编码 / 解码
Shiro 提供了 base64 和 16 进制字符串编码 / 解码的 API 支持,方便一些编码解码操作。Shiro 内部的一些数据的存储 / 表示都使用了 base64 和 16 进制字符串。
Base64:
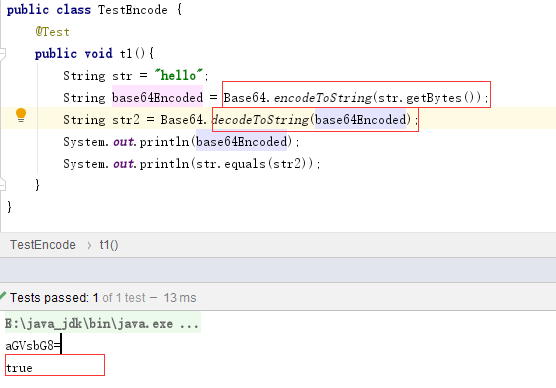
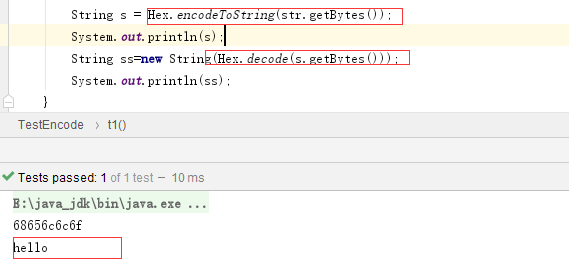
16进制HEX
散列算法
散列算法一般用于生成数据的摘要信息,是一种不可逆的算法,一般适合存储密码之类的数据,常见的散列算法如 MD5、SHA 等。
一般进行散列时最好提供一个 salt(盐),比如加密密码 “admin”,产生的散列值是 “21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3”,可以到一些 md5 解密网站很容易的通过散列值得到密码 “admin”,即如果直接对密码进行散列相对来说破解更容易,此时我们可以加一些只有系统知道的干扰数据,如用户名和 ID(即盐);这样散列的对象是 “密码 + 用户名 +ID”,这样生成的散列值相对来说更难破解。

还可以指定散列次数:

加密在Realm中应该怎么用
首先,毋庸置疑的是,在你的真实项目中,插入用户密码的时候,需要先进行加密处理,再插入数据库的表。在验证用户密码的时候,再使用相同的加密算法计算用户输入的密码。
开始:
先计算出加密后的密码:就是存在数据库中的加密密码(123+盐+3次散列)

配置文件:shiro-decode.ini
[main] myrealm=com.lc.demo.EncodeRealm securityManager.realms=$myrealm
自定义的Realm:
public class EncodeRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { @Override public String getName() { return "myrealm"; } public EncodeRealm(){ //密码123在本类初始化时已经被MD5加密3次 //采用md5算法 HashedCredentialsMatcher passwordMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher("md5"); //循环加密3次 passwordMatcher.setHashIterations(3); //再将这个加密组件注入到我们的Realm中 this.setCredentialsMatcher(passwordMatcher); } @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { String username =(String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal(); SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo= new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( username, "9d7281eeaebded0b091340cfa658a7e8", //模拟从数据库中拿到加密的密码(123+salt+3次散列) ByteSource.Util.bytes(username), //计算盐值 getName()); //就是上面的方法。获取realm的名字 return simpleAuthenticationInfo; //返回计算盐值加密后的密码的值.与红色部分对比, } @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { return null; } }
测试代码:
@Test public void t3(){ //1、获取SecurityManager工厂,此处使用Ini配置文件初始化SecurityManager Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-encode.ini"); //2、得到SecurityManager实例 并绑定给SecurityUtils org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //3、得到Subject及创建用户名/密码身份验证Token(即用户身份/凭证) Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //验证密码123456是否能够登录成功 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "123"); try { //4、登录,即身份验证 subject.login(token); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { //5、身份验证失败 e.printStackTrace(); } Assert.assertEquals(true, subject.isAuthenticated()); //断言用户已经登录 //6、退出 subject.logout(); }
总结:
- 1. 为什么使用 MD5 盐值加密:
- 希望即使两个原始密码相同,但是加密得到的两个字符串也不同(数据库中存储)。
- 2. 如何做到:
- 1). 在 doGetAuthenticationInfo 方法返回值创建 SimpleAuthenticationInfo 对象的时候, 需要使用SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName) 构造器
- 2). 使用 ByteSource.Util.bytes() 来计算盐值.
- 3). 盐值需要唯一: 一般使用随机字符串或 user id
- 4). 使用 new SimpleHash(hashAlgorithmName, credentials, salt, hashIterations); 来计算盐值加密后的密码的值.
密码重试次数限制
如在 1 个小时内密码最多重试 5 次,如果尝试次数超过 5 次就锁定 1 小时,1 小时后可再次重试,如果还是重试失败,可以锁定如 1 天,以此类推,防止密码被暴力破解。我们通过继承 HashedCredentialsMatcher,且使用 Ehcache 记录重试次数和超时时间。
RetryLimitHashedCredentialsMatcher: public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) { String username = (String)token.getPrincipal(); //retry count + 1 Element element = passwordRetryCache.get(username); if(element == null) { element = new Element(username , new AtomicInteger(0)); passwordRetryCache.put(element); } AtomicInteger retryCount = (AtomicInteger)element.getObjectValue(); if(retryCount.incrementAndGet() > 5) { //if retry count > 5 throw throw new ExcessiveAttemptsException(); } boolean matches = super.doCredentialsMatch(token, info); if(matches) { //clear retry count passwordRetryCache.remove(username); } return matches; }
如上代码逻辑比较简单,即如果密码输入正确清除 cache 中的记录;否则 cache 中的重试次数 +1,如果超出 5 次那么抛出异常表示超出重试次数了。