原始数据
Line1: C A B
Line2: A B D
Line3: A B
Line4: C E
1、 按照单词数量逆排序(小于支撑度的单词舍弃)
Line1: A B C
Line2: A B D
Line3: A B
Line4: C E
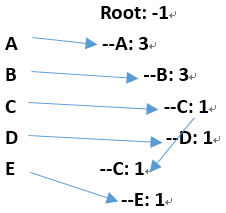
2、 构建FP树
Root: -1
--A: 3
--B: 3
--C: 1
--D: 1
--C: 1
--E: 1
3、构建包含线索的FP树
代码如下
package com.coshaho.fptree;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* FP树节点:仅考虑算法
* @author coshaho
* @since 2020/1/5
*/
public class FPNode {
// 单词
private String word;
// 单词出现次数
private int count = 1;
// 子节点
Map<String, FPNode> children = new HashMap<>();
// 父节点
private FPNode father;
// 线索:指向下一个相同单词节点
private FPNode next;
// 是否有线索指向自己
private boolean visited = false;
public FPNode(String word, int count) {
this.word = word;
this.count = count;
}
public void increase() {
count++;
}
public void print(int n) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(i == n - 1) {
System.out.print("--");
} else {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println(word + ": " + count);
for(FPNode child : children.values()) {
child.print(n + 1);
}
}
public String getWord() {
return word;
}
public void setWord(String word) {
this.word = word;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public Map<String, FPNode> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(Map<String, FPNode> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public FPNode getFather() {
return father;
}
public void setFather(FPNode father) {
this.father = father;
}
public FPNode getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(FPNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
public boolean isVisited() {
return visited;
}
public void setVisited(boolean visited) {
this.visited = visited;
}
}
package com.coshaho.fptree;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* FP树:仅考虑算法
* @author coshaho
* @since 2020/1/5
*/
public class FPTree {
// FP树根节点
FPNode root = new FPNode("Root", -1);
// FP树节点线索头
Map<String, FPNode> firstNodeTable = new HashMap<>();
// FP树节点线索尾
Map<String, FPNode> lastNodeTable = new HashMap<>();
// 支持度
private int support = 1;
public FPTree(List<List<String>> data, int support) {
this.support = support;
data = sort(data);
// line为一行日志
for(List<String> line : data) {
FPNode curNode = root;
for(String word : line) {
if(curNode.getChildren().containsKey(word)) {
// 子节点存在则访问次数加一
curNode.getChildren().get(word).increase();
} else {
// 子节点不存在则新增子节点
FPNode child = new FPNode(word, 1);
curNode.getChildren().put(word, child);
child.setFather(curNode);
}
curNode = curNode.getChildren().get(word);
// 当前节点有线索指向,则不必重复建立线索
if(curNode.isVisited()) {
continue;
}
// 创建线索
if(firstNodeTable.containsKey(word)) {
lastNodeTable.get(word).setNext(curNode);
} else {
firstNodeTable.put(word, curNode);
}
lastNodeTable.put(word, curNode);
curNode.setVisited(true);
}
}
}
private List<List<String>> sort(List<List<String>> data) {
Map<String, Integer> wordCount = new HashMap<>();
// 统计单词出现的次数
for(List<String> line : data) {
for(String word : line) {
if(wordCount.containsKey(word)) {
wordCount.put(word, wordCount.get(word) + 1);
} else {
wordCount.put(word, 1);
}
}
}
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 单词排序
for(List<String> line : data) {
List<String> newLine = line.stream().filter(word -> wordCount.get(word) >= support)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(word -> wordCount.get(word)).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
if(null != newLine && 0 != newLine.size()) {
result.add(newLine);
}
}
return result;
}
public void print() {
root.print(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> line1 = new ArrayList<>();
line1.add("C");
line1.add("A");
line1.add("B");
List<String> line2 = new ArrayList<>();
line2.add("A");
line2.add("B");
line2.add("D");
List<String> line3 = new ArrayList<>();
line3.add("A");
line3.add("B");
List<String> line4 = new ArrayList<>();
line4.add("C");
line4.add("E");
List<List<String>> data = new ArrayList<>();
data.add(line1);
data.add(line2);
data.add(line3);
data.add(line4);
FPTree tree = new FPTree(data, 1);
tree.print();
}
}