前提知识
写在前面,为什么num&(length - 1) 在length是2的n次幂的时候等价于num%length
n - 1意味着比n最高位小的位都为1,而高的位都为0,因此通过与可以剔除位数比n最高位更高的部分,只保留比n最高位小的部分,也就是取余了。
而且用位运算取代%,效率会比较高。
基于以上几点,我们再看看hashmap中如何计算hash值得
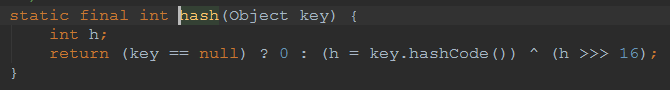
这里吧key的hashcode取出来,然后把它右移16位,然后取异或
这里从我Google得到的信息是,int是4个字节,也就是32位,我们右移16位也即是把高位的数据右移到低位的16位,然后做异或,那就是把高位和低位的数据进行重合
同时保留了低位和高位的信息
但是为什么是右移16位,这边保留疑问,我要是右移8位,4位,2位呢???
不做右移肯定不是,不做右移直接异或,那不就是0么
我们直接做个测试
public static int hash(Object key) { int h; //也就将key的hashCode无符号右移16位然后与hashCode异或从而得到hash值在putVal方法中(n - 1)& hash计算得到桶的索引位置 //注意,这里h是int值,也就是32位,然后无符号又移16位,那么就是折半,折半之后和原来的数据做异或操作,正好整合了高位和低位的数据 //混合原始哈希码的高位和低位,以此来加大低位的随机性,而且混合后的低位掺杂了高位的部分特征,这样高位的信息也被变相保留下来。 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); } //测试,如果我们不做高位低位的操作看看hash冲突是大还是小 public static int hash2(Object key) { return (int) key; } public static int hash3(Object key) { int h = key.hashCode(); //我们不做右移试试,那就自己跟自己异或。。。没意义,只能是0了 return (key == null) ? 0 : h ^ h; } public static int hash4(Object key) { int h; //我们不做右移试试,或者右移8位试试 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 8); } public static int hash5(Object key) { int h; //我们不做右移试试,或者右移8位试试 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 4); } public static int hash6(Object key) { int h; //我们不做右移试试,或者右移8位试试 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 2); }
hash3的测试可以去除不用考虑了
public void testHash() { //产生随机数 int init = 64 * 64; int size = 64 * 64; for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) { // int size = init * (j+1); size *= 2; int hash1[] = new int[size]; int hash2[] = new int[size]; int hash3[] = new int[size]; int hash4[] = new int[size]; int hash5[] = new int[size]; int hash6[] = new int[size]; int testCount = size; int exist1 = 0; int exist2 = 0; int exist3 = 0; int exist4 = 0; int exist5 = 0; int exist6 = 0; for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1); if(hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist1++; } else { hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } } for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1); if(hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist2++; } else { hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } } // for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { // // int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1); // // if(hash3[MyHashMap.hash3(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { // exist3++; // } else { // hash3[MyHashMap.hash3(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; // } // } for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1); if(hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist4++; } else { hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } } for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1); if(hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist5++; } else { hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } } for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1); if(hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist6++; } else { hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } } System.out.println("冲突比较: 1:" + exist1 + " 2:" + exist2 + " 4:" + exist4 + " 5:" + exist5 + " 6:" + exist6); } }
开始测试:
上面是size会递增的,现在我们先测size不变的情况看看效果
size=64 * 64
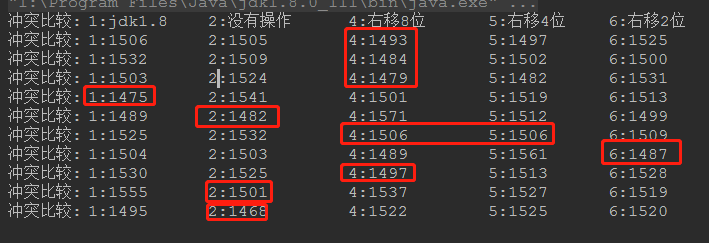
从结果上看明显是右移8位冲突比较少!!!
我们把size扩大一倍

再扩大一倍
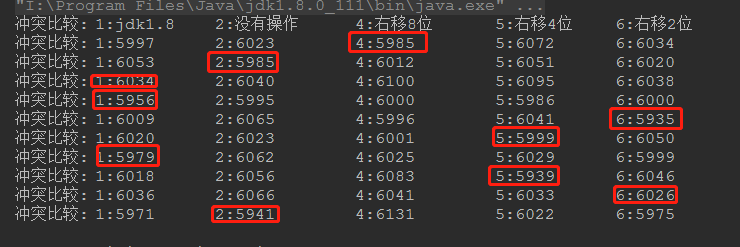
这次还比较平价
有人会说这是因为每次随机的数不一样的,每次都是产生新的随机数,没有可比性
那么我们每次用一个固定的数去进行hash碰撞
还是64*64开始,依次乘以2,4
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test public void testHash2() throws InterruptedException { //产生随机数 int init = 64 * 64; int size = 8; System.out.println("冲突比较: 1:jdk1.8 2:没有操作 4:右移8位 5:右移4位 6:右移2位"); for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) { // int size = init * (j+1); size = 8 * j + size; int hash1[] = new int[size]; int hash2[] = new int[size]; int hash4[] = new int[size]; int hash5[] = new int[size]; int hash6[] = new int[size]; int testCount = size / 3; int exist1 = 0; int exist2 = 0; int exist4 = 0; int exist5 = 0; int exist6 = 0; for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) { Thread.sleep(i + 1); int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1) * j * (i + 1); if(hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist1++; } else { hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } if(hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist2++; } else { hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } if(hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist4++; } else { hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } if(hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist5++; } else { hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } if(hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) { exist6++; } else { hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] = 1; } } System.out.println("冲突比较: 1:" + exist1 + " 2:" + exist2 + " 4:" + exist4 + " 5:" + exist5 + " 6:" + exist6); } }
我们还是执行三次比较:

从第一次看结果好像jdk自带的方式冲突还比较多。。。
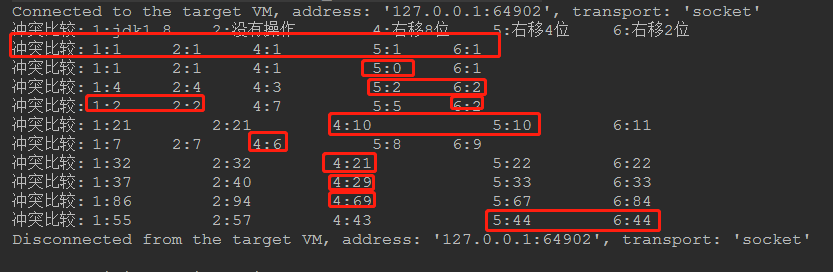
我最后再来一次,怎么感觉越来越不对劲。。。
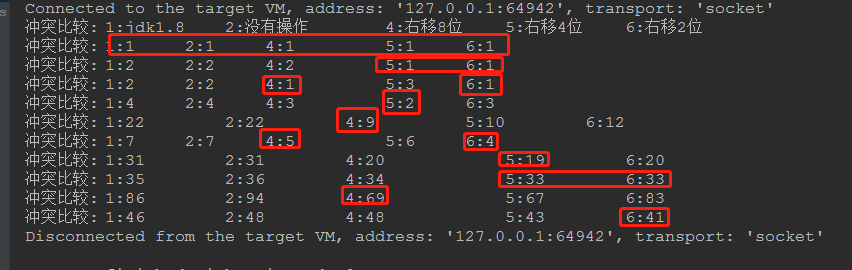
总结:我懵逼了啊!!!为什么啊,我测试出来感觉jdk自带的右移16位的方式,并不能有效减少冲突,反而右移4或者8位测试效果比较好!!!
求大神解答!!!