A tree is an undirected graph with exactly one simple path between each pair of vertices. We call a set of simple paths kk-valid if each vertex of the tree belongs to no more than one of these paths (including endpoints) and each path consists of exactly kk vertices.
You are given a tree with nn vertices. For each kk from 11 to nn inclusive find what is the maximum possible size of a kk-valid set of simple paths.
The first line of the input contains a single integer nn (2≤n≤1000002≤n≤100000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
Then following n−1n−1 lines describe the tree, each of them contains two integers vv, uu (1≤v,u≤n1≤v,u≤n) — endpoints of the corresponding edge.
It is guaranteed, that the given graph is a tree.
Output nn numbers, the ii-th of which is the maximum possible number of paths in an ii-valid set of paths.
7
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7
3
2
1
1
1
1
6
1 2
2 3
2 4
1 5
5 6
6
2
2
1
1
0
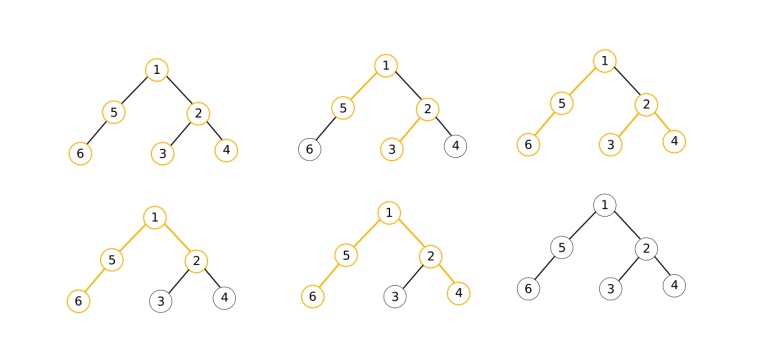
One way to achieve the optimal number of paths for the second sample is illustrated in the following picture:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define lowbit(x) x&(-x) using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 5e5 + 108; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; int ooo = 800; struct node{ int to,nx; }o[maxn]; int n,tot,head[maxn],cal[maxn],res[maxn]; int path; inline void add_edge(int u,int v){ o[++tot].to=v; o[tot].nx=head[u]; head[u]=tot; } inline void dfs(int cur,int fa,int chose){ cal[cur]=0; bool flag=false; for(register int i=head[cur];i;i=o[i].nx){ int to=o[i].to; if(to==fa)continue; dfs(to,cur,chose); if(cal[cur]+cal[to]>=chose-1)flag=true; cal[cur]=max(cal[cur],cal[to]); } if(flag||chose==1){ ++path; cal[cur]=0; } else{ ++cal[cur]; } } inline void solve(int l,int r,int res_l,int res_r){ if(l>r)return; if(res_l==res_r){ for(register int i=l;i<=r;++i){ res[i]=res_l; } return; } int mid=l+r>>1; path=0; dfs(1,0,mid); res[mid]=path; solve(l,mid-1,res[mid],res_r); solve(mid+1,r,res_l,res[mid]); } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin); #endif scanf("%d",&n); for(register int i=1,u,v;i<n;++i){ scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); add_edge(u,v); add_edge(v,u); } solve(1,n,0,n); for(register int i=1;i<=n;++i){ printf("%d ",res[i]); } return 0; }