程序员必知的8大排序(一)-------直接插入排序,希尔排序(java实现)
程序员必知的8大排序(二)-------简单选择排序,堆排序(java实现)
程序员必知的8大排序(三)-------冒泡排序,快速排序(java实现)
程序员必知的8大排序(四)-------归并排序,基数排序(java实现)
程序员必知的8大排序(五)-------总结
7、归并排序

(1)基本排序:归并(Merge)排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序序列。
(2)实例:

(3)用java实现
import java.util.Arrays; public class mergingSort { public mergingSort(){ } public static void main(String[] args) { int a[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98,54,56,17,18,23,34,15,35,25,53,51}; sort(a,0,a.length-1); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) System.out.println(a[i]); } public static void sort(int[] data, int left, int right) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(left<right){ //找出中间索引 int center=(left+right)/2; //对左边数组进行递归 sort(data,left,center); //对右边数组进行递归 sort(data,center+1,right); //合并 merge(data,left,center,right); } } public static void merge(int[] data, int left, int center, int right) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int [] tmpArr=new int[data.length]; int mid=center+1; //third记录中间数组的索引 int third=left; int tmp=left; while(left<=center&&mid<=right){ //从两个数组中取出最小的放入中间数组 if(data[left]<=data[mid]){ tmpArr[third++]=data[left++]; }else{ tmpArr[third++]=data[mid++]; } } //剩余部分依次放入中间数组 while(mid<=right){ tmpArr[third++]=data[mid++]; } while(left<=center){ tmpArr[third++]=data[left++]; } //将中间数组中的内容复制回原数组 while(tmp<=right){ data[tmp]=tmpArr[tmp++]; } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); } }
8、基数排序
(1)基本思想:将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后,数列就变成一个有序序列。
(2)实例:
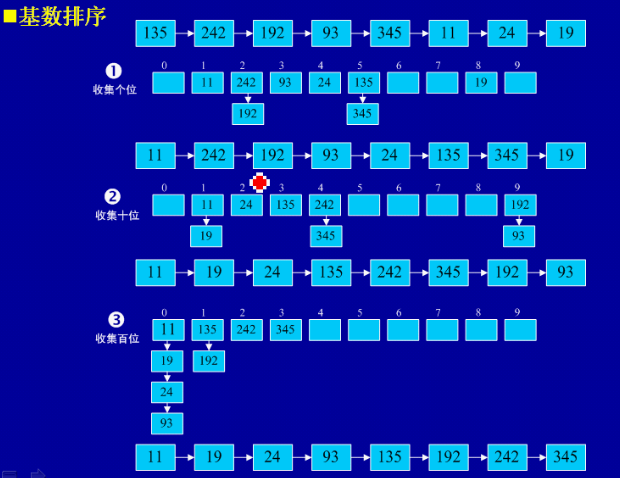
(3)用java实现
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class radixSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = { 49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49, 78, 34, 12, 64, 5, 4, 62, 99, 98, 54, 101, 56, 17, 18, 23, 34, 15, 35, 25, 53, 51 }; sort(a); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) System.out.println(a[i]); } public static void sort(int[] array) { // 首先确定排序的趟数; int max = array[0]; for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { if (array[i] > max) { max = array[i]; } } int time = 0; // 判断位数; while (max > 0) { max /= 10; time++; } // 建立10个队列; List<ArrayList> queue = new ArrayList<ArrayList>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ArrayList<Integer> queue1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); queue.add(queue1); } // 进行time次分配和收集; for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) { // 分配数组元素; for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) { // 得到数字的第time+1位数; int x = array[j] % (int) Math.pow(10, i + 1) / (int) Math.pow(10, i); ArrayList<Integer> queue2 = queue.get(x); queue2.add(array[j]); queue.set(x, queue2); } int count = 0;// 元素计数器; // 收集队列元素; for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) { while (queue.get(k).size() > 0) { ArrayList<Integer> queue3 = queue.get(k); array[count] = queue3.get(0); queue3.remove(0); count++; } } } } }