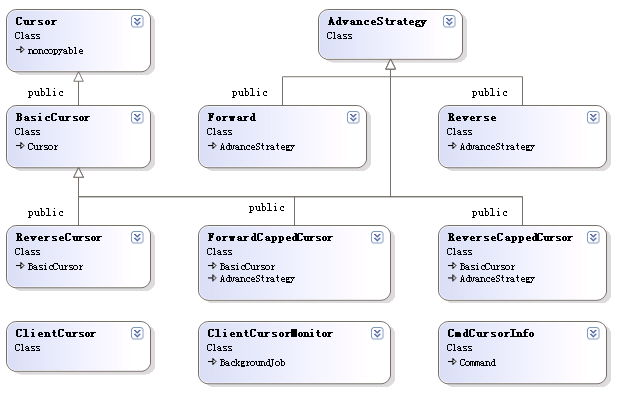
从该图中,可以看到除了(ClientCursor)之外,其余游标均继承自Cursor这个类(基类),下面我们看一下其具体实现:
{
virtual bool ok() = 0;//游标当前指向的对象是否有效
bool eof() { return !ok(); }//是否已到尾部
virtual Record* _current() = 0;//游标当前指向的记录(记录是组成数据文件的最基本单位)
virtual BSONObj current() = 0;//游标当前指向的BSONObj对象
virtual DiskLoc currLoc() = 0;//游标当前指向的DiskLoc
virtual bool advance() = 0; /*true=ok,将游标指向到下一条记录所在位置*/
virtual BSONObj currKey() const { return BSONObj(); }
/* 标识游标是否为Tailable类型,该类型支持获取最后一条记录后,不马上关闭游标,以便持续获取后面新添加的记录*/
virtual bool tailable() {
return false;
}
//设置游标为Tailable类型
virtual void setTailable() {}
.....
}
在mongodb中,提供了两种遍历数据集合的方向,分别是“向前”和“倒转”方式,其声明如下:
public:
virtual ~AdvanceStrategy() { }
virtual DiskLoc next( const DiskLoc &prev ) const = 0;
};
const AdvanceStrategy *forward(); //向前
const AdvanceStrategy *reverse(); //倒转
下面是其实现方式如下:
virtual DiskLoc next( const DiskLoc &prev ) const {
return prev.rec()->getNext( prev );
}
} _forward;
class Reverse : public AdvanceStrategy {
virtual DiskLoc next( const DiskLoc &prev ) const {
return prev.rec()->getPrev( prev );
}
} _reverse;
const AdvanceStrategy *forward() {
return &_forward;
}
const AdvanceStrategy *reverse() {
return &_reverse;
}
看到这里,我们有必须简要说明一下mongofile文件的结构,见下面说明:
----------------------
DataFileHeader :数据头文件信息,包括版本,文件长度,使用情况等
----------------------
Extent (for a particular namespace) 特定namespace下的extent,可理解为数据集合
Record : 单条数据记录
...
Record (some chained for unused space)
----------------------
more Extents... 其它extent
----------------------
*/
在一个数据库文件中,同一个namespace的extent可以有多个,每一个extent都有一些记录(record)组成,如果访问record,可以使用diskloc加上文件偏移(getOfs:位于diskloc中)获取。
同时每个extent中包括还包括两个重要属性:
它们分别记录了同一namespace下,在extent链表中,当前extent的前或后一个extent的位置信息,上面AdvanceStrategy中的next方法即实现了在两种遍历方向(上面已提到)上,在extent链接中跳转的方式,比如在forward方向:
//如果当前 Record的nextOfs偏移不为空,表示在当前extent中还有后续记录可访问
if ( nextOfs != DiskLoc::NullOfs ) {
/* defensive */
if ( nextOfs >= 0 && nextOfs < 10 ) {//是否为已删除的记录
sayDbContext("Assertion failure - Record::getNext() referencing a deleted record?");
return DiskLoc();
}
return DiskLoc(myLoc.a(), nextOfs);//获取下一条记录
}
Extent *e = myExtent(myLoc);//获取当前记录所属的Extent
while ( 1 ) {
if ( e->xnext.isNull() )
return DiskLoc(); //已到表尾.
e = e->xnext.ext();//跳转到下一个extent(以便进行next遍历)
if ( !e->firstRecord.isNull() )
break;
// entire extent could be empty, keep looking
}
return e->firstRecord;//获取下一个extent中的第一条记录
}
在每个extent对象中,其还包括另外两个属性 firstRecord,lastRecord,两者皆为DiskLoc类型,顾名思义,它们分别指向当前extent的第一条和最后一条记录所在位置,这种定义它们是为了后者在extent中进行跳转时使用,当前如果在更加复杂的capped collection情况下,其值在会删除记录等操作时不断更新,比如下面代码:
void DataFileMgr::_deleteRecord(NamespaceDetails *d, const char *ns, Record *todelete, const DiskLoc& dl) {
......
//extents是一个数据文件区域,该区域有所有记录(records)均属于同一个名空间namespace
/* remove ourself from extent pointers */
{
Extent *e = getDur().writing( todelete->myExtent(dl) );
if ( e->firstRecord == dl ) {//如果要删除记录为该extents区域第一条记录时
if ( todelete->nextOfs == DiskLoc::NullOfs )//且为唯一记录时
e->firstRecord.Null();//则该空间第一元素为空
else //将当前空间第一条(有效)记录后移一位
e->firstRecord.set(dl.a(), todelete->nextOfs);
}
if ( e->lastRecord == dl ) {//如果要删除记录为该extents区域最后一条记录时
if ( todelete->prevOfs == DiskLoc::NullOfs )//如果要删除记录的前一条信息位置为空时
e->lastRecord.Null();//该空间最后一条记录清空
else //设置该空间最后一条(有效)记录位置前移一位
e->lastRecord.set(dl.a(), todelete->prevOfs);
}
}
......
}
介绍了cursor基类的定义和遍历方向这两个基本概念后,下面介绍一下在mongodb中,广泛使用的是basicCursor,其定义如下:
public:
BasicCursor(DiskLoc dl, const AdvanceStrategy *_s = forward()) : curr(dl), s( _s ), _nscanned() {
incNscanned();
init();
}
BasicCursor(const AdvanceStrategy *_s = forward()) : s( _s ), _nscanned() {
init();
}
bool ok() { return !curr.isNull(); }
Record* _current() {
assert( ok() );
return curr.rec();
}
BSONObj current() {
Record *r = _current();
BSONObj j(r);
return j;
}
virtual DiskLoc currLoc() { return curr; }
virtual DiskLoc refLoc() { return curr.isNull() ? last : curr; }
bool advance();
virtual string toString() { return "BasicCursor"; }
virtual void setTailable() {
if ( !curr.isNull() || !last.isNull() )
tailable_ = true;
}
virtual bool tailable() { return tailable_; }
......
};
可认看到在其构造函数时,使用了forward方向的遍历方式, 即然定义了Forward方向的游标,mongodb接下来定义了Reverse方向的游标:
class ReverseCursor : public BasicCursor {
public:
ReverseCursor(DiskLoc dl) : BasicCursor( dl, reverse() ) { }
ReverseCursor() : BasicCursor( reverse() ) { }
virtual string toString() { return "ReverseCursor"; }
};
另外为了支持capped collection集合类型(有关capped collection,参见这篇链接),mongodb分别定义了ForwardCappedCursor和ReverseCappedCursor:
public:
ForwardCappedCursor( NamespaceDetails *nsd = 0, const DiskLoc &startLoc = DiskLoc() );
virtual string toString() {
return "ForwardCappedCursor";
}
virtual DiskLoc next( const DiskLoc &prev ) const;
virtual bool capped() const { return true; }
private:
NamespaceDetails *nsd;
};
class ReverseCappedCursor : public BasicCursor, public AdvanceStrategy {
public:
ReverseCappedCursor( NamespaceDetails *nsd = 0, const DiskLoc &startLoc = DiskLoc() );
virtual string toString() {
return "ReverseCappedCursor";
}
virtual DiskLoc next( const DiskLoc &prev ) const;
virtual bool capped() const { return true; }
private:
NamespaceDetails *nsd;
};
只不过在ForwardCappedCursor和ReverseCappedCursor中,实现next方法会更复杂一下,因为其要考虑删除的记录不在遍历结果中的情况。相当内容详见cursor.cpp的实现代码:)
介绍游标和mongofile结构之后,我们大体知道了mongodb如果遍历数据文件,另外mongodb使用了b树索引来加快查询效率,因此mongodb也提供了相应的btreeCursor,其主要用于遍历内存中的b树索引。
除此以外,为了方便client端使用cursor访问数据库,mongodb提供了ClientCursor,其对Cursor进一步封装(详见clientcursor.h)。
下面我们看一下mongodb如果要据查询方式来确定使用那种类型游标的:
shared_ptr<Cursor> DataFileMgr::findAll(const char *ns, const DiskLoc &startLoc) {
NamespaceDetails * d = nsdetails( ns );
if ( ! d )
return shared_ptr<Cursor>(new BasicCursor(DiskLoc()));
DiskLoc loc = d->firstExtent;
Extent *e = getExtent(loc);
......
if ( d->capped )
return shared_ptr<Cursor>( new ForwardCappedCursor( d , startLoc ) );
if ( !startLoc.isNull() )
return shared_ptr<Cursor>(new BasicCursor( startLoc ));
......
return shared_ptr<Cursor>(new BasicCursor( e->firstRecord ));
}
到这里,可以看了,mongodb在cursor的设计和使用方式上是基于“策略模式”(strategy pattern)的,如下图:
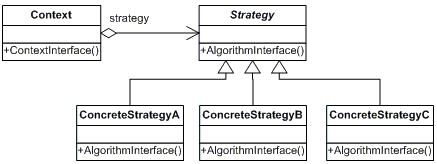
其中cursor就是各种遍历数据集合的策略,而pdfile.cpp就是持有相应cursor的上下文(context) ,该模式也是使用比较广泛的一种设置模式,好处这里就不多说了。
好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落了,在接下来的文章中,将会介绍mongodb中mmap的使用场景。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/15/mongodb_cursor_source_code.html
作者: daizhj, 代震军
微博: http://t.sina.com.cn/daizhj
Tags: mongodb,c++,cursor