Given the root of a binary tree, collect a tree's nodes as if you were doing this:
- Collect all the leaf nodes.
- Remove all the leaf nodes.
- Repeat until the tree is empty.
Example 1:
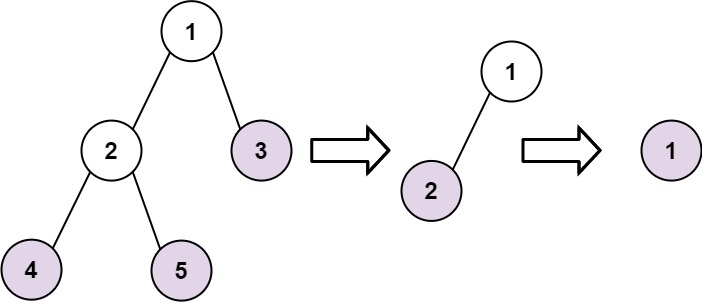
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [[4,5,3],[2],[1]] Explanation: [[3,5,4],[2],[1]] and [[3,4,5],[2],[1]] are also considered correct answers since per each level it does not matter the order on which elements are returned.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
寻找二叉树的叶子节点。
给你一棵二叉树,请按以下要求的顺序收集它的全部节点:
- 依次从左到右,每次收集并删除所有的叶子节点
- 重复如上过程直到整棵树为空
思路是后序遍历,跟104题求树的最大深度的方式很接近。在用后序遍历处理的时候,判断叶子节点的方式就是看看当前这个节点是不是没有左右孩子,如果满足这个条件,就可以把当前节点放入他对应的 sublist 里面。事实上因为每个节点都需要被放到某一个 sublist 中,其实我们并不是那么在意到底是不是叶子节点。
但是每个节点如何得知应该放到哪个 sublist 的呢?在做后序遍历的时候,我们同时是可以知道这个树的深度的,知道了树的深度,也就知道了结果集到底有几个 sublist。如果当前结果集里面 sublist 的个数小于树的深度,就加一个 sublist。注意我们这里所谓的深度其实是反过来的,叶子节点的深度是 0,根节点的深度是最大的。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public List<List<Integer>> findLeaves(TreeNode root) { 18 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); 19 // corner case 20 if (root == null) { 21 return res; 22 } 23 helper(root, res); 24 return res; 25 } 26 27 private int helper(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> res) { 28 // base case 29 if (root == null) { 30 return -1; 31 } 32 int left = helper(root.left, res); 33 int right = helper(root.right, res); 34 int depth = Math.max(left, right) + 1; 35 if (res.size() < depth + 1) { 36 res.add(new ArrayList<>()); 37 } 38 res.get(depth).add(root.val); 39 return depth; 40 } 41 }
相关题目
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree