题目链接 Problems
Problem A
快速幂累加即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
LL ans = 0;
LL n, d;
int T;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
inline LL Pow(LL a, LL b, LL Mod){
LL ret(1);
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= Mod) if (b & 1) (ret *= a) %= Mod;
return ret;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
cin >> n >> d;
ans = 0;
rep(i, 1, n){
ans += Pow(i, d, mod);
ans %= mod;
}
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Problem B
对于每个帮派,并查集维护就可以了。
求第$k$大的时候树状数组上二分就好了。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int T;
int sz[N], c[N], father[N];
int n, m;
int num;
void update(int x, int val){
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x) c[x] += val;
}
int query(int x){
int ret = 0;
for (; x; x -= x & -x) ret += c[x];
return ret;
}
int getfather(int x){
return father[x] == x ? x : father[x] = getfather(father[x]);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
memset(father, 0, sizeof father);
rep(i, 1, n) father[i] = i;
rep(i, 1, n) update(1, 1);
num = n;
rep(i, 1, n) sz[i] = 1;
while (m--){
int op;
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1){
int x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
int fx = getfather(x), fy = getfather(y);
if (fx == fy) continue;
father[fy] = fx;
int f1 = sz[fx], f2 = sz[fy], f3 = sz[fx] + sz[fy];
sz[fx] += sz[fy];
sz[fy] = 0;
--num;
update(f1, -1);
update(f2, -1);
update(f3, 1);
}
else{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
if (num < x){
puts("-1");
continue;
}
int l = 1, r = n;
while (l + 1 < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (num - query(mid - 1) >= x) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
if (num - query(r - 1) >= x) printf("%d
", r);
else printf("%d
", l);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Problem C
递推。$f_{n} = 2f_{n-1} + f_{n-3}$
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
const int A = 5;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
struct matrix{ LL a[A][A];} init, unit, aa;
int n;
LL m;
int T;
matrix Mul(matrix a, matrix b){
matrix c;
rep(i, 1, n) rep(j, 1, n){
c.a[i][j] = 0;
rep(k, 1, n) (c.a[i][j] += (a.a[i][k] * b.a[k][j] % mod)) %= mod;
}
return c;
}
matrix Pow(matrix a, LL k){
matrix ret(unit); for (; k; k >>= 1ll, a = Mul(a, a)) if (k & 1) ret = Mul(ret, a); return ret;
}
int main(){
n = 3;
matrix dd;
memset(dd.a, 0, sizeof dd.a);
memset(unit.a, 0, sizeof unit.a);
rep(i, 1, n) unit.a[i][i] = 1ll;
dd.a[1][1] = 2; dd.a[1][2] = 0; dd.a[1][3] = 1;
dd.a[2][1] = 1;
dd.a[3][2] = 1;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
scanf("%lld", &m);
LL fuck = m - 3;
if (m <= 3){
if (m == 1ll) puts("1");
if (m == 2ll) puts("2");
if (m == 3ll) puts("5");
continue;
}
matrix cc = Pow(dd, fuck);
LL ans = cc.a[1][1] * 5ll + cc.a[1][2] * 2ll + cc.a[1][3] * 1ll;
ans %= mod;
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Problem D
最坏的情况即为斐波那契数列中的某几项。
那么当询问元素个数超过一定的时候(大概$87$)直接输出Yes就好了。
否则就暴力特判。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
LL a[100010];
LL c[100010];
int n, q;
int cnt = 0;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%lld", a + i);
scanf("%d", &q);
while (q--){
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
if (r - l + 1 >= 100){
puts("Yes");
continue;
}
cnt = 0;
rep(i, l, r) c[++cnt] = a[i];
sort(c + 1, c + cnt + 1);
int fg = 0;
rep(i, 1, cnt - 2) if (c[i] + c[i + 1] > c[i + 2]){
fg = 1;
break;
}
puts(fg ? "Yes" : "No");
}
return 0;
}
Problem E
分解质因数之后令$a_{i}$为每个质因数的指数。
答案为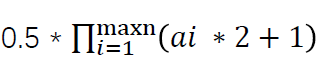
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
LL n;
int T;
LL bs;
LL cc;
LL ans;
int main(){
while (~scanf("%d", &T)){
while (T--){
scanf("%lld", &n);
LL bs = sqrt(n);
ans = 1;
for (LL i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); ++i){
LL cc = 0;
while (n % i == 0) ++cc, n /= i;
ans *= (2 * cc + 1ll);
}
if (n > 1) ans *= 3;
++ans;
ans /= 2;
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
Problem F
答案为$2^{n-3} * n^{2} * (n+3)$
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int T;
LL n, ans;
inline LL Pow(LL a, LL b, LL Mod){
LL ret(1);
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= Mod) if (b & 1) (ret *= a) %= Mod;
return ret;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
scanf("%lld", &n);
if (n == 1ll){
puts("1");
continue;
}
if (n == 2ll){
puts("10");
continue;
}
if (n == 3ll){
puts("54");
continue;
}
LL ans = Pow(2, n - 3, mod);
ans *= n;
ans %= mod;
ans *= n;
ans %= mod;
ans *= (n + 3ll);
ans %= mod;
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Problem G
从小到大枚举答案,每次做一遍极大极小搜索,若符合题意就直接输出。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e3 + 10;
LL a[N];
LL f[2][N];
LL s[N];
LL xxx;
int n;
int m;
int ans;
LL dp(int x, int pos){
if (~f[x][pos]) return f[x][pos];
if (pos == m){
if (x) return f[x][pos] = a[pos];
else return f[x][pos] = 0;
}
LL ret = 0;
if (x){
ret = a[pos] + dp(x ^ 1, pos + 1);
ret = max(ret, dp(x, pos + 1));
}
else{
ret = dp(x ^ 1, pos + 1);
ret = min(ret, a[pos] + dp(x, pos + 1));
}
return f[x][pos] = ret;
}
int main(){
while (~scanf("%d", &n) && n != -1){
rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%lld", a + i);
scanf("%lld", &xxx);
s[0] = 0;
rep(i, 1, n) s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
ans = -1;
for (m = 1; m <= n; ++m){
memset(f, -1, sizeof f);
LL gg = dp(1, 1);
if (gg >= xxx){
ans = m;
break;
}
}
printf("%d
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Problem H
贪心。求出每个块的大小,然后枚举每个块。记块的个数为$cnt$
两边的块如果有不小于$2$的,那么答案用$cnt + 1$更新。
中间的块大小如果有不小于$3$的,那么答案用$cnt + 2$更新。
UPD:哦草我好像没考虑0011然后翻转中间的0和1的情况,这也是一个case
代码就不改乐
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int c[N];
int n, cnt, xx, now;
int ans;
int main(){
while (~scanf("%d", &n)){
rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%1d", a + i);
xx = -1;
cnt = -1; now = 0;
rep(i, 1, n){
if (a[i] != xx){
c[++cnt] = now;
now = 1;
}
else ++now;
xx = a[i];
}
c[++cnt] = now;
ans = cnt;
if (c[1] == 2 || c[cnt] == 2) ans = max(ans, cnt + 1);
rep(i, 1, cnt) if (c[i] >= 3) ans = max(ans, cnt + 2);
printf("%d
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Problem I
模拟题。
#include <cstdio>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
char s[11010];
int T;
set <string> mp;
int l;
int n;
set <string> :: iterator it;
int judge(char ch){
if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') || (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') || (ch == '-') || (ch == '_')) return 1;
return 0;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
mp.clear();
scanf("%d", &n);
getchar();
rep(op, 1, n){
gets(s);
l = strlen(s);
string s1 = "";
int i;
for (i = 0; i < l; ++i){
if (s[i] == '@'){
if (i && judge(s[i - 1])) continue;
s1 = "";
for (; i + 1 < l && judge(s[i + 1]); ){
s1 += s[i + 1];
++i;
}
if (s1 != "") mp.insert(s1);
}
}
}
printf("%d
", (int)mp.size());
for (it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); ++it) cout << *it << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem J
签到。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define dec(i, a, b) for (int i(a); i >= (b); --i)
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef long long LL;
int a[100010], b[100010];
int n ;
int T;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
scanf("%d", &n);
rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%d", a + i);
rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%d", b + i);
int ff = 1, fg = 1;
rep(i, 1, n) if (a[i] > b[i]) ff = 0;
rep(i, 1, n) if (a[i] > b[n - i + 1]) fg = 0;
if (ff && fg) puts("both");
else if (ff && !fg) puts("front");
else if (!ff && fg) puts("back");
else puts("none");
}
return 0;
}