A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Constraints:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomis null or pointing to a node in the linked list.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
复制带随机指针的链表。
题意是input给了一个带有next和random两个指针的链表,对其进行深度复制(deep copy)。例子,

Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
明确一下什么叫做深度复制。
这样叫做shallow copy浅复制,a和b在内存中是share一个地址。
ListNode a = new ListNode(0);
ListNode b = a;
这样叫做深度复制,a和b在内存中各自有各自的地址。
ListNode a = new ListNode(0);
ListNode b = new ListNode(0);
这道题有两种思路,一是用hashmap,key是每个node,value是存每个node的copy。复制完毕之后再遍历一遍,做每个node的指针复制。
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
JavaScript实现
1 /** 2 * @param {Node} head 3 * @return {Node} 4 */ 5 var copyRandomList = function(head) { 6 if (head === null) return null; 7 let map = new Map(); 8 let cur = head; 9 while (cur !== null) { 10 map.set(cur, new Node(cur.val, cur.next, cur.random)); 11 cur = cur.next; 12 } 13 cur = head; 14 while (cur !== null) { 15 map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next) || null; 16 map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random) || null; 17 cur = cur.next; 18 } 19 return map.get(head); 20 };
Java实现
1 class Solution { 2 public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { 3 HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); 4 Node cur = head; 5 while (cur != null) { 6 map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val)); 7 cur = cur.next; 8 } 9 cur = head; 10 while (cur != null) { 11 map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); 12 map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random); 13 cur = cur.next; 14 } 15 return map.get(head); 16 } 17 }
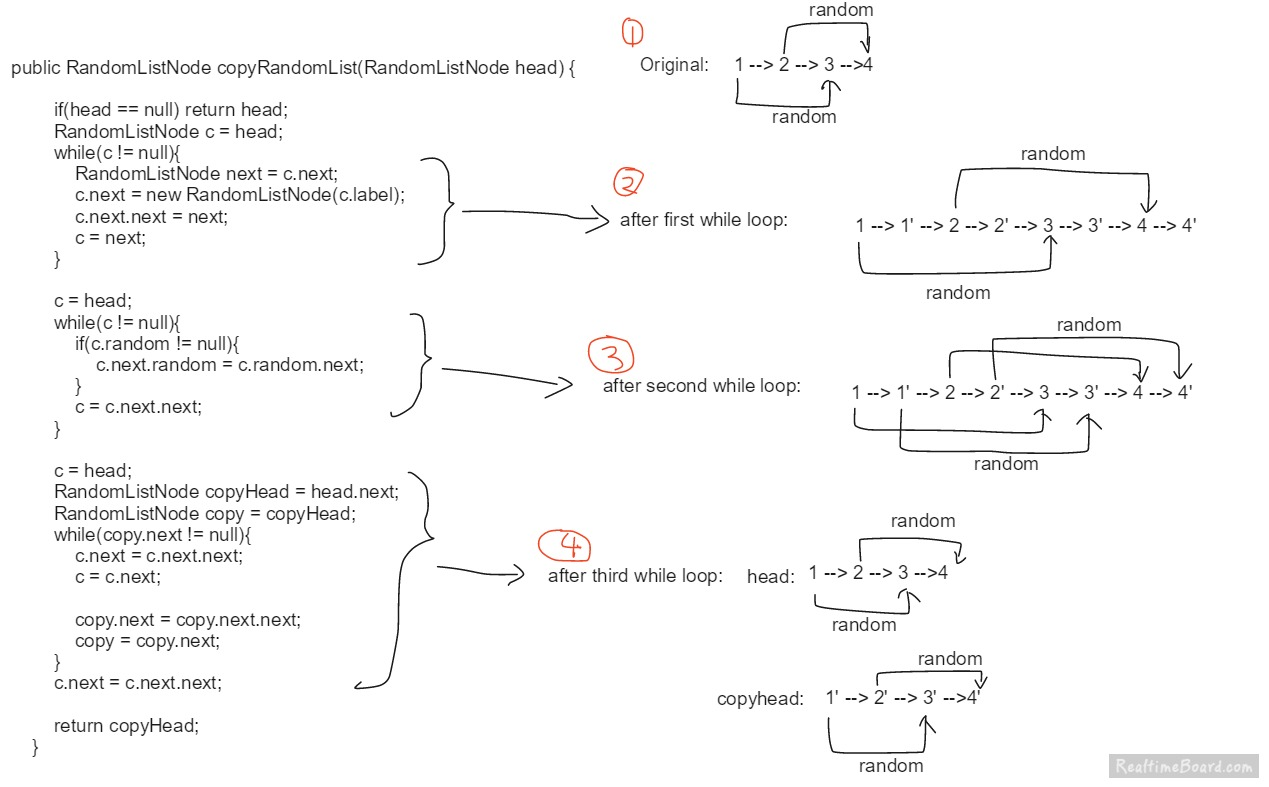
另外一种思路是首先复制整个链表,将每一个复制的节点copy加到原节点后面。然后将每个copy node的random node也链接好,再断开原链表和复制的链表。这种做法无需额外空间。
注意因为random node其实也是来自于这个链表,跟next指针的区别在于next指针是指向每个node的下一个node,random指针是随机指向了整个链表中的某个node,所以当第一遍复制好了copy node之后,也需要把cur.next.random指向cur.random.next,因为
- cur.next.random = copy.random
- cur.random.next = 某一个copy node
时间O(n)
空间O(1)
JavaScript实现
1 /** 2 * @param {Node} head 3 * @return {Node} 4 */ 5 var copyRandomList = function (head) { 6 // make copy of each node 7 let cur = head; 8 while (cur) { 9 let next = cur.next; 10 let copy = new Node(cur.val); 11 cur.next = copy; 12 copy.next = next; 13 cur = next; 14 } 15 16 // set random property 17 cur = head; 18 while (cur) { 19 if (cur.random !== null) { 20 cur.next.random = cur.random.next; 21 } 22 cur = cur.next.next; 23 } 24 25 // detach copied list 26 cur = head; 27 let dummyHead = new Node(0); 28 let newHead = dummyHead; 29 while (cur) { 30 let next = cur.next.next; 31 // extract the copy 32 let copy = cur.next; 33 newHead.next = copy; 34 newHead = copy; 35 // restore the original list 36 cur.next = next; 37 cur = next; 38 } 39 return dummyHead.next; 40 };
Java实现
1 class Solution { 2 public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { 3 // corner case 4 if (head == null) { 5 return null; 6 } 7 8 // copy all the cur nodes 9 Node cur = head; 10 while (cur != null) { 11 Node next = cur.next; 12 Node copy = new Node(cur.val); 13 cur.next = copy; 14 copy.next = next; 15 cur = next; 16 } 17 18 // copy all the random nodes 19 cur = head; 20 while (cur != null) { 21 if (cur.random != null) { 22 // cur.random.next是某个random节点的copy 23 // cur.next.random是当前节点的copy的random指针 24 cur.next.random = cur.random.next; 25 } 26 cur = cur.next.next; 27 } 28 29 // separate two lists 30 cur = head; 31 Node dummy = new Node(0); 32 Node copyHead = dummy; 33 Node copy; 34 while (cur != null) { 35 Node next = cur.next.next; 36 copy = cur.next; 37 copyHead.next = copy; 38 copyHead = copy; 39 cur.next = next; 40 cur = next; 41 } 42 return dummy.next; 43 } 44 }
最后附上discussion里面一个非常好的图解。
相关题目
138. Copy List with Random Pointer