▶ 继续改进决策树的代码,对连续型变量和含缺失值的变量进行分类,以及画图的代码(头一回采用递归的画图,Python 的 plt 到处随便调不用考虑句柄传递的问题,很爽)。
● 代码,仅注释了与简单决策树不同的地方
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import operator 4 import warnings 5 6 warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") 7 dataSize = 1000 8 trainRatio = 0.3 9 randomSeed = 107 10 11 def dataSplit(data, part): 12 return data[0:part], data[part:] 13 14 def kernel(x, i, n): # 用来分类的分段函数 15 return np.select([x < 1-i/n, True], [i*x/(n-i), n*(x-1)/i-x+2]) 16 17 def createData(dim, kind, len): # 取连续值,没有 option 选项 18 np.random.seed(randomSeed) 19 temp = np.random.rand(len, dim) 20 x = np.sum(temp[:,:-1],1) / (dim - 1) 21 if kind == 2: 22 f = temp[:,-1] > x * (32 / 3 * (x-1) * (x-1/2) + 1) # 过 (0,0),(1/4,3/4),(1/2,1/2),(1,1) 的三次曲线 23 elif kind == 3: 24 f = (temp[:,-1] > x ** 2).astype(int) + (temp[:,-1] > 1 - (1-x)**2).astype(int) # 把单位正方形三等分了的两条抛物线 25 else: 26 f = np.zeros(len) 27 fi = np.frompyfunc(kernel, 3, 1) # 让 kernel 能接受向量输入 28 for i in range(1, kind): # 在单位正方形不过原点的对角线上等距取点 29 f += temp[:,-1] > fi(x,i,kind).astype(float) # 分别连接 (0,0) 和 (1,1),划分区域 30 31 output = [ temp[i].tolist() + [str(f[i])] for i in range(len) ] 32 label = [ chr(i + 65) for i in range(dim) ] 33 #for line in output: 34 # print(line) 35 print("dim = %d, kind = %d, dataSize = %d, weightedMean = %4f"%(dim, kind, dataSize, np.sum(f.astype(int)) / (len *(kind-1)))) 36 return output, label 37 38 def plogp(x, isScalar): 39 output = x * np.log2(x) 40 if isScalar: 41 return [0 if np.isnan(output) else output][0] 42 output[np.isnan(output)] = 0.0 43 return output 44 45 def calculateGain(table, alpha = 0): # 公式跟离散情形一模一样 46 sumC = np.sum(table, 0) 47 sumR = np.sum(table, 1) 48 sumA = np.sum(sumC) 49 temp = -( np.sum(plogp(sumC,False)) - plogp(sumA,True) - np.sum(plogp(table,False)) + np.sum(plogp(sumR,False)) ) / sumA 50 if alpha == 0: 51 return temp 52 elif alpha == 1: 53 return temp * (-1.0 / np.sum(plogp(sumR / sumA,False))) 54 else: 55 return sumA / ( np.sum(sumR * (1 - np.sum(table * table, 0) / (sumR * sumR))) ) 56 57 def chooseFeature(data,label): 58 size, dim = np.shape(data) 59 dim -= 1 60 realMaxGain = 0 61 realPoint = -1 62 maxi = -1 63 kindTable = list(set([ data[j][-1] for j in range(size) ])) 64 for i in range(dim): 65 valueTable = [ data[j][i] for j in range(size) ] 66 sortedValueTable = sorted(valueTable) 67 tSet = [ (sortedValueTable[i] + sortedValueTable[i+1])/2 for i in range(size-1)]# 分点集合 68 maxGain = 0 69 point = -1 70 for t in tSet: # 尝试每个分点 71 table = np.zeros([2,2],dtype=int) 72 for j in range(size): 73 table[int(data[j][-1] == kindTable[0]),int(data[j][i] < t)] += 1 74 gain = calculateGain(table) 75 if (gain > maxGain): # 内部关于 t 找一次最大值 76 maxGain = gain 77 point = t 78 if (maxGain > realMaxGain): # 外部关于 i 找一次最大值 79 realMaxGain = maxGain 80 maxi = i 81 realPoint = point 82 return (maxi, realPoint) # 不再返回最佳属性的取值表,而是返回分点 83 84 def vote(kindList): 85 kindCount = {} 86 for i in kindList: 87 if i not in kindCount.keys(): 88 kindCount[i] = 0 89 kindCount[i] += 1 90 output = sorted(kindCount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse = True) 91 return output[0][0] 92 93 def createTree(data,label): 94 #if data == []: 95 # return '?' 96 if len(data[0]) == 1: 97 return vote([ line[-1] for line in data ]) 98 classList = set([i[-1] for i in data]) 99 if len(classList) == 1: 100 return list(classList)[0] 101 102 bestFeature, point = chooseFeature(data, label) 103 bestLabel = label[bestFeature] 104 myTree = {(bestLabel,point):{}} # 树中属性节点,附上分点数据 105 106 childData = [] # 分左右两半进行递归,0 表示小于分点的数据,1 表示大于分点的数据 107 for line in data: # 只有两个分支,做循环展开 108 if line[bestFeature] <= point: 109 childData.append(line) 110 myTree[(bestLabel,point)][0] = createTree(childData, label) 111 childData = [] 112 for line in data: 113 if line[bestFeature] > point: 114 childData.append(line) 115 myTree[(bestLabel,point)][1] = createTree(childData, label) 116 return myTree 117 118 def draw(xMin, xMax, yMin, yMax, nowTree,kindType): 119 #plt.plot([xMin,xMax],[yMin,yMin],color=[1,1,1]) 120 #plt.plot([xMin,xMax],[yMax,yMax],color=[1,1,1]) 121 #plt.plot([xMin,xMin],[yMin,yMax],color=[1,1,1]) 122 #plt.plot([xMax,xMax],[yMin,yMax],color=[1,1,1]) 123 direction,value = list(nowTree)[0] 124 if(direction)=='A': # 画竖线 125 plt.plot([value,value],[yMin,yMax],color=[0,0,0]) 126 branch0,branch1 = list(nowTree.values())[0].values() 127 if type(branch0) == kindType: # 左支 128 plt.text((xMin+value)/2,(yMin+2*yMax)/3, str(branch0[0]), 129 size = 9, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 130 else: 131 draw(xMin, value, yMin, yMax, branch0, kindType) 132 if type(branch1) == kindType: # 右支 133 plt.text((xMax+value)/2,(2*yMin+yMax)/3, str(branch1[0]), 134 size = 9, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 135 else: 136 draw(value, xMax, yMin, yMax, branch1, kindType) 137 else: # 画横线 138 plt.plot([xMin,xMax],[value,value],color=[0,0,0]) 139 branch0,branch1 = list(nowTree.values())[0].values() 140 if type(branch0) == kindType: # 下支 141 plt.text((xMin+2*xMax)/3,(yMin+value)/2, str(branch0[0]), 142 size = 9, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 143 else: 144 draw(xMin, xMax, yMin, value, branch0, kindType) 145 if type(branch1) == kindType: # 上支 146 plt.text((2*xMin+xMax)/3,(yMax+value)/2, str(branch1[0]), 147 size = 9, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 148 else: 149 draw(xMin, xMax, value, yMax, branch1, kindType) 150 151 def test(dim, kind): 152 allData, labelName = createData(dim, kind, dataSize) 153 trainData, testData = dataSplit(allData, int(dataSize * trainRatio)) 154 outputTree = createTree(trainData, labelName) 155 print(outputTree) 156 157 myResult = [] 158 #count = 0 159 for line in testData: 160 #print(count) 161 tempTree = outputTree 162 while(True): 163 judgeName = list(tempTree)[0] 164 judgeValue = list(tempTree.values())[0] 165 value = line[labelName.index(judgeName[0])] # 取属性节点的属性名 166 resultNow = judgeValue[int(value > judgeName[1])] # 取属性节点的分点值来做比较 167 if type(resultNow) == type(allData[0][-1]): 168 myResult.append(resultNow) 169 break 170 tempTree = resultNow 171 #count+=1 172 173 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 174 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 175 plt.ylim(-0.0,1.0) 176 xT = [] 177 xF = [] 178 yT = [] 179 yF = [] 180 for i in range(len(testData)): 181 if testData[i][-1] == 'True': 182 xT.append(testData[i][0]) 183 yT.append(testData[i][1]) 184 else: 185 xF.append(testData[i][0]) 186 yF.append(testData[i][1]) 187 plt.scatter(xT,yT,color=[1,0,0],label = "classT") 188 plt.scatter(xF,yF,color=[0,0,1],label = "classF") 189 plt.legend(loc=[0.85, 0.1], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 190 draw(0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0,outputTree,type(allData[0][-1])) 191 fig.savefig("R:\dim" + str(dim) + ".png") 192 plt.close() 193 print("errorRatio = %4f"%( sum(map(lambda x,y:int(x!=y[-1]), myResult, testData)) / (dataSize*(1-trainRatio)) )) 194 195 if __name__=='__main__': 196 test(2, 2) 197 #test(2, 2) 198 #test(3, 2) 199 #test(4, 2)
● 输出结果(数字精度砍掉了,不然太长了)
{('B',0.3032): {0: {('A',0.0408): {0: {('A',0.0352): {0: 'False',
1: 'True'
}
},
1: 'False'
}
},
1: {('B',0.6816): {0: {('A',0.5020): {0: {('A',0.0797): {0: {('B',0.3171): {0: 'False',
1: 'True'
}
},
1: {('B',0.6223): {0: {('A',0.4835): {0: 'False',
1: {('A',0.4932): {0: 'True',
1: 'False'
}
}
}
},
1: {('A',0.3897): {0: {('A',0.1309): {0: 'True',
1: 'False'
}
},
1: 'True'
}
}
}
}
}
},
1: {('A',0.9160): {0: {('A',0.5407): {0: {('A',0.5327): {0: 'True',
1: 'False'
}
},
1: 'True'
}
},
1: 'False'
}
}
}
},
1: {('A',0.9450): {0: {('B',0.7335): {0: {('B',0.7262): {0: 'True',
1: 'False'
}
},
1: 'True'
}
},
1: 'False'
}
}
}
}
}
}
errorRatio = 0.054286
● 画图
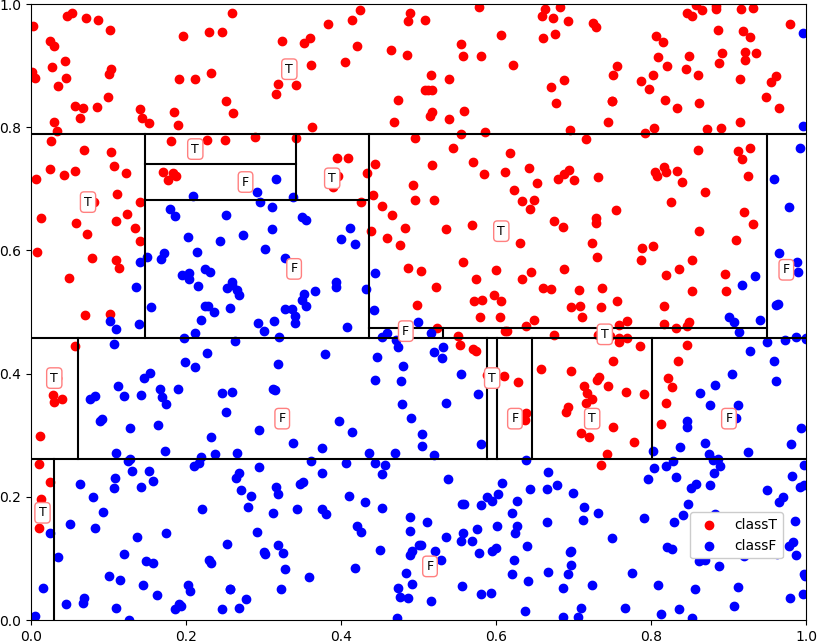
● 有缺失值时,在函数 chooseFeature 中为表格 table 增加一行来保存分属各类别的样本频数,带入以下函数中计算增益
1 def calculateGain(table, alpha = 0): # 有缺失值情况,table 多一行来保存分属各类别的样本频数 2 sumC = np.sum(table[:-1], 0) # 行列求和不包括缺失值的行 3 sumR = np.sum(table[:-1], 1) 4 sumA = np.sum(sumC) 5 temp = -( np.sum(plogp(sumC,False)) - plogp(sumA,True) - np.sum(plogp(table,False)) + np.sum(plogp(sumR,False)) ) / (sumA + np.sum(table[-1])) # 总分母要算上缺失行的频数,就算是乘以了 ρ 6 if alpha == 0: 7 return temp 8 elif alpha == 1: 9 return temp * (-1.0 / np.sum(plogp(sumR / sumA,False))) 10 else: 11 return sumA / ( np.sum(sumR * (1 - np.sum(table * table, 0) / (sumR * sumR))) )
● 留坑,类别数大于 2 时的的画图函数