什么是进程(process):
狭义定义:进程是正在运行的程序的实例。
广义定义:进程是一个具有一定独立功能的程序关于某个数据集合的一次运行活动。它是操作系统动态执行的基本单元,在传统的操作系统中,进程既是基本的分配单元,也是基本的执行单元。
什么是线程(thread):
在进程中独立运行的子任务。
是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。
多线程的优势:不单单是一个排队等待一个任务的完成,可以多个任务之间来回切换,是系统的运行效率大大提高。
多线程是异步的,代码的顺序不是线程执行的顺序,线程被调用是随机的。
每个线程对象都是和某个Thread类的实例相联合的。
使用Thread对象创建并发程序共有两种策略:
- 为了直接控制线程创建和管理,可以简单的实例化Thread。
- 为了把线程和应用程序其他部分抽离开来,把此程序的任务传给一个执行器(executor)。
实现多线程编程方式主要有两种:
- 子类继承Thread类
- 实现Runnable接口
//源代码中Thread类实现了Runnable接口 public class Thread implements Runnable {
子类继承Thread类创建线程
1、继承Thread类创建新线程,不支持多继承。
创建线程是使用Thread类的start方法。执行start()之后,线程是创建成功处于休眠状态,然后CPU调度线程时,自动执行run()方法,方法内部包括线程执行语句,从就绪状态到执行状态。
继承Thread类都要重写run()方法。
注意run()单独执行和程序自动执行的区别:
run()方法是一个普通的方法,单独使用时不是线程,通过执行代码可以看出程序是顺序执行的。
而执行start()方法会自动执行run()的情况就是创建线程的过程。线程调度是随机的,不一定按代码创建线程顺序执行线程。
调用start()启动线程:
public class MyThread extends Thread {//继承Thread类创建线程 @Override public void run() { super.run(); System.out.println(this.currentThread().getName());//打印当前线程的名字 } }
//测试代码 public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new MyThread(); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(); MyThread t3 = new MyThread(); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start();//启动线程 } }
运行结果:

线程启动顺序与start()顺序无关。
单独使用run():
public class MyThread extends Thread {//继承Thread类创建线程 @Override public void run() { super.run(); System.out.println(this.currentThread().getName());//打印当前线程的名字 } } //测试代码 public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new MyThread(); MyThread t2 = new MyThread(); MyThread t3 = new MyThread(); t1.run(); t2.run(); t3.run(); } }
运行结果:

没有启动新线程,是由main()主线程来调用run()方法。
停止线程:
(1)异常法
(2)沉睡中停止
(3)暴力法stop()已被废弃
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
interrupt()方法:
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { System.out.println("i="+i); } } public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { MyThread thread = new MyThread(); thread.start();//启动线程 Thread.sleep(2000);//主线程main休眠2s,sleep是静态方法 thread.interrupt();//在thread上打断点 }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main catch");// e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:
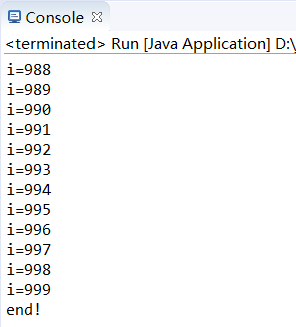
线程并没有停止。
interrupt()方法只能打上一个停止标记,不能终止一个正在运行的线程,还需要加入一个判断才停止线程。
以下有两种判断方法:
1、interrupted()
2、isInterrupted()

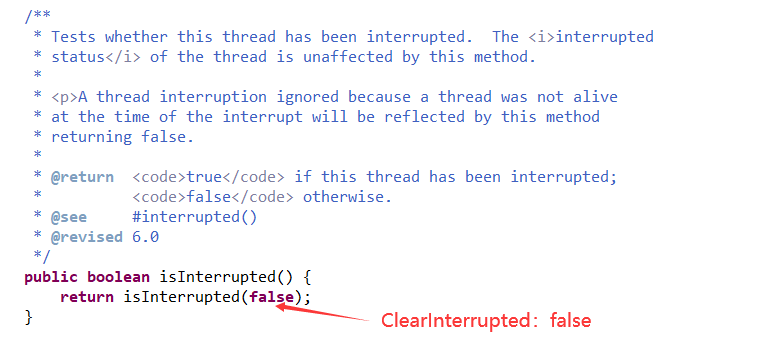
源码中说明了:
interrupted()静态方法,返回当前线程的中断状态,并且会清除状态标志保持默认值false。
isInterrupted()实例方法,返回调用该方法对象的线程的中断状态,不会清除状态标志。
1、测试一下interrupted()

静态方法要使用静态方式访问
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { MyThread thread = new MyThread(); thread.start();//启动线程
Thread.sleep(2000);//主线程main休眠2s,sleep()是静态方法不用创建对象 thread.interrupt();//在thread上打断点//到底是哪个线程? System.out.println("线程是否停止?"+Thread.interrupted()); System.out.println("线程是否停止?"+Thread.interrupted()); }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main catch");// e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:
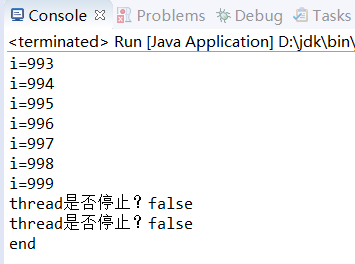
测试出当前线程没有处于停止状态,因为thread.interrupt()只是把中断标记打在thread对象上。
当前线程是main,从未中断过,所以打印的结果是两个false。
当中断状态打在当前线程main上:
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { MyThread thread = new MyThread(); thread.start();//启动线程 Thread.sleep(2000);//主线程main休眠2s,sleep()是静态方法不用创建对象 Thread.currentThread().interrupt();//在main线程上打断点 System.out.println("线程是否停止?"+Thread.interrupted()); System.out.println("线程是否停止?"+Thread.interrupted()); }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main catch"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:

这次中断标记打在main线程上,发现同一线程打印两次中断状态时,结果不一样?
原因是interrupted()方法具有清除状态标志的功能,所以第二次及以后调用都返回false。
那么问题来了:既然interrupted只能检测当前线程是否中断,thread对象能不能是当前线程呢?
在我尝试了几次后,可以这样做:thread对象是当前线程,情况只能是在MyThread类里面。然后在main打断点,在MyThread里面interrupted看是否处于中断状态。
代码实现:
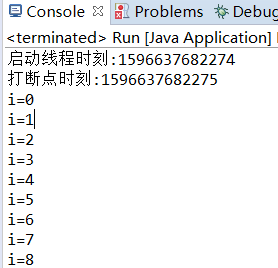
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { System.out.println("i="+i); } System.out.println("线程"+MyThread.currentThread().getName()+"是否停止?"+MyThread.interrupted()); System.out.println("run()执行完成时刻:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); } } public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { MyThread thread = new MyThread(); System.out.println("启动线程时刻:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); thread.start();//启动线程 Thread.sleep(2000);//主线程main休眠2s System.out.println("打断点时刻:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); thread.interrupt();//在thread上打断点 }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main catch"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:

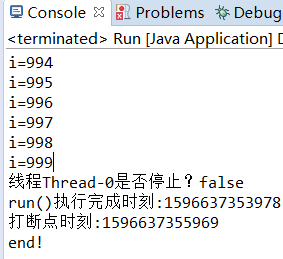
改变打断点的顺序:
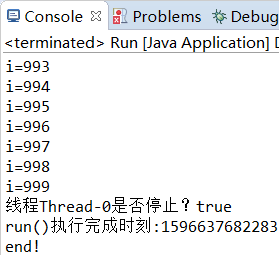
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { System.out.println("i="+i); } System.out.println("线程"+MyThread.currentThread().getName()+"是否停止?"+MyThread.interrupted()); System.out.println("run()执行完成时刻:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); } } public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { MyThread thread = new MyThread(); System.out.println("启动线程时刻:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); thread.start();//启动线程 System.out.println("打断点时刻:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); thread.interrupt();//在thread上打断点 Thread.sleep(2000);//主线程main休眠2s }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main catch"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:
对比两种结果的发现:
1、确实只能在方法内部用interrupted检测thread对象的的中断状态。
2、第二种情况的断点在run()执行完毕之前就能打在thread上,在run()检测到当前thread-0线程的中断状态是true,反映出多线程是异步执行的。线程main和thread-0在交替执行。
现在interrupted()告一段落,如果要在主线程中检测thread对象的中断状态用isInterrupted()。
(1)异常法
在MyThread中判断中断状态,已中断就抛出异常。
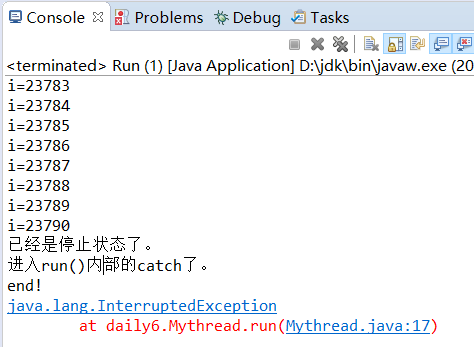
public class Mythread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); try { for(int i=0;i<50000;i++) { System.out.println("i="+i); if(this.isInterrupted()) {//可以替换为Thread.interrupted() System.out.println("已经是停止状态了。"); throw new InterruptedException(); } } System.out.println("for后面会执行吗?"); }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("进入run()内部的catch了。"); e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Mythread thread = new Mythread(); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(100);//主线程睡眠时间缩短,否则打不上断点 thread.interrupt(); }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Run.main()"); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:
(2)沉睡中停止
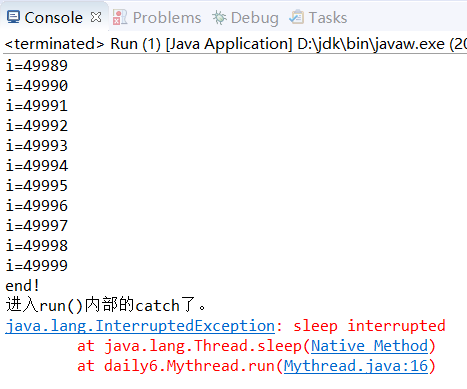
public class Mythread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); try { for(int i=0;i<50000;i++) { System.out.println("i="+i); } Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("for后面会执行吗?"); }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("进入run()内部的catch了。"); e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Mythread thread = new Mythread(); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread.interrupt(); }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Run.main()"); } System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:
(3)使用return停止
将方法interrupt()与return结合起来也能实现停止线程的效果。
public class Mythread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); while(true) { if(this.isInterrupted()) { System.out.println("停止了!"); return; } System.out.println("timer="+System.currentTimeMillis()); } } } public class Run { //throws就可以不用try-catch么 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{ Mythread thread = new Mythread(); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread.interrupt(); System.out.println("end!"); } }
运行结果:
