1.if条件判断的格式
if (条件) { 代码块 }
if (条件) { 代码块1 } else { 代码块2 }
if (条件1) { 代码块1 } else if { 代码块2 } else { 代码块3 }
2.整型判断
条件判断注意的事项:
- 注意判断顺序
- 注意边界条件
int n = 100;
if (n >= 90){
System.out.println("优秀");
}else if(n >= 60){
System.out.println("及格");
}else{
System.out.println("挂科");
}
3.浮点数判断
- 浮点数 == 判断不靠谱 利用差值小于某个临界值判断
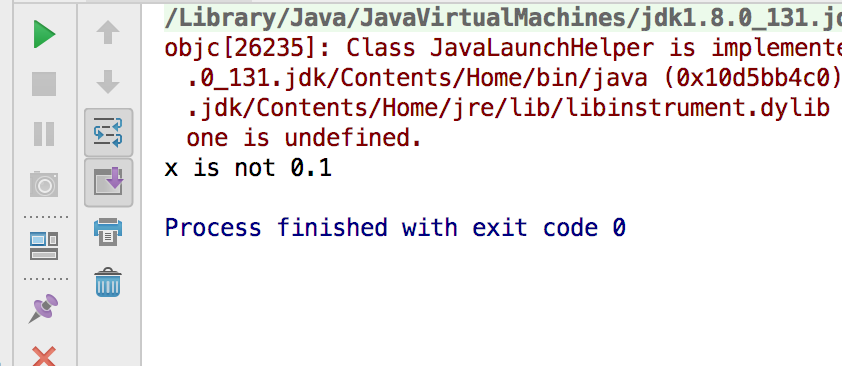
double x = 1 - 9.0 / 10;
if (x == 0.1){
System.out.println("x is 0.1");
}else{
System.out.println("x is not 0.1");
}
 ```#java
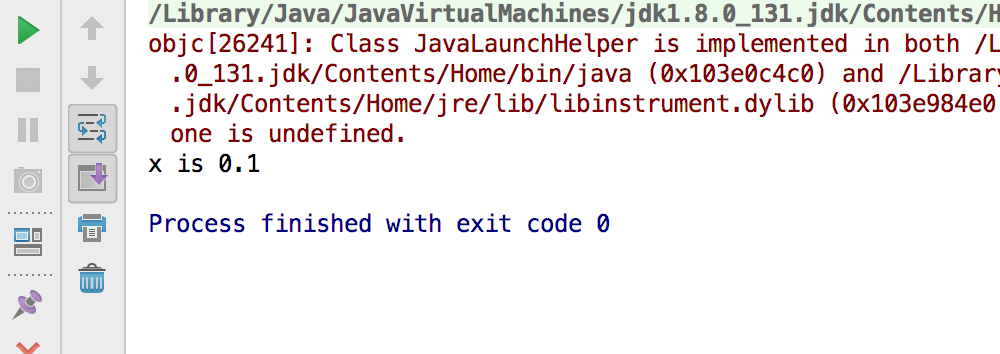
double x = 1 - 9.0 / 10;
//修改上面的代码,改为范围比较
if (Math.abs(x - 0.1) < 0.00001){
System.out.println("x is 0.1");
}else{
System.out.println("x is not 0.1");
}
}
```
```#java
double x = 1 - 9.0 / 10;
//修改上面的代码,改为范围比较
if (Math.abs(x - 0.1) < 0.00001){
System.out.println("x is 0.1");
}else{
System.out.println("x is not 0.1");
}
}
```
 # 4.引用类型判断
* 引用类型 == 判断是否指向同一对象
* equals()判断内容是否相等
* 如果变量为null,调用equals()会报错。利用短路运算符&&可以避免这个问题
```#java
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO".toLowerCase();
if (s1 == s2){
System.out.println("s1 == s2");
}
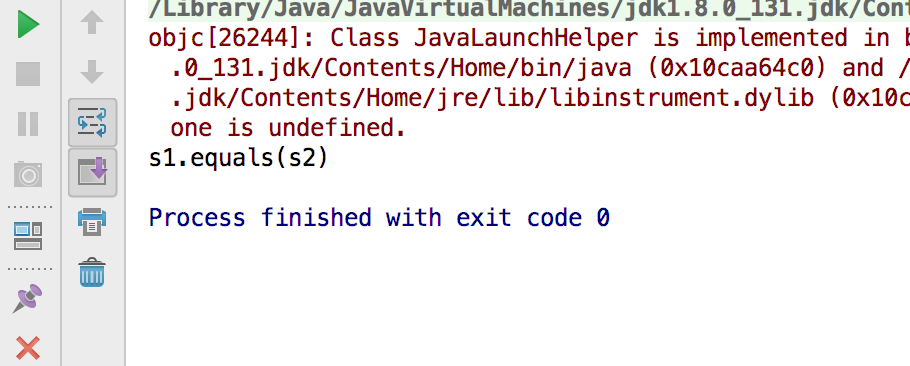
if (s1.equals(s2)){
System.out.println("s1.equals(s2)");
}
String s3 = null;
if (s3 != null && s3.equals("hello")){
System.out.println("yes");
}
```
# 4.引用类型判断
* 引用类型 == 判断是否指向同一对象
* equals()判断内容是否相等
* 如果变量为null,调用equals()会报错。利用短路运算符&&可以避免这个问题
```#java
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO".toLowerCase();
if (s1 == s2){
System.out.println("s1 == s2");
}
if (s1.equals(s2)){
System.out.println("s1.equals(s2)");
}
String s3 = null;
if (s3 != null && s3.equals("hello")){
System.out.println("yes");
}
```
5.总结
- if ...else可以做条件判断,else是可选的
- 只有一个执行语句可以省略{},但不推荐省略{}
- 多条件串联要注意判断顺序
- 要注意边界条件
- 要注意浮点数相等判断
- 引用类型判断相等用equals(),注意避免NullPointerException