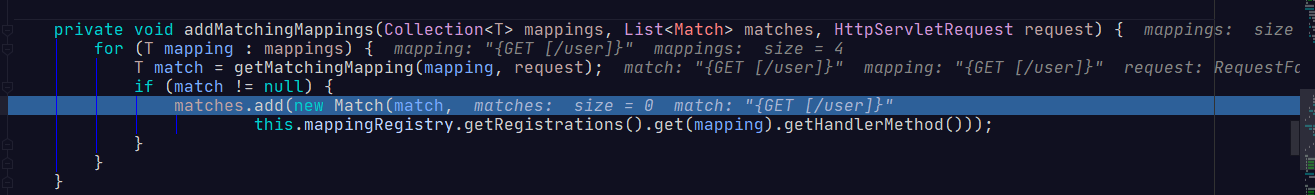
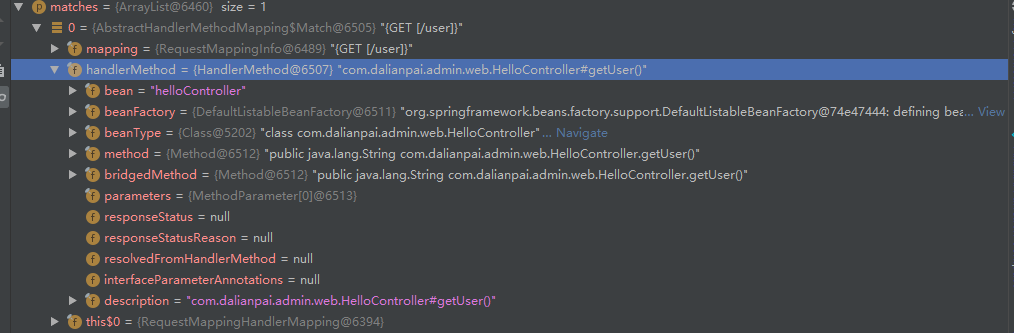
然后找到匹配的请求后,会封装成一个Match,具体信息如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
//这步,会把方法放到拦截器当中。
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
//这里会遍历所有的拦截器
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
这里先分析到请求进来,然后找到合适的处理器映射器,再到绑定拦截器,下面的流程后面在分析。