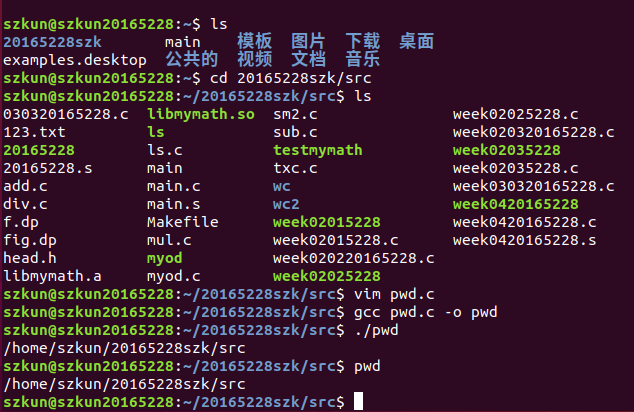
学习pwd命令
通过man -k pwd
man 1 pwd得到pwd帮助文档
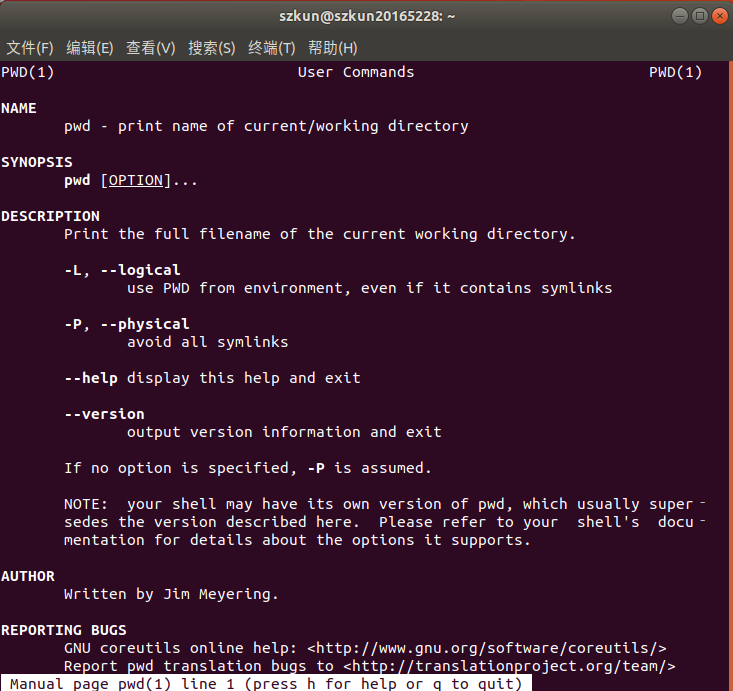
pwd - print name of current/working directory
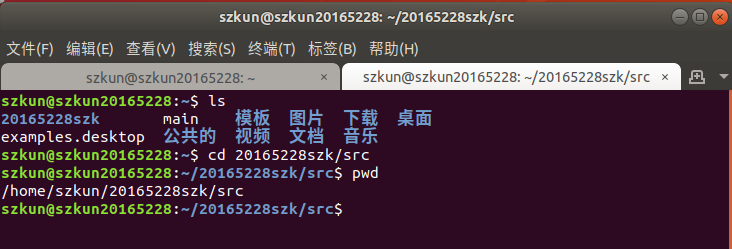
即执行pwd指令可立刻得知您目前所在的工作目录的绝对路径名称。
**pwd [选项] **
**参数: **
**-L:--logical,显示当前的路径,有连接文件时,直接显示连接文件的路径,(不加参数时默认此方式),参考示例1。 **
**-p:--physical,显示当前的路径,有连接文件时,不使用连接路径,直接显示连接文件所指向的文件,参考示例2。 当包含多层连接文件时,显示连接文件最终指向的文件,参考示例3。 **
--help:显示帮助信息。
--version:显示版本信息。
分析
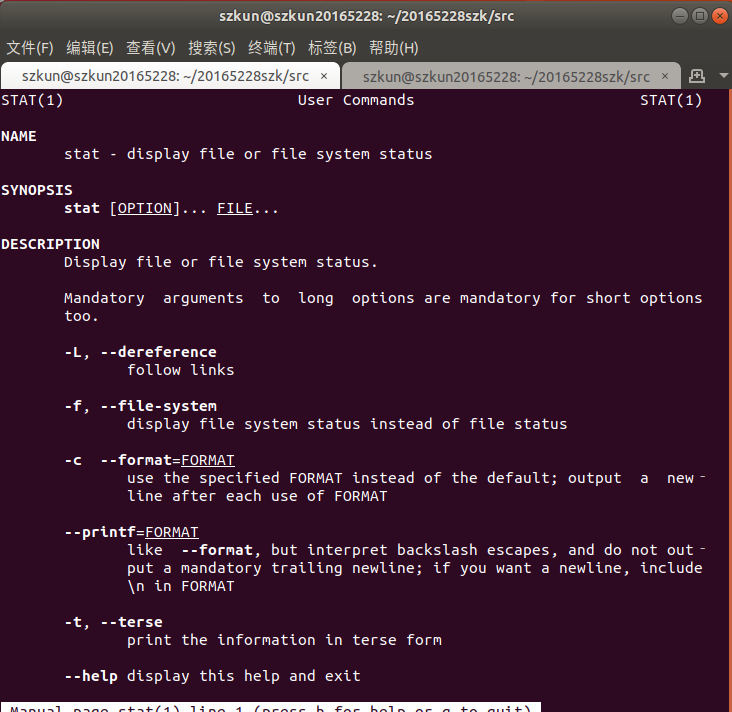
- stat:查看文件或者文件系统的状态 ,可以查看时间等属性
- opendir:打开目录
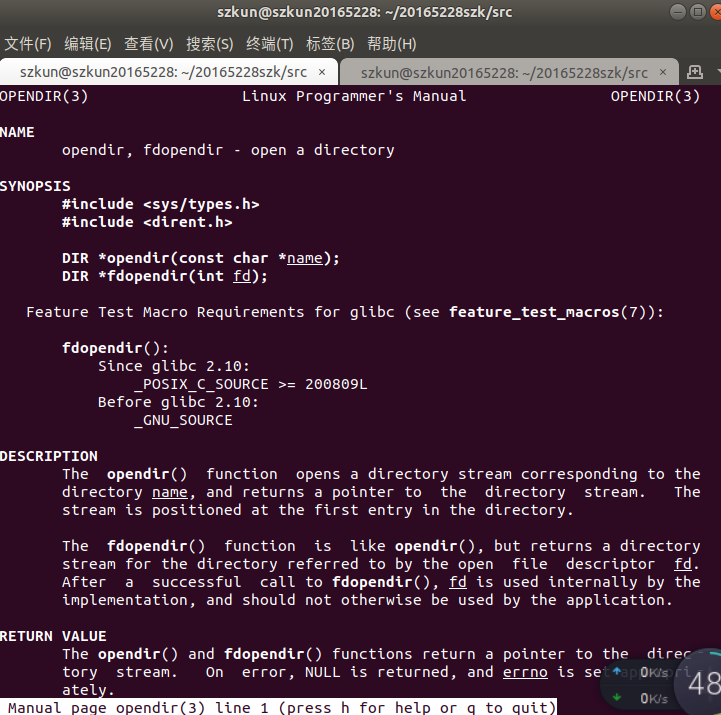
需要头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
-
fprintf:
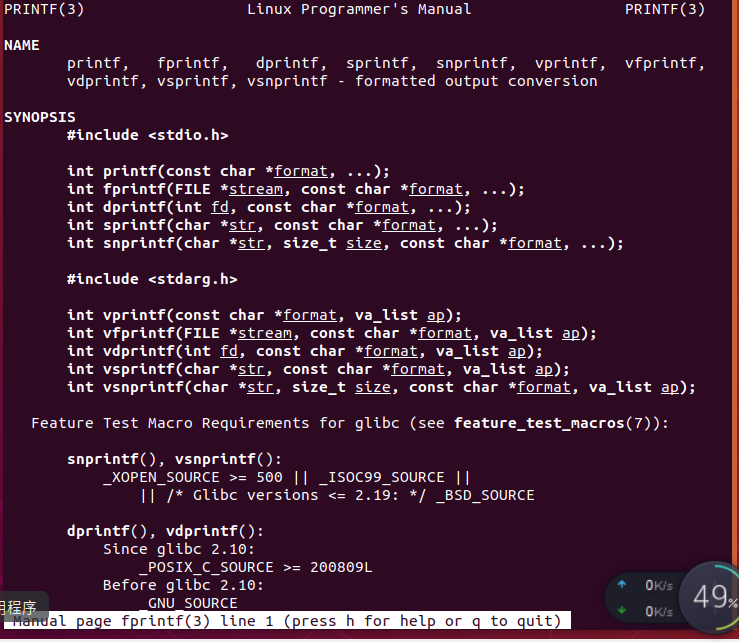
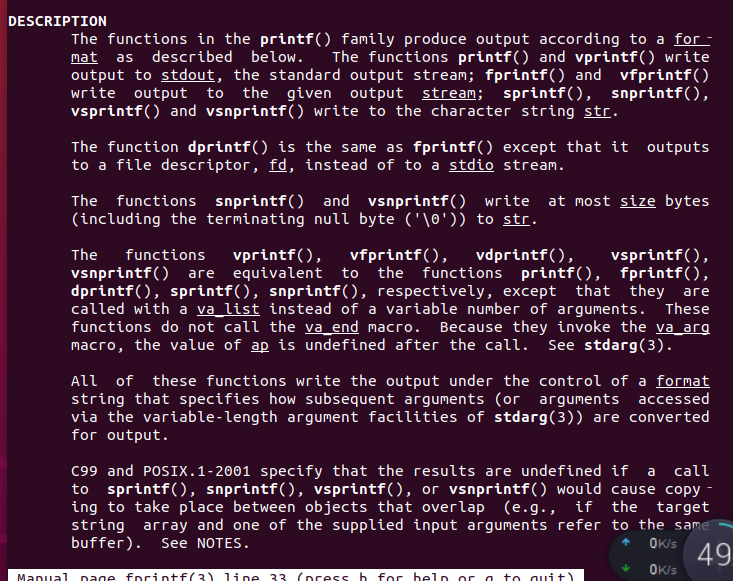
-
readdir:
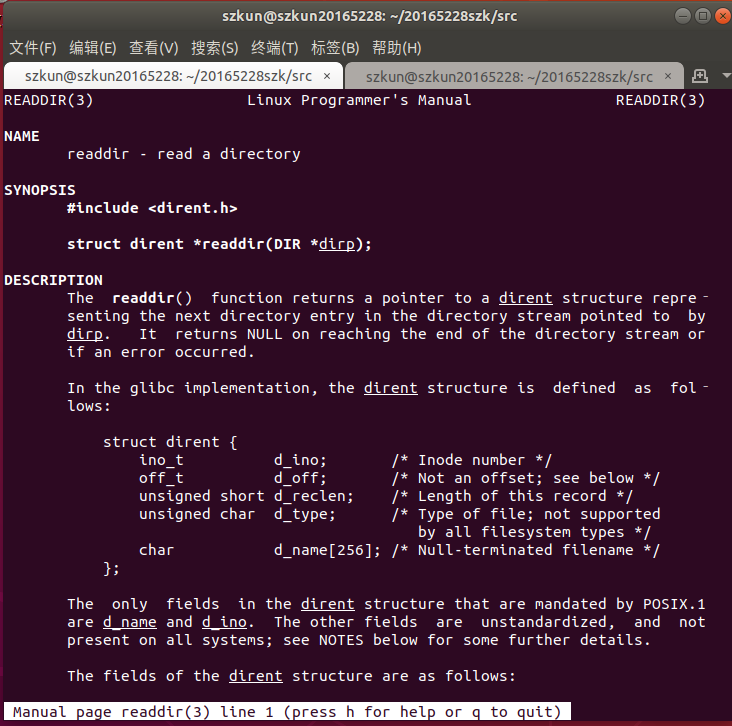
-
strdup:

-
closedir:
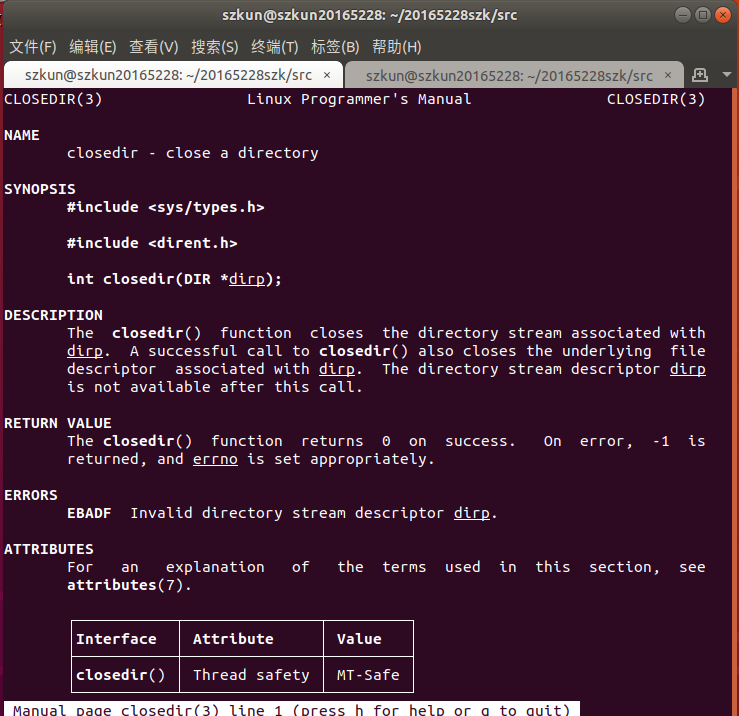
-
stdout:
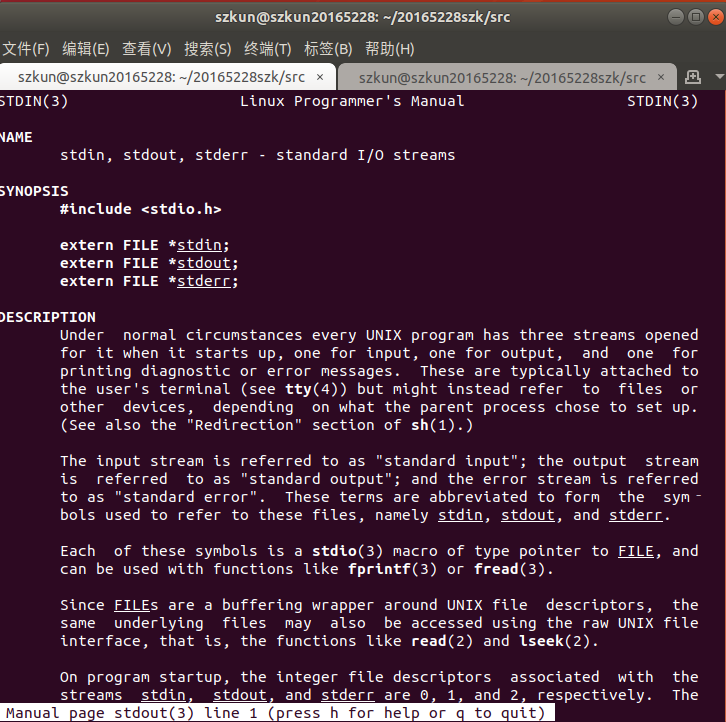
实现pwd
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAX_DIR_DEPTH (256)
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
ino_t get_ino_byname(char *filename)
{
struct stat file_stat;
if(0 != stat(filename, &file_stat))
{
perror("stat");
exit(-1);
}
return file_stat.st_ino;
}
char *find_name_byino(ino_t ino)
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
struct dirent *dptr = NULL;
char *filename = NULL;
if(NULL == (dp = opendir(".")))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can not open Current Directory
");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
while(NULL != (dptr = readdir(dp)))
{
if(dptr->d_ino == ino)
{
filename = strdup(dptr->d_name);
break;
}
}
closedir(dp);
}
return filename;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *dir_stack[MAX_DIR_DEPTH];
unsigned current_depth = 0;
while(TRUE)
{
ino_t current_ino = get_ino_byname(".");
ino_t parent_ino = get_ino_byname("..");
if(current_ino == parent_ino)
break; /*两个inode-number不一样*/
chdir("..");
dir_stack[current_depth++] = find_name_byino(current_ino);
if(current_depth >= MAX_DIR_DEPTH) {
fprintf(stderr, "Directory tree is too deep.
");
exit(-1);
}
}
int i = current_depth - 1;
for(i = current_depth - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
fprintf(stdout, "/%s", dir_stack[i]);
}
fprintf(stdout, "%s
", current_depth == 0 ? "/" : "");
return 0;
}
pwd测试