A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)Initializes the data structure with therootof the complete binary tree.int insert(int v)Inserts aTreeNodeinto the tree with valueNode.val == valso that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the insertedTreeNode.TreeNode get_root()Returns the root node of the tree.
Example 1:
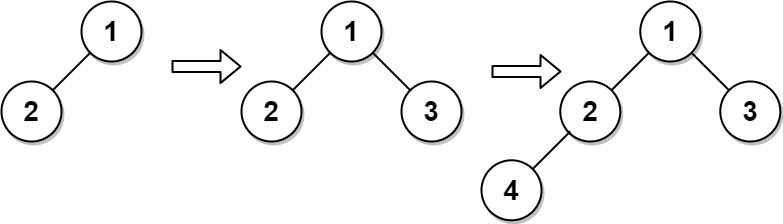
Input ["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"] [[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []] Output [null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]] Explanation CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]); cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1 cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2 cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5000rootis a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000- At most
104calls will be made toinsertandget_root.
完全二叉树插入器。
完全二叉树 是每一层(除最后一层外)都是完全填充(即,节点数达到最大)的,并且所有的节点都尽可能地集中在左侧。
设计一种算法,将一个新节点插入到一个完整的二叉树中,并在插入后保持其完整。
实现 CBTInserter 类:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root) 使用头节点为 root 的给定树初始化该数据结构;
CBTInserter.insert(int v) 向树中插入一个值为 Node.val == val的新节点 TreeNode。使树保持完全二叉树的状态,并返回插入节点 TreeNode 的父节点的值;
CBTInserter.get_root() 将返回树的头节点。来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/complete-binary-tree-inserter
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
这是一道设计题,我提供两种做法。题意是要求找一个 complete tree 下一个可以插入节点的位置。complete tree 的定义参考题目,每一层(除最后一层外)都是完全填充(即,节点数达到最大)的,并且所有的节点都尽可能地集中在左侧。那么大致思路可以往BFS上靠。
第一种做法,我们用 Queue 逐层遍历这棵树,对于每个节点 cur,我们判断他是否有左孩子和右孩子,如果有缺失,则把 val 包装成一个节点并接在 cur 节点身上。
这种做法,在树的遍历/构造上,复杂度是O(1);insert 节点 O(n),因为要走到那个需要插入的地方
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class CBTInserter { 17 private TreeNode root; 18 19 public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) { 20 this.root = root; 21 } 22 23 public int insert(int val) { 24 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 25 queue.offer(root); 26 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 27 TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); 28 if (cur.left == null) { 29 cur.left = new TreeNode(val); 30 return cur.val; 31 } 32 queue.offer(cur.left); 33 if (cur.right == null) { 34 cur.right = new TreeNode(val); 35 return cur.val; 36 } 37 queue.offer(cur.right); 38 } 39 return val; 40 } 41 42 public TreeNode get_root() { 43 return root; 44 } 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: 49 * CBTInserter obj = new CBTInserter(root); 50 * int param_1 = obj.insert(val); 51 * TreeNode param_2 = obj.get_root(); 52 */ 53 54 // O(1) build tree + O(n) insert
第二种做法,还是用 Queue 逐层遍历这棵树,但是我们先做一下预处理,让 cur 走到那个有节点缺失的地方;然后直接插入新节点。
这种做法预处理需要 O(n) 的时间,插入操作O(1) 的时间。
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class CBTInserter { 17 private TreeNode root; 18 private Queue<TreeNode> queue; 19 20 // O(N) build tree: Find the first node which doesn't have both left and right child 21 public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) { 22 this.root = root; 23 queue = new LinkedList<>(); 24 queue.offer(root); 25 // while true 是无限循环,只能在里面写break才会跳出 26 while (true) { 27 TreeNode cur = queue.peek(); 28 if (cur.left != null && cur.right != null) { 29 queue.offer(cur.left); 30 queue.offer(cur.right); 31 queue.poll(); 32 } else { 33 break; 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 38 public int insert(int val) { 39 TreeNode cur = queue.peek(); 40 // 停下的位置一定是有问题的所以要看到底是左孩子有问题还是右孩子有问题 41 if (cur.left == null) { 42 cur.left = new TreeNode(val); 43 } else { 44 cur.right = new TreeNode(val); 45 queue.offer(cur.left); 46 queue.offer(cur.right); 47 queue.poll(); 48 } 49 return cur.val; 50 } 51 52 public TreeNode get_root() { 53 return root; 54 } 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: 59 * CBTInserter obj = new CBTInserter(root); 60 * int param_1 = obj.insert(val); 61 * TreeNode param_2 = obj.get_root(); 62 */ 63 64 // O(n) build tree + O(1) insert