There are nn cities and mm roads in Berland. Each road connects a pair of cities. The roads in Berland are one-way.
What is the minimum number of new roads that need to be built to make all the cities reachable from the capital?
New roads will also be one-way.
The first line of input consists of three integers nn, mm and ss (1≤n≤5000,0≤m≤5000,1≤s≤n1≤n≤5000,0≤m≤5000,1≤s≤n) — the number of cities, the number of roads and the index of the capital. Cities are indexed from 11 to nn.
The following mm lines contain roads: road ii is given as a pair of cities uiui, vivi (1≤ui,vi≤n1≤ui,vi≤n, ui≠viui≠vi). For each pair of cities (u,v)(u,v), there can be at most one road from uu to vv. Roads in opposite directions between a pair of cities are allowed (i.e. from uu to vv and from vv to uu).
Print one integer — the minimum number of extra roads needed to make all the cities reachable from city ss. If all the cities are already reachable from ss, print 0.
9 9 1 1 2 1 3 2 3 1 5 5 6 6 1 1 8 9 8 7 1
3
5 4 5 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1
1
The first example is illustrated by the following:
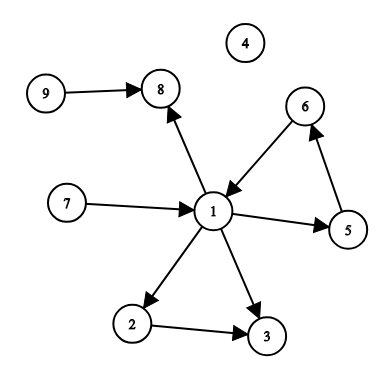
For example, you can add roads (6,46,4), (7,97,9), (1,71,7) to make all the cities reachable from s=1s=1.
The second example is illustrated by the following:
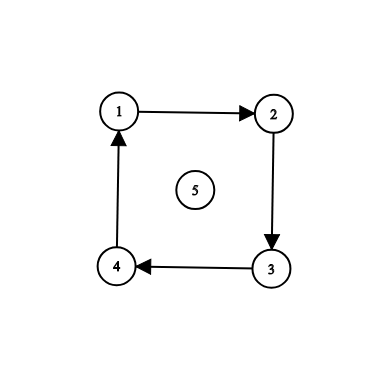
In this example, you can add any one of the roads (5,15,1), (5,25,2), (5,35,3), (5,45,4) to make all the cities reachable from s=5s=5.
题意:就是给你很多条路,这些路,城市之间的是无向的,而城市与首都之间的只能由首都到达城市不能由城市到首都。
题解:用到了拓扑图,我们可以把不能通到首都的城市加一条需边使其能到达城市,然后遍历每一条虚边,如果新加的虚边能够使前面加的虚边联通的城市联通,则取消原来的标记。最后标记的数量即为答案;
AC代码为:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5010;
int n,m,k,u,v,tot,cnt;
int first[maxn],vis[maxn],judge[maxn],connect[maxn];
struct Node{
int to,net;
} node[maxn<<1];
void Init()
{
tot=1,cnt=0;
memset(first,-1,sizeof first);
}
void add(int u,int v)
{
node[tot].to=v;
node[tot].net=first[u];
first[u]=tot++;
}
void dfs(int st)
{
vis[st]=connect[st]=1;
for(int e=first[st];e!=-1;e=node[e].net)
{
int v=node[e].to;
if(!vis[v])
{
judge[v]=0;
dfs(v);
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
Init();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>u>>v;
add(u,v);
}
dfs(k);
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!connect[i])
{
judge[i]=1;
dfs(i);
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(judge[i]) cnt++;
cout<<cnt<<endl;
return 0;
}