共享存储
docker默认是无状态,当有状态服务时需要用到共享存储
- 为什么需要共享存储:
- 1.最常见有状态服务,本地存储有些程序会把文件保存在服务器目录中,如果容器重新启停则会丢失。
- 2.如果使用volume将目录挂载到容器中,涉及到备份及高可用问题。如果宿主机出现问题则会造成不可用状态。
kubernetes中提供了共享存储
1.pv(PresistentVolume持久卷)
2.pvc (PresistentVolumeClaim持久卷声明)
PV
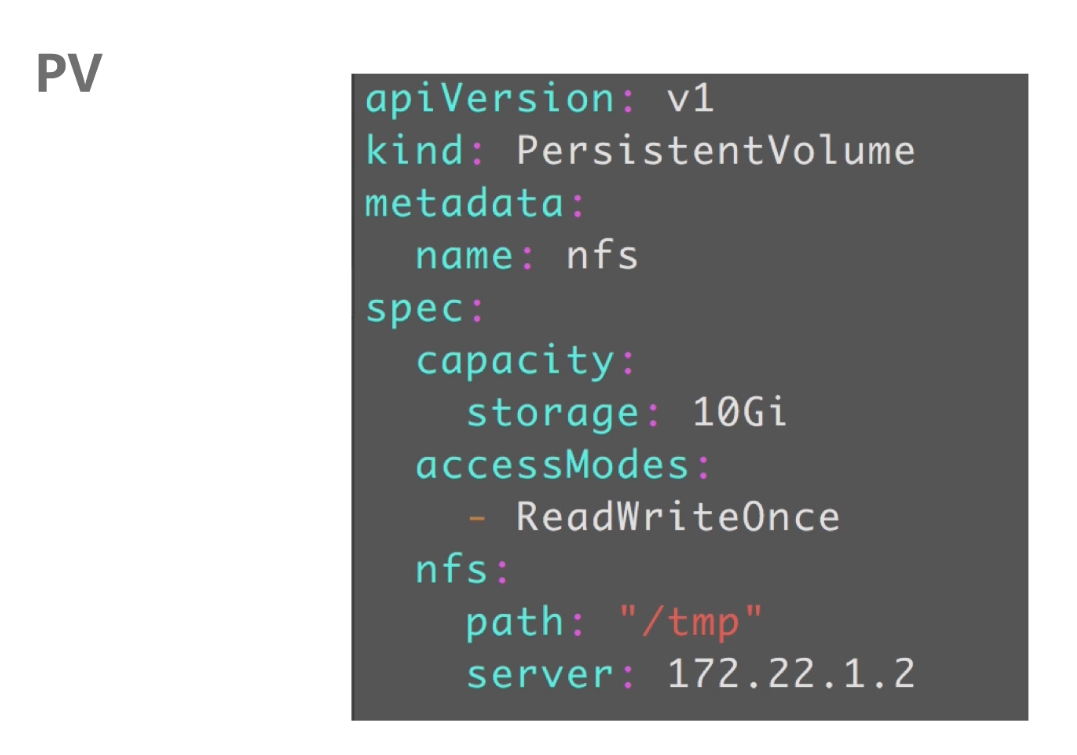
pv中定义了:
pv的容量
pv的访问模式(readWriteOnce:可读可写,但支持被单个pod挂载,replicas为1
readOnlyMany:表示以只读的方式被多个pod挂载,就是replicas可以大于1
readWriteMany:这种存储可以以读写方式被多个pod共享,就是replicas可以大于1)
pv连接的存储后端地址
pv使用nfs类型:
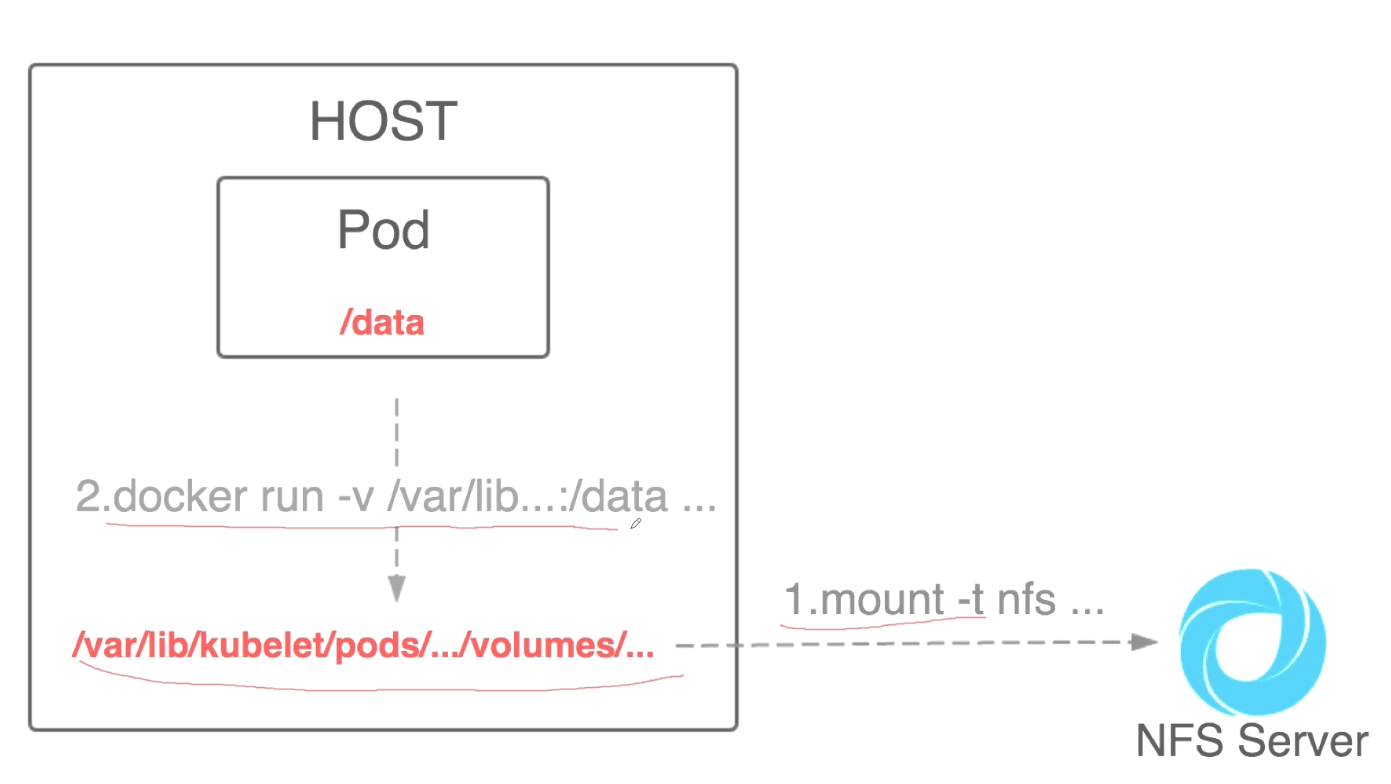
###将nfs mount到本地目录中,然后挂载到pod里。
StorageClass管理pv与pvc
StorageClass管理GFS pv例子:
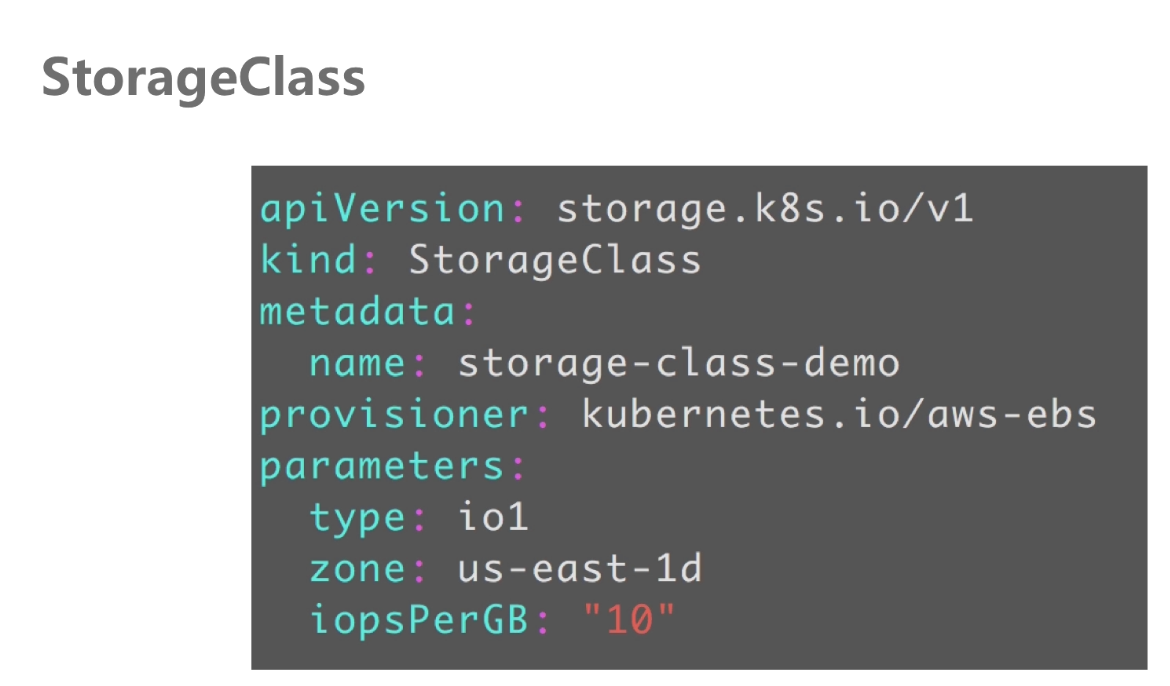
kubernetes中自动管理共享存储pv api,当pod数量过多共享存储需求量大,所以对应的有了storage-class,能够帮助我们自动的去创建pv。省去了pv的创建与回收。

##pvc通过pv StorageClass-name去绑定pv
架构图如下:
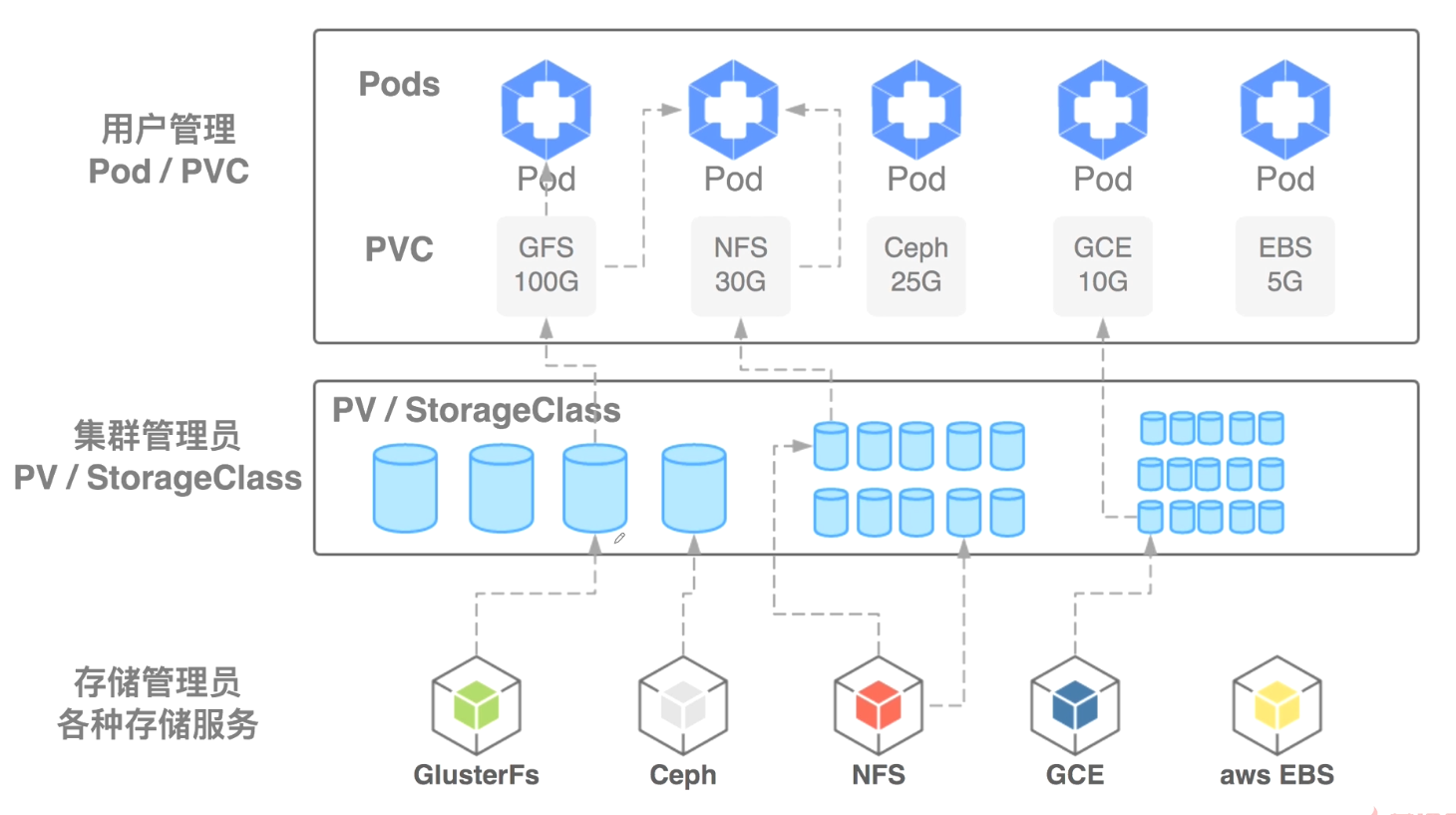
##手动pv事先创建好,一个pv只能绑定一个后端。当pvc使用时进行绑定。
##自动的后端对应一个StorageClass,pvc根据StorageClass去创建相应大小的pv。pvc与pod是由用户去负责,用户创建了pvc匹配不到的话 pod及pvc会处于pendding状态。如果匹配到k8s就会为他们自动建立起绑定关系。
##一个pv可以给多个pvc使用,一个pvc只能绑定一个pv,一个pv只能绑定一个后端存储。
storageclass创建pv

apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: glusterfs-storage-class provisioner: kubernetes.io/glusterfs parameters: resturl: "http://10.155.20.120:30001" restauthenabled: "false"
##指定了后端存储地址以及storageclass name
storageclass创建pv

kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: glusterfs-pvc spec: storageClassName: glusterfs-storage-class accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 1Gi
###指定了storageclass name以及权限和大小
验证pvc
kubectl apply -f gluster-pvc.yaml kubetctl get pvc kubectl get pv 查看是否绑定 查看yaml中是否互相绑定了volumeName
pod使用pvc

apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: web-deploy spec: strategy: rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 25% maxUnavailable: 25% type: RollingUpdate selector: matchLabels: app: web-deploy replicas: 2 template: metadata: labels: app: web-deploy spec: containers: - name: web-deploy image: hub.mooc.com/kubernetes/springboot-web:v1 ports: - containerPort: 8080 volumeMounts: - name: gluster-volume mountPath: "/mooc-data" readOnly: false volumes: - name: gluster-volume persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: glusterfs-pvc
glusterFS部署
glusterfs部署要求:
- 至少需要3个节点(保证数据存在三个副本)
- 每个节点要有一块裸磁盘没有经过分区

1、各个节点运行 yum -y install glusterfs glusterfs-fuse 2、查看api-server和kubelet是否支持 ps -ef |grep apiserver |grep allow-pri 需要--allow-privileged=true
运行glusterfs以deamonset方式运行

kind: DaemonSet apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 metadata: name: glusterfs labels: glusterfs: daemonset annotations: description: GlusterFS DaemonSet tags: glusterfs spec: template: metadata: name: glusterfs labels: glusterfs: pod glusterfs-node: pod spec: nodeSelector: storagenode: glusterfs hostNetwork: true containers: - image: gluster/gluster-centos:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: glusterfs env: # alternative for /dev volumeMount to enable access to *all* devices - name: HOST_DEV_DIR value: "/mnt/host-dev" # set GLUSTER_BLOCKD_STATUS_PROBE_ENABLE to "1" so the # readiness/liveness probe validate gluster-blockd as well - name: GLUSTER_BLOCKD_STATUS_PROBE_ENABLE value: "1" - name: GB_GLFS_LRU_COUNT value: "15" - name: TCMU_LOGDIR value: "/var/log/glusterfs/gluster-block" resources: requests: memory: 100Mi cpu: 100m volumeMounts: --- kind: DaemonSet apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 metadata: name: glusterfs labels: glusterfs: daemonset annotations: description: GlusterFS DaemonSet tags: glusterfs spec: template: metadata: name: glusterfs labels: glusterfs: pod glusterfs-node: pod spec: nodeSelector: storagenode: glusterfs #在要部署的node上打上标签 hostNetwork: true containers: - image: gluster/gluster-centos:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: glusterfs env: # alternative for /dev volumeMount to enable access to *all* devices - name: HOST_DEV_DIR value: "/mnt/host-dev" # set GLUSTER_BLOCKD_STATUS_PROBE_ENABLE to "1" so the # readiness/liveness probe validate gluster-blockd as well - name: GLUSTER_BLOCKD_STATUS_PROBE_ENABLE value: "1" - name: GB_GLFS_LRU_COUNT value: "15" - name: TCMU_LOGDIR value: "/var/log/glusterfs/gluster-block" resources: requests: memory: 100Mi cpu: 100m volumeMounts: - name: glusterfs-heketi mountPath: "/var/lib/heketi" - name: glusterfs-run mountPath: "/run" - name: glusterfs-lvm mountPath: "/run/lvm" - name: glusterfs-etc mountPath: "/etc/glusterfs" - name: glusterfs-logs mountPath: "/var/log/glusterfs" - name: glusterfs-config mountPath: "/var/lib/glusterd" - name: glusterfs-host-dev mountPath: "/mnt/host-dev" - name: glusterfs-misc mountPath: "/var/lib/misc/glusterfsd" - name: glusterfs-block-sys-class mountPath: "/sys/class" - name: glusterfs-block-sys-module mountPath: "/sys/module" - name: glusterfs-cgroup mountPath: "/sys/fs/cgroup" readOnly: true - name: glusterfs-ssl mountPath: "/etc/ssl" readOnly: true - name: kernel-modules mountPath: "/usr/lib/modules" readOnly: true securityContext: capabilities: {} privileged: true readinessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 40 exec: command: - "/bin/bash" - "-c" - "if command -v /usr/local/bin/status-probe.sh; then /usr/local/bin/status-probe.sh readiness; else systemctl status glusterd.service; fi" periodSeconds: 25 successThreshold: 1 failureThreshold: 50 livenessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 40 exec: command: - "/bin/bash" - "-c" - "if command -v /usr/local/bin/status-probe.sh; then /usr/local/bin/status-probe.sh liveness; else systemctl status glusterd.service; fi" periodSeconds: 25 successThreshold: 1 failureThreshold: 50 volumes: - name: glusterfs-heketi hostPath: path: "/var/lib/heketi" - name: glusterfs-run - name: glusterfs-lvm hostPath: path: "/run/lvm" - name: glusterfs-etc hostPath: path: "/etc/glusterfs" - name: glusterfs-logs hostPath: path: "/var/log/glusterfs" - name: glusterfs-config hostPath: path: "/var/lib/glusterd" - name: glusterfs-host-dev hostPath: path: "/dev" - name: glusterfs-misc hostPath: path: "/var/lib/misc/glusterfsd" - name: glusterfs-block-sys-class hostPath: path: "/sys/class" - name: glusterfs-block-sys-module hostPath: path: "/sys/module" - name: glusterfs-cgroup hostPath: path: "/sys/fs/cgroup" - name: glusterfs-ssl hostPath: path: "/etc/ssl" - name: kernel-modules hostPath: path: "/usr/lib/modules"
为glusterfs节点打上标签并部署
kubectl label node node-2 storagenode=glusterfs kubectl apply -f glusterfs-deamonset.yaml kubectl get pods -o wide
为了方便操作引用heketi服务
heketi部署

apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: heketi-clusterrolebinding roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: heketi-clusterrole subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: heketi-service-account namespace: default --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: heketi-service-account namespace: default --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: heketi-clusterrole rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods - pods/status - pods/exec verbs: - get - list - watch - create

kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: heketi labels: glusterfs: heketi-service deploy-heketi: support annotations: kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: heketi labels: glusterfs: heketi-service deploy-heketi: support annotations: description: Exposes Heketi Service spec: selector: name: heketi ports: - name: heketi port: 80 targetPort: 8080 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: tcp-services namespace: ingress-nginx data: "30001": default/heketi:80 --- kind: Deployment apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 metadata: name: heketi labels: glusterfs: heketi-deployment annotations: description: Defines how to deploy Heketi spec: replicas: 1 template: metadata: name: heketi labels: name: heketi glusterfs: heketi-pod spec: serviceAccountName: heketi-service-account containers: - image: heketi/heketi:dev imagePullPolicy: Always name: heketi env: - name: HEKETI_EXECUTOR value: "kubernetes" - name: HEKETI_DB_PATH value: "/var/lib/heketi/heketi.db" - name: HEKETI_FSTAB value: "/var/lib/heketi/fstab" - name: HEKETI_SNAPSHOT_LIMIT value: "14" - name: HEKETI_KUBE_GLUSTER_DAEMONSET value: "y" ports: - containerPort: 8080 volumeMounts: - name: db mountPath: /var/lib/heketi readinessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 3 httpGet: path: /hello port: 8080 livenessProbe: timeoutSeconds: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 30 httpGet: path: /hello port: 8080 volumes: - name: db hostPath: path: "/heketi-data"
进入heketi容器中环境变量
export HEKETI_CLI_SERVER=http://localhost:8080
修改clusterfs配置文件指明clusterfs node ip以及裸磁盘路径

{ "clusters": [ { { { { { "nodes": [ { "node": { "hostnames": { "manage": [ "gluster-01" ], "storage": [ "10.155.56.56" ] }, "zone": 1 }, "devices": [ { "name": "/dev/sdb", "destroydata": false } ] }, { "node": { "hostnames": { "manage": [ "gluster-02" ], "storage": [ "10.155.56.57" ] }, "zone": 1 }, "devices": [ { "name": "/dev/sdb", "destroydata": false } ] }, { "node": { "hostnames": { "manage": [ "gluster-03" ], "storage": [ "10.155.56.102" ] }, "zone": 1 }, "devices": [ { "name": "/dev/sdb", "destroydata": false } ] } ] } ] }
把配置文件写入heketi容器中
heketi-cli topology load --json topology.json#heketi根据配置文件找到glusterfs node对glusterfs做初始化操作 heketi-cli topology info #查看当前clusterfs集群拓扑 进入clusterfs node中验证是否成功 gluster peer status #查看信息
pvc

pvc中定义了对所需的资源的一个描述,以及需要的权限

pv与pvc进行绑定 1.pv要满足pvc的需求(存储大小,读写权限) 2.pv要与pvc storage-classname要相同 3.描述中根据字段storageclassname去自动的绑定互相绑定对方volumeName
#本质上在pvc资源描述对象中把pv的名字添加进去
pvc的使用
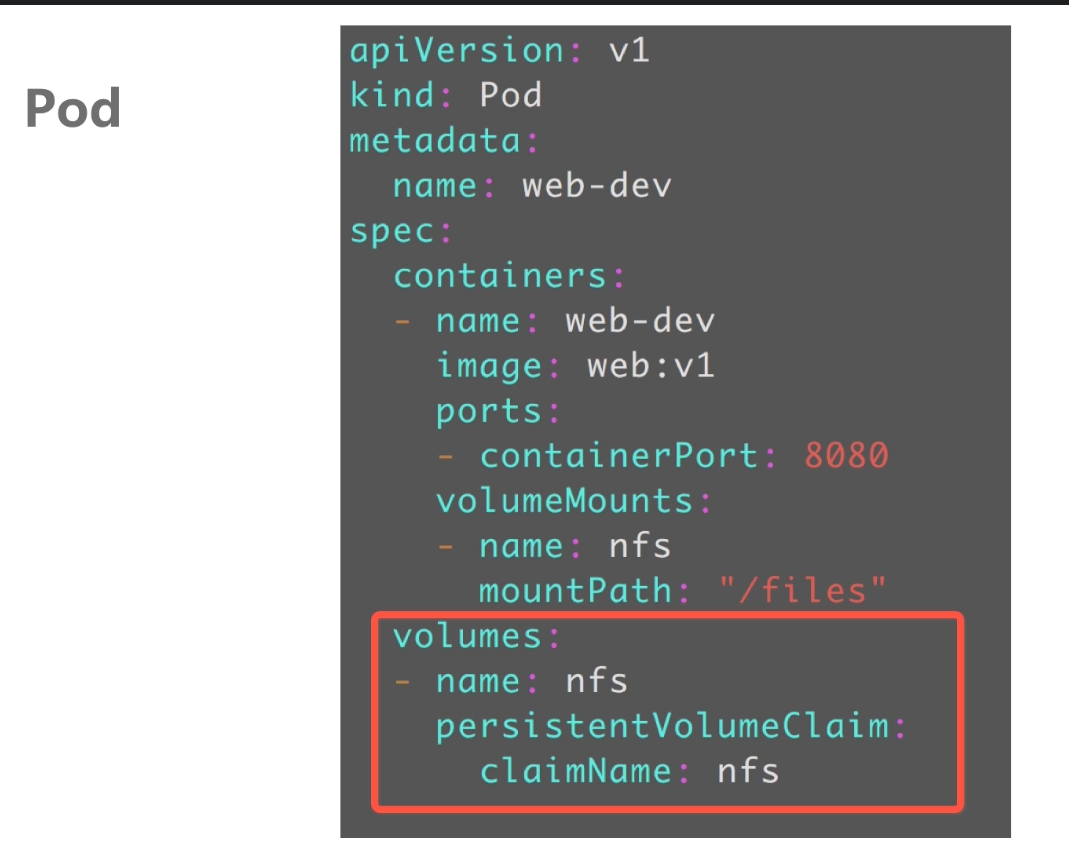
#原理:通过pv及pvc的两层抽象,pod在使用共享存储时非常的简单。pod中声明了pvc的名字,pvc中描述了pod的需求。pvc绑定了pv,pv中描述了具体存储后端,如何访问,具体参数。
简单总结:
1.pv独立于pod存在 2.pv可以创建动态pv或者静态pv。动态pv不需要手动去创建。静态pv需要手动创建 3.访问模式:ReadWriteOnce:可读可写只能mount到一个节点. ReadOnlyMany:PV能模式挂载到多个节点 4.回收规则:PV 支持的回收策略有: Retain. Recycle.delete Retain 管理员回收:kubectl delete pv pv-name 创建:kubectl apply -f pv-name.yaml ;Retain策略 在删除pvc后PV变为Released不可用状态, 若想重新被使用,需要管理员删除pv,重新创建pv,删除pv并不会删除存储的资源,只是删除pv对象而已;若想保留数据,请使用该Retain, Recycle策略 – 删除pvc自动清除PV中的数据,效果相当于执行 rm -rf /thevolume/*. 删除pvc时.pv的状态由Bound变为Available.此时可重新被pvc申请绑定 Delete – 删除存储上的对应存储资源,例如 AWS EBS、GCE PD、Azure Disk、OpenStack Cinder Volume 等,NFS不支持delete策略 5.storageClassName :在pvc的请求存储大小和访问权限与创建的pv一致的情况下 根据storageClassName进行与pv绑定。常用在pvc需要和特定pv进行绑定的情况下。举例:当有创建多个pv设置存储的大小和访问权限一致时,且pv,pvc没有配置storageClassName时,pvc会根据存储大小和访问权限去随机匹配。如果配置了storageClassName会根据这三个条件进行匹配。当然也可以用其他方法实现pvc与特定pv的绑定如标签.标签方法上一篇就是,这里就不再赘述。
StatefulSet --- 有状态应用的守护者
解决多实例不对等pod的问题

创建无头服务(不分配ip,service对应后端pod-ip,通过dns svr记录解析)

apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: springboot-web-svc spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 protocol: TCP clusterIP: None selector: app: springboot-web
创建StatefulSet

apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: springboot-web namespace: dev spec: serviceName: springboot-web-svc #声明使用哪个headless service来解析pod replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: springboot-web template: metadata: labels: app: springboot-web spec: containers: - name: springboot-web image: 172.17.166.217/kubenetes/springboot-web:v1 ports: - containerPort: 8080 livenessProbe: tcpSocket: port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 3 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 5 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /hello?name=test port: 8080 scheme: HTTP initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 1 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 5
监控创建过程
kubectl get pod -l app=spring-boot-web -w
#statefulset创建pod名称相对固定,前边为pod name后端为相固定的数字编号 例如spring-boot-web-01,只有第一个启动处于READY状态才会去启动第二个。pod之间可通过hostname访问对方,ping spring-boot-web-01.springboot-web-svc.default。
StatefulSet 创建volume pod

apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: springboot-web spec: serviceName: springboot-web-svc replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: springboot-web template: metadata: labels: app: springboot-web spec: containers: - name: springboot-web image: hub.mooc.com/kubernetes/springboot-web:v1 ports: - containerPort: 8080 livenessProbe: tcpSocket: port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 3 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 5 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /hello?name=test port: 8080 scheme: HTTP initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 1 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 5 volumeMounts: - name: data mountPath: /mooc-data volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: data spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce storageClassName: glusterfs-storage-class resources: requests: storage: 1Gi
#自动创建不同编号pvc,对应pod名称。为每个pod绑定不同的pvc,本质上是通过StatefulSet创建pod相固定的数字编号。
KubernetesAPI ---如何开发一个基于kubernetes的容器管理平台

apiserver 路径规范:
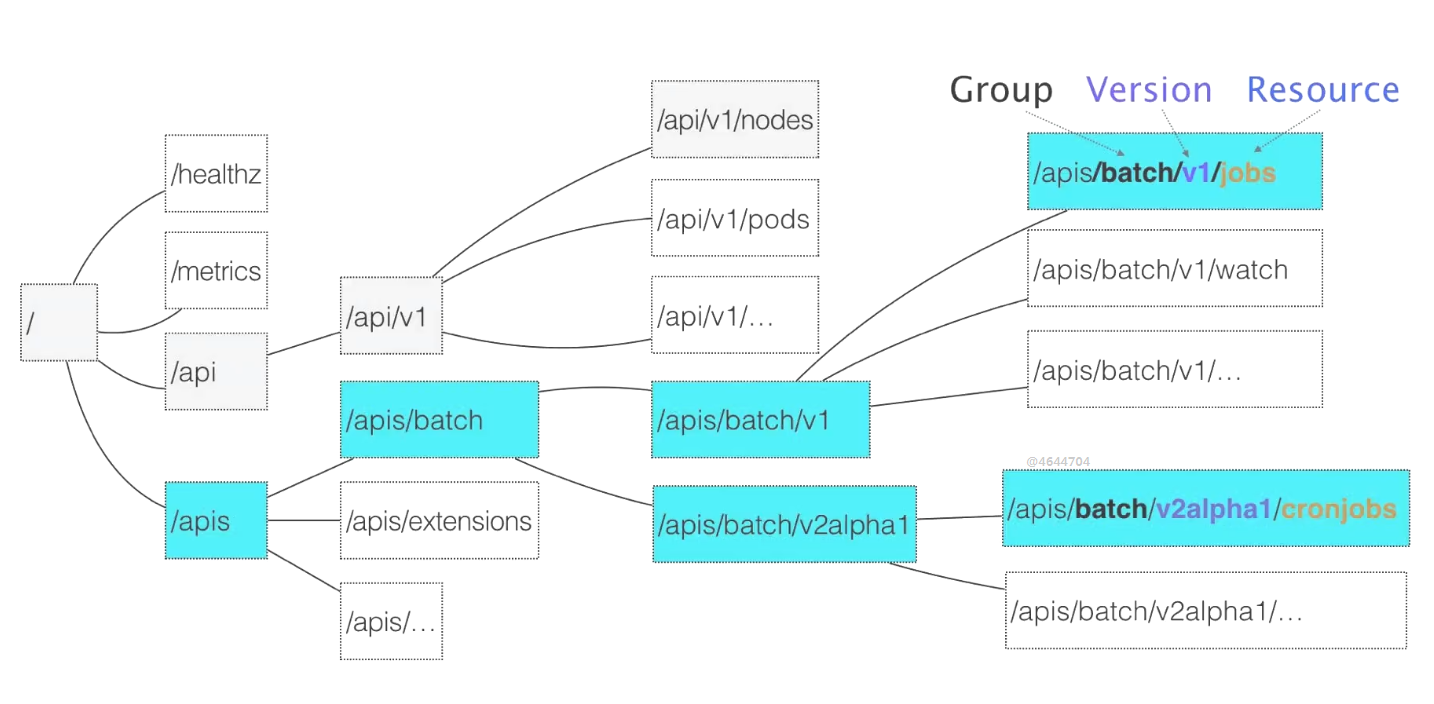
api之下都是核心的api,是没有api分组的。核心组只有两级,一级是版本一级是核心的资源。
apis非核心的api,每个api资源都用三级来表示,第一级分组,第二组版本信息,第三级是具体的资源。
分组可以更清晰整洁,使用户能够很容易的区分来源结构。
#资料https://kubermetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubernetes-api/
常用客户端:https://github.com/kubernetes-client 基于各种语言
官方客户端:https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go

