EnableEurekaServer注解作用
通过 @EnableEurekaServer 激活EurekaServer
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class) public @interface EnableEurekaServer { }
此类有一个重要作用:导入EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration配置类实例化了一个Marker的bean对
象,此对象是实例化核心配置类的前提条件
/** * Responsible for adding in a marker bean to activate * {@link EurekaServerAutoConfiguration} * * @author Biju Kunjummen */ @Configuration public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration { @Bean public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() { return new Marker(); } class Marker { } }
自动装载核心配置类
SpringCloud对EurekaServer的封装使得发布一个EurekaServer无比简单,根据自动装载原则可以在
spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server-2.1.0.RELEASE.jar 下找到 spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EurekaServerAutoConfiguration
@Configuration @Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class) @ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class, InstanceRegistryProperties.class }) @PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties") public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { /** * List of packages containing Jersey resources required by the Eureka server */ private static final String[] EUREKA_PACKAGES = new String[] { "com.netflix.discovery", "com.netflix.eureka" }; @Autowired private ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager; @Autowired private EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig; @Autowired private EurekaClientConfig eurekaClientConfig; @Autowired private EurekaClient eurekaClient;
现在我们展开来说这个Eureka服务端的自动配置类;
1. 这个配置类实例化的前提条件是上下文中存在 EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker 这个
bean,解释了上面的问题
2. 通过@EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,InstanceRegistryProperties.class })导入了两个配置类
1. EurekaDashboardProperties : 配置 EurekaServer的管控台
2. InstanceRegistryProperties : 配置期望续约数量和默认的通信数量
3. 通过@Import({EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class})引入启动配置类
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration
@Configuration public class EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration implements ServletContextAware, SmartLifecycle, Ordered { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class); @Autowired private EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig; private ServletContext servletContext; @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Autowired private EurekaServerBootstrap eurekaServerBootstrap; private boolean running; private int order = 1; @Override public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) { this.servletContext = servletContext; } @Override public void start() { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { //TODO: is this class even needed now? eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext); log.info("Started Eureka Server"); publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig())); EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true; publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig())); } catch (Exception ex) { // Help! log.error("Could not initialize Eureka servlet context", ex); } } }).start(); }
可以看到EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration实现了SmartLifecycle,也就意味着Spring容器启动时
会去执行start()方法。加载所有的EurekaServer的配置
EurekaServerAutoConfiguration
实例化了EurekaServer的管控台的Controller类 EurekaController

实例化EurekaServerBootstrap类

实例化jersey相关配置类
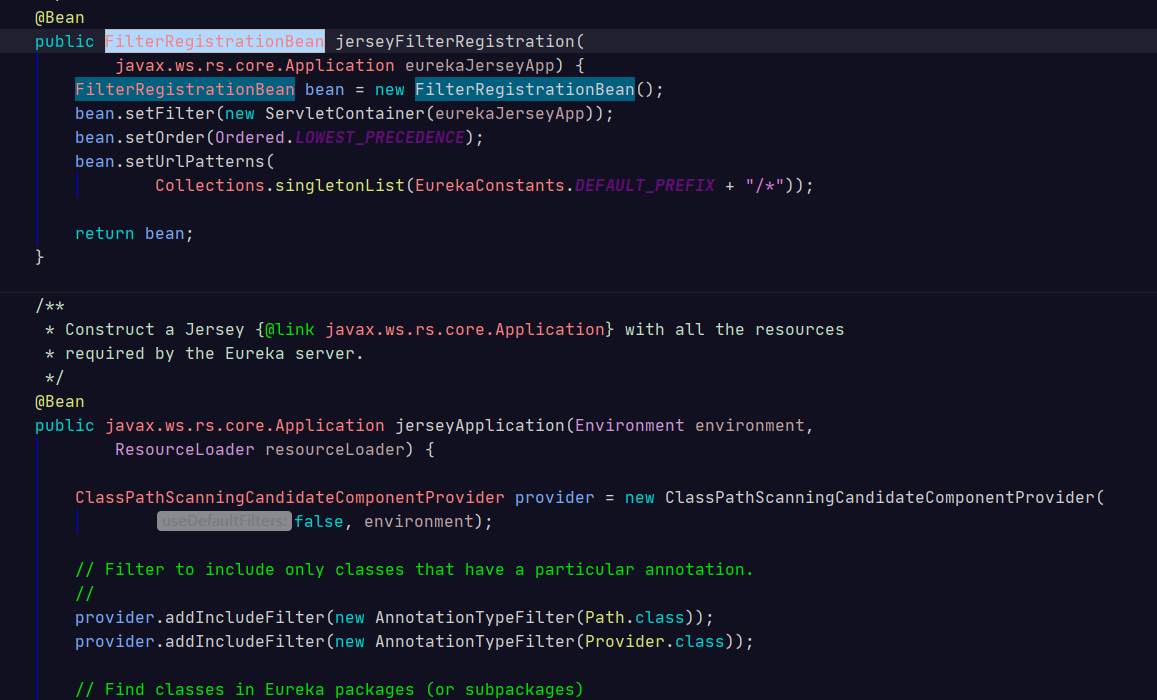
jerseyApplication 方法,在容器中存放了一个jerseyApplication对象,jerseyApplication()方法里的
东西和Spring源码里扫描@Component逻辑类似,扫描@Path和@Provider标签,然后封装成
beandefinition,封装到Application的set容器里。通过filter过滤器来过滤url进行映射到对象的Controller
暴露的服务端接口
由于集成了Jersey,我们可以找到在EurekaServer的依赖包中的 eureka-core-1.9.8.jar ,可以看到一些列的XXXResource

这些类都是通过Jersey发布的供客户端调用的服务接口。
服务端接受客户端的注册
在ApplicationResource.addInstance()方法中可以看到 this.registry.register(info,"true".equals(isReplication));
继续找到父类的register方法可以看到整个注册的过程
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) { try { read.lock(); Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName()); REGISTER.increment(isReplication); if (gMap == null) { final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>(); gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap); if (gMap == null) { gMap = gNewMap; } } Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId()); // Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a lease if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) { Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp(); Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp(); logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp); // this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted // InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy. if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) { logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" + " than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp); logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant"); registrant = existingLease.getHolder(); } } else { // The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration synchronized (lock) { if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) { // Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); } } logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration"); } Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration); if (existingLease != null) { lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp()); } gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease); synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) { recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>( System.currentTimeMillis(), registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")")); } // This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happens if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) { logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the " + "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId()); if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) { logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId()); overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus()); } } InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId()); if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) { logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap); registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap); } // Set the status based on the overridden status rules InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication); registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus); // If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) { lease.serviceUp(); } registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED); recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease)); registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp(); invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress()); logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})", registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication); } finally { read.unlock(); } }
服务端接受客户端的续约
在InstanceResource的renewLease方法中完成客户端的心跳(续约)处理,其中最关键的方法就是
this.registry.renew(this.app.getName(), this.id, isFromReplicaNode)
public boolean renew(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) { RENEW.increment(isReplication); Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName); Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToRenew = null; if (gMap != null) { leaseToRenew = gMap.get(id); } if (leaseToRenew == null) { RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication); logger.warn("DS: Registry: lease doesn't exist, registering resource: {} - {}", appName, id); return false; } else { InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToRenew.getHolder(); if (instanceInfo != null) { // touchASGCache(instanceInfo.getASGName()); InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = this.getOverriddenInstanceStatus( instanceInfo, leaseToRenew, isReplication); if (overriddenInstanceStatus == InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN) { logger.info("Instance status UNKNOWN possibly due to deleted override for instance {}" + "; re-register required", instanceInfo.getId()); RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication); return false; } if (!instanceInfo.getStatus().equals(overriddenInstanceStatus)) { logger.info( "The instance status {} is different from overridden instance status {} for instance {}. " + "Hence setting the status to overridden status", instanceInfo.getStatus().name(), instanceInfo.getOverriddenStatus().name(), instanceInfo.getId()); instanceInfo.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus); } } renewsLastMin.increment(); leaseToRenew.renew(); return true; } }
服务剔除
在AbstractInstanceRegistry.postInit()方法,在此方法里开启了一个每60秒调用一次
EvictionTask.evict()的定时器。
public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) { logger.debug("Running the evict task"); if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) { logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled."); return; } // We collect first all expired items, to evict them in random order. For large eviction sets, // if we do not that, we might wipe out whole apps before self preservation kicks in. By randomizing it, // the impact should be evenly distributed across all applications. List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>(); for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) { Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue(); if (leaseMap != null) { for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) { Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue(); if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) { expiredLeases.add(lease); } } } } // To compensate for GC pauses or drifting local time, we need to use current registry size as a base for // triggering self-preservation. Without that we would wipe out full registry. int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize(); int registrySizeThreshold = (int) (registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold; int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); if (toEvict > 0) { logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) { // Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm) int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i); Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next); Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i); String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName(); String id = lease.getHolder().getId(); EXPIRED.increment(); logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id); internalCancel(appName, id, false); } } }
自动装载
在服务消费者导入的坐标中有 spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client-2.1.0.RELEASE.jar 找到其中
的 spring.factories 可以看到所有自动装载的配置类
服务注册,心跳续约等,感兴趣的可以自己看一下
在renew()这个方法中,首先向注册中心执行了心跳续约的请求,StatusCode为200成功,若为404则执行
register()重新注册操作;
最后总结一下eureka客户端做的事情;
1.根据配置文件初始化bean,创建客户端实例信息 InstanceInfo
2.第一次全量拉取注册中心服务列表(url=/apps),初始化周期任务:
2.1 CacheRefreshThread 定时刷新本地缓存服务列表,若是客户端第一次拉取,则会全量拉取,后面
则增量拉取.若增量拉取失败则全量拉取,配置属性为eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds=30默
认拉取一次;
2.2 HeartbeatThread 通过renew()续约任务,维持于注册中心的心跳(url=/apps/ {id}),若
返回状态码为404则说明该服务实例没有在注册中心注册,执行register()向注册中心注册实例信息;
2.3 ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener 注册实例状态监听类,监听服务实例状态变化,
向注册中心同步实例状态;
2.4 InstanceInfoReplicator 定时刷新实例状态,并向注册中心同步,默认
eureka.client.instanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds=30执行一次.若实例状态有变更,则重新执行注册