作业要求来源于:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gzcc/GZCC-16SE2/homework/2696
1.列表,元组,字典,集合分别如何增删改查及遍历。
(1)列表
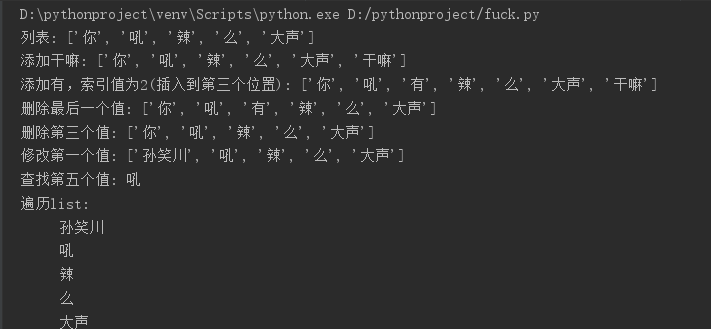
#列表list
list=["你","吼","辣","么","大声"];
print("列表:",list);
list.append("干嘛");
print("添加干嘛:",list);
list.insert(2,"有");
print("添加有,索引值为2(插入到第三个位置):",list)
list.pop();
print("删除最后一个值:",list);
list.pop(2);
print("删除第三个值:",list)
list[0]="孙笑川";
print("修改第一个值:",list);
print("查找第五个值:",list[1]);
#遍历
print("遍历list:");
for l in list:
print(" ",l);
执行效果图如下图所示
(2)元组
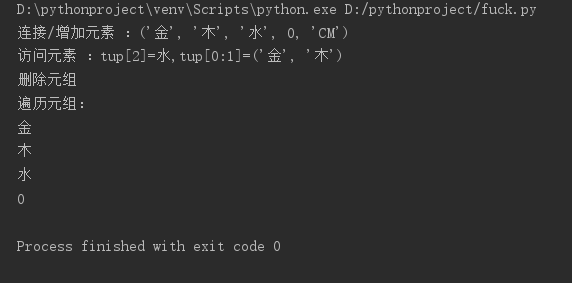
tup=('金','木','水',0) tup2=('CM',) tup3=tup+tup2 print("连接/增加元素 :{}".format(tup3)) #访问元素 tup=('金','木','水',0) print("访问元素 :tup[2]={},tup[0:1]={}".format(tup3[2],tup[0:2])) #删除元素 tup=('金','木','水',0) print("删除元组") del tup #遍历元素 tup=('金','木','水',0) print("遍历元组:") for t in tup: print(t)
执行效果如下图所示:
(3)字典
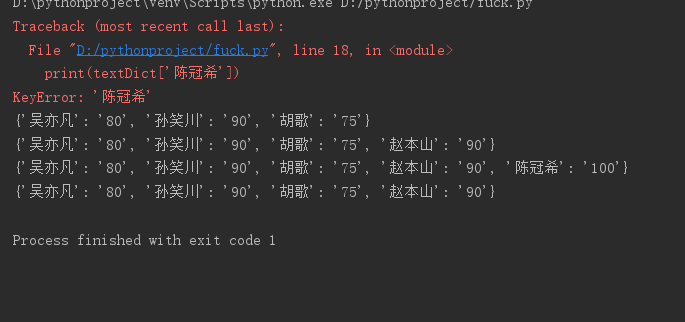
# 创建字典
textDict = {'吴亦凡':'80','孙笑川':'90','胡歌':'75'}
print(textDict)
# 增加
textDict['赵本山']='90'
print(textDict)
# 修改
textDict['陈冠希']='100'
print(textDict)
# 删除
del textDict['陈冠希']
print(textDict)
# 查找
print(textDict['陈冠希'])
# 遍历
for s in textDict:
print( "%s : %s"%(s,textDict[s]))
执行效果如下图所示:
(4)集合
set=set(["金","木","水","火","土"]);
print("集合:",set);
set.add("金");
print("增加‘金’(无法增加,set中午重复值):",set);
set.add("天");
print("增加‘天’:",set);
if "木" in set:
set.remove("木");
print("删除‘木’:",set); set.pop();
print("删除一个值:",set);
#遍历
print("遍历set:")
for s in set: print(" ",s);
执行效果如下图所示:

2.总结列表,元组,字典,集合的联系与区别。参考以下几个方面:
下列以列表,元组,字典,集合为默认顺序:
- 括号 ------ (1)列表:[ ] (2)元组:( ) (3)字典:{ } (4) 集合:( )
- 有序无序------(1)有序 (2)有序 (3)无序 (4)无序
- 可变不可变-----(1)可变 (2)可变 (3)不可变,元组中的元素不可修改、不可删除(4)可变
- 重复不可重复-----(1)可以重复(2)可以重复(3)可以重复(4)不可以重复
- 存储与查找方式------(1)① 找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置,如:list.index(‘a’)② 使用下标索引,如:list[1] (2)使用下标索引,如:tuple[1](3)通过使用相应的键来查找,如:dict[‘a’] (4)通过判断元素是否在集合内,如:1 in dict
3.词频统计
fo = open(r'D:pythonprojectCrimes and Punishments.txt', encoding='utf-8-sig')
theLittlePrinceTxt = fo.read()
txt = theLittlePrinceTxt.lower()
fo.close()
sep = ''' ,./:?/! '
" [] () ~ '''
stops = {'ours', 'over', 'once', 'having', 'against', 'don', 'has', 'but', 'wouldn', 'with', 'other', 'doesn', 'itself', 'aren', 'when',}
for s in sep:
txt = txt.replace(s, " ")
allWord = txt.split()
mset = set(allWord) # 去掉重复的单词,将文本转换为集合
mset = mset - stops # 去除停用词
mdict = {} # 定义字典,作用输出
for m in mset:
mdict[m] = allWord.count(m) # 统计每个字典的key的频数
mlist = list(mdict.items()) # 字典转换成列表
mlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # 列表排序
#输出数目前20的词汇
print(mlist[0:10])
print(mlist[10:20])
# 排序好的单词列表word保存成csv文件
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(data=word).to_csv('Harry Potter.csv',encoding='utf-8')
词云可视化结果如下
