1. 概述
Java NIO (New IO) 由以下三个核心组件组成:
- Channels (通道)
- Buffers (缓冲区)
- Selectors (选择器)
通常,在NIO中,IO从一个Channel开始。数据可以从Channel中读到Buffer,也可以从Buffer中写道Channel。而Selector允许单个线程处理多个Channel。
2. Channel
Channels和Streams很像,但还是有一些不同的:
- 在一个Channels上既可以读又可以写,而Streams只能读或写;
- Channels可以异步读写;
- Channels总是从Buffer中读,或写到Buffer中;
如上所述,数据从通道读取到缓冲区中,从缓冲区写入通道中,如下图所示:
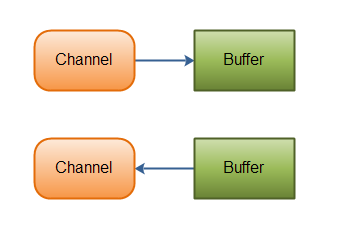
Channel最重要的四种实现:
- FileChannel : 从文件中读数据
- DatagramChannel : 可以通过UDP在网络上读写数据
- SocketChannel : 可以通过TCP在网络上读写数据
- ServerSocketChannel : 监听TCP连接
3. Buffer
在Java NIO中Buffer用来和Channel交互,数据从channel读到buffer中,从buffer写到channel中。
Buffer本质上是一个内存块,可以在其中写入数据,然后在以后再次读取。该内存块包装在NIO Buffer对象中,该对象提供了一组方法,可以更轻松地使用该内存块。
使用Buffer读写数据,典型地分为四步:
- 写数据到Buffer
- 调用buffer.flip()
- 从Buffer中读数据
- 调用 buffer.clear() 或者 buffer.compact()
当你向一个buffer中写数据时,buffer会跟踪你已经写了多少数据了。一旦你需要读取数据,你需要调用flip()方法将buffer从写入模式切换为读取模式。在读取模式下,buffer使你可以读取写入缓冲区的所有数据。
一旦你已经读取了所有数据,你需要清除buffer,以使得它可以再次被写入数据。有两个方法可以达到这个效果:clear()或者compact()。clear()方法会清理整个buffer,compact()方法只清理你已经读过的数据。任何未读的数据都将移至缓冲区的开头,并且将来写入buffer的数据在现在未读的数据之后。
1 RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("data/nio-data.txt", "rw");
2 FileChannel inChannel = aFile.getChannel();
3
4 // create buffer with capacity of 48 bytes
5 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
6
7 int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf); //read into buffer.
8 while (bytesRead != -1) {
9
10 buf.flip(); //make buffer ready for read
11
12 while(buf.hasRemaining()){
13 System.out.print((char) buf.get()); // read 1 byte at a time
14 }
15
16 buf.clear(); //make buffer ready for writing
17 bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf);
18 }
19 aFile.close();
Buffer有三个属性:
- capacity
- position
- limit
position和limit的含义取决于Buffer是处于读模式还是写模式,无论哪种模式下capacity的含义总是不变的。
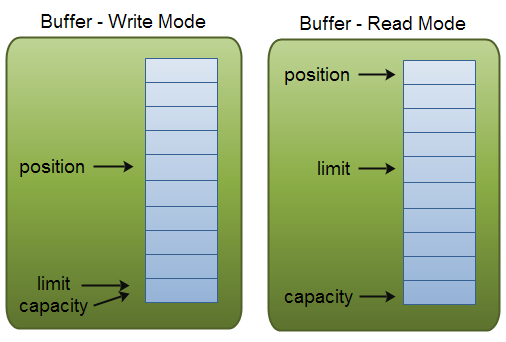
Capacity
作为一个内存块,Buffer有一个固定大小,也被称作“capacity”。一旦Buffer满了,就需要清空它(读取数据或清除数据),然后才能将更多数据写入其中。
Position
当你将数据写入Buffer时,你需要在一个明确的位置写入。初始位置是0,当有数据被写入后,position会向前移动以指向下一个可写入的位置。position的最大值是capacity-1。
当你从Buffer中读取数据时,也需要从一个给定的位置处开始读取。当你将Buffer从写模式切换为读模式时,position会被重置为0。
Limit
在写模式下,limit表示你可以写多少数据到Buffer。在写模式下,limit的值等于capacity。
在读模式下,limit表示你可以从Buffer中读多少数据。因此,当从写模式切换为读模式时,limit被设置为在写模式是的position。换言之,写了多少就能读多少。
3.1. 分配一个缓冲区
为了获得一个Buffer,首先必须先给它分配空间。每种类型的Buffer都有一个allocate()方法来做这件事。
1 // 分配字节缓冲区,容量为48字节
2 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
3 // 分配字符缓冲区,容量为1024个字符
4 CharBuffer buf = CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
3.2. 写数据到Buffer
有两种方式向Buffer中写数据:
- 从Channel中向Buffer写数据
- 从Buffer本身向自己写数据,通过put()方法
1 //read into buffer
2 int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf);
3
4 buf.put(127);
flip()
flip()方法将Buffer从写模式切换为读模式,调用flip()将设置position为0,limit不变还是在刚才的位置。
3.3. 从Buffer中读数据
有两种方式从Buffer中读数据:
- 从Buffer中读数据到Channel
- 从Buffer自身读取,通过get()方法
1 //read from buffer into channel
2 int bytesWritten = inChannel.write(buf);
3
4 byte aByte = buf.get();
rewind()
Buffer.rewind()设置position为0,以至于你可以从头再读一遍Buffer中的所有数据。
clear()
clear()方法将position置为0,并且limit与capacity相等。换句话说,Buffer被清除了。其实,Buffer上的数据并没有被真正清除,只是告诉你你可以将数据写到哪里。
compact()
compact()方法将所有未读的数据复制到Buffer的开头,然后它将position设置在最后一个未读元素的右侧,limit仍然等于capacity。现在,Buffer可以写了,只不过你不能覆盖之前那些未读的数据。
mark() 和 reset()
通过调用Buffer.mark()你可以标记一个给定的位置。你可以在随后调用Buffer.reset()返回到刚才标记的位置那里。

4. Selector
Selector是一个组件,它可以检查一个或多个Channel实例,并决定哪些Channel已经准备好读或写。通过这种方式,一个线程可以管理多个通道,从而实现管理多个网络连接(PS:Selelctor可以确定哪些Channel可读或可写,这样只需要一个线程就能管理多个网络连接)
4.1. 为什么要用Selector
使用单个线程来处理多个通道的优点是,处理通道所需的线程更少。事实上,你可以使用一个线程来处理所有的通道。对于操作系统来说,线程之间的切换非常昂贵,而且每个线程也会占用操作系统中的一些资源(内存)。因此,使用的线程越少越好。(PS:但是请记住,现代操作系统和CPU在多任务处理方面变得越来越好,因此,随着时间的推移,多线程的开销会越来越小。)
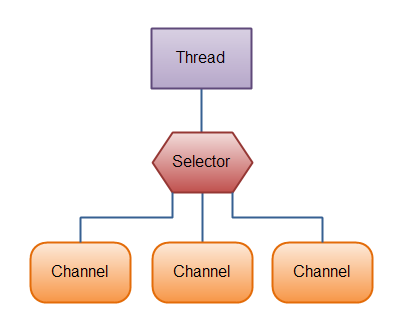
4.2. 创建Selector
1 // 创建一个Selector
2 Selector selector = Selector.open();
3
4 // 注册Channel到Selector
5 channel.configureBlocking(false);
6 SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
Channel必须是非阻塞模式才能和Selector一起使用。这就意味着FileChannel不能和Selector一起用,因为FileChannel不能切换成非阻塞模式。
register()方法的第二个参数表示你希望通过Selector在Channel中监听的事件。有四种不同的事件可以被监听:
- Connect
- Accept
- Read
- Write
这四种事件用SelectionKey的四个常量来表示:
- SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
- SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
- SelectionKey.OP_READ
- SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
如果你对多个事件都感兴趣,可以这样写:
1 int interestSet = SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;
4.3. 通过Selector选择Channel
在调用任意一个select()方法以后,会返回你感兴趣的并且相应事件已经准备好的channel给你。简单地来说就是,如果你对已经为读取做好准备的channel感兴趣,那么你将从select()方法中接收到这样的channel。
- select() : 阻塞,直到至少有一个你注册的事件准备好的channel
- select(long timeout) : 跟select()很像,多了一个超时时间
- selectNow() : 不阻塞,无论有没有已经准备好的channel都立刻返回
select()方法的返回值是一个int值,表示有多少个准备好的channel。也就是说,在上一次调用select()以后有多少个channel变成已准备好。
完整的示例:
1 Selector selector = Selector.open();
2
3 channel.configureBlocking(false);
4
5 SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
6
7 while (true) {
8
9 int readyChannels = selector.selectNow();
10
11 if (readyChannels == 0) continue;
12
13
14 Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
15
16 Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
17
18 while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
19
20 SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
21
22 if (key.isAcceptable()) {
23 // a connection was accepted by a ServerSocketChannel.
24
25 } else if (key.isConnectable()) {
26 // a connection was established with a remote server.
27
28 } else if (key.isReadable()) {
29 // a channel is ready for reading
30
31 } else if (key.isWritable()) {
32 // a channel is ready for writing
33 }
34
35 keyIterator.remove();
36 }
37 }
5. SocketChannel
Java NIO SocketChannel是连接到TCP网络Socket的通道。
创建SocketChannel有两种方式:
- 打开一个SocketChannel并连接到服务器上
- 当一个输入连接到达ServerSocketChannel时,也会创建一个SocketChannel
1 // Opening a SocketChannel
2 SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
3 socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9000));
4
5 // Closing a SocketChannel
6 socketChannel.close();
5.1. 从SocketChannel中读取
1 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
2 int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buf);
SocketChannel.read()方法将数据从SocketChannel读到Buffer中,其返回值表示有多少字节被写道Buffer中。如果返回-1,则表示到达流的末尾。
5.2. 写数据到SocketChannel
1 String newData = "hahaha";
2
3 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
4 buf.clear();
5 buf.put(newData.getBytes());
6
7 buf.flip();
8
9 while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
10 channel.write(buf);
11 }
注意,SocketChannel.write()是放在while循环体中的。由于无法保证write()方法将多少字节写入SocketChannel,因此,要重复调用write()方法,直到缓冲区没有字节可写为止。
5.3. 非阻塞模式
当一个SocketChannel被设置为非阻塞模式时,你就可以异步地调用connect(), read(), write()方法了。
connect()
如果SocketChannel是非阻塞模式,那么当你调用connect()方法时,该方法可能在建立连接之前返回。为了确定连接是否已经成功建立,可以调用finishConnect()方法。
1 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
2 socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9000));
3
4 while(! socketChannel.finishConnect() ){
5 //wait, or do something else...
6 }
write() 和 read()
在非阻塞模式下,write()方法可能会在未写入任何内容的情况下返回,因此需要在循环中调用write()。同样的,在非阻塞模式下,read()方法可能在没有读取任何数据的情况下就返回了,因此,需要注意返回的int,它告诉我们读取了多少字节。
6. ServerSocketChannel
Java NIO ServerSocketChannel是一个可以监听输入TCP连接的通道,就像标准Java网络中的ServerSocket一样。
1 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
2
3 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
4
5 while(true){
6 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
7 //do something with socketChannel...
8 }
6.1. Listening for Incoming Connections
通过调用ServerSocketChannel.accept()方法可以监听输入的连接。当accept()方法有返回的时候,它返回一个带有输入连接的SocketChannel。因此,accept()会阻塞直到有输入连接到来为止。通常的做法是这样的:
1 while(true){
2 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
3 //do something with socketChannel...
4 }
6.2. 非阻塞模式
ServerSocketChannel可以设置为非阻塞模式。在非阻塞模式下,调用accept()方法会立即返回,因此如果没有输入连接到达,它返回的可能是null。因此,必须检查返回的SocketChannel是否为null,下面是一个例子:
1 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
2
3 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
4 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
5
6 while(true){
7 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
8
9 if(socketChannel != null){
10 //do something with socketChannel...
11 }
12 }
7. Java NIO vs. IO
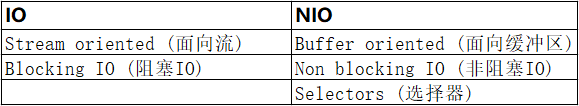
7.1. Stream Oriented vs. Buffer Oriented
Java NIO和IO之间的第一个大区别是IO是面向流的,而NIO是面向缓冲区的。 那是什么意思呢?
面向流的Java IO意味着你一次从流中读取一个或多个字节。如何处理读取的字节由你自己决定。它们不会被缓存到任何地方。此外,你不能在流中的数据中来回移动。如果需要来回移动从流中读取的数据,需要首先将其缓存到缓冲区中。
Java NIO的面向缓冲区的方法略有不同。数据被读入缓冲区,以后再从缓冲区中进行处理。你可以根据需要在缓冲区中来回移动。这使得在处理过程中更具灵活性。但是,你还需要检查缓冲区是否包含你需要的所有数据,以便对其进行完全处理。并且,你需要确保在将更多数据读入缓冲区时,不会覆盖缓冲区中尚未处理的数据。
7.2. Blocking vs. Non-blocking IO
Java IO的各种流被阻塞。这意味着,当线程调用read()或write()时,该线程将被阻塞,直到有一些数据需要读取,或者数据被完全写入。 在此期间,线程无法执行其他任何操作。
Java NIO的非阻塞模式允许线程请求从通道读取数据,并且只获取当前可用的数据,如果当前没有可用的数据,则什么也得不到。在数据可以读取之前,线程不会一直处于阻塞状态,而是可以继续执行其他操作。
非阻塞写入也是如此。线程可以请求将某些数据写入通道,但不等待将其完全写入。然后线程可以继续运行,同时执行其他操作。
当线程在IO调用中没有被阻塞时,它们的空闲时间通常在其他通道上执行IO。也就是说,单个线程现在可以管理输入和输出的多个通道。
7.3. Selectors
Java NIO的Selector允许单个线程监视多个输入通道。可以使用Selector注册多个通道,然后使用一个线程“select”具有可用于处理输入的通道,或者选择准备好进行写入的通道。这种选择器机制使单个线程可以轻松管理多个通道。
7.4. 不同的数据读取方式
Java IO: Reading data from a blocking stream
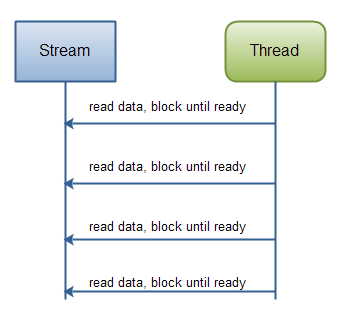
Java NIO: Reading data from a channel until all needed data is in buffer

8. 示例
ChatServer.java
1 package com.cjs;
2
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
5 import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
6 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
7 import java.nio.channels.Selector;
8 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
9 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
10 import java.nio.charset.Charset;
11 import java.util.Iterator;
12 import java.util.Set;
13
14 public class ChatServer {
15
16 private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
17 private Selector selector;
18
19 private ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
20 private ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
21
22 private static final Charset CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
23
24 public ChatServer(int port) {
25 try {
26 serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
27 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
28 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
29
30 selector = Selector.open();
31 serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
32
33 } catch (IOException e) {
34 e.printStackTrace();
35 }
36 }
37
38 /**
39 * 监听客户端连接
40 */
41 public void listen() throws IOException {
42 System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
43 while(true) {
44
45 int readyChannels = selector.selectNow();
46
47 if(readyChannels == 0) {
48 continue;
49 }
50
51 Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
52
53 Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
54
55 while(keyIterator.hasNext()) {
56
57 SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
58
59 if(key.isAcceptable()) {
60 // a connection was accepted by a ServerSocketChannel.
61 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
62 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
63 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
64 socketChannel.write(CHARSET.encode("来自服务器的问候: 你好!"));
65 } else if (key.isConnectable()) {
66 // a connection was established with a remote server.
67 } else if (key.isReadable()) {
68 // a channel is ready for reading
69 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
70 String msg = "";
71 while (socketChannel.read(readBuffer) > 0) {
72 readBuffer.flip();
73 msg += CHARSET.decode(readBuffer).toString();
74 }
75 System.out.println(msg);
76 readBuffer.clear();
77
78 // 给客户端回复消息
79 writeBuffer.put("服务器对你说: 收到".getBytes());
80 writeBuffer.flip();
81 socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
82 writeBuffer.clear();
83
84 } else if (key.isWritable()) {
85 // a channel is ready for writing
86 }
87
88 keyIterator.remove();
89 }
90 }
91 }
92
93 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
94 ChatServer chatServer = new ChatServer(9000);
95 chatServer.listen();
96 }
97 }
ChatClient.java
1 package com.cjs;
2
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
5 import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
6 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
7 import java.nio.channels.Selector;
8 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
9 import java.nio.charset.Charset;
10 import java.util.Iterator;
11 import java.util.Scanner;
12
13 public class ChatClient {
14
15 private SocketChannel socketChannel;
16 private Selector selector;
17
18 private ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
19
20 private static final Charset CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
21
22 public ChatClient(String host, int port) {
23 try {
24 socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
25 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
26 socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));
27
28 while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
29 System.out.println("正在等待连接");
30 }
31
32 System.out.println("连接成功");
33
34 selector = Selector.open();
35 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
36
37 new Thread(new Handler(selector)).start();
38
39 } catch (IOException e) {
40 e.printStackTrace();
41 }
42 }
43
44 /**
45 * 给服务器发消息
46 */
47 public void start() throws IOException {
48 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
49 while (scanner.hasNext()) {
50 String line = scanner.nextLine();
51 if (null != line && !"".equals(line.trim())) {
52 socketChannel.write(CHARSET.encode(line));
53 }
54 }
55 }
56
57 /**
58 * 接收来自服务器的消息
59 */
60 class Handler implements Runnable {
61
62 private Selector selector;
63
64 public Handler(Selector selector) {
65 this.selector = selector;
66 }
67
68 @Override
69 public void run() {
70 try {
71 while (true) {
72
73 int readyChannels = selector.selectNow();
74
75 if (readyChannels == 0) continue;
76
77 Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
78
79 while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
80
81 SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
82
83 if (key.isReadable()) {
84 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
85 String msg = "";
86 while (socketChannel.read(readBuffer) > 0) {
87 // 从写模式切换为读模式
88 readBuffer.flip();
89 msg += CHARSET.decode(readBuffer);
90 }
91 System.out.println(msg);
92 readBuffer.clear();
93 }
94
95 keyIterator.remove();
96 }
97 }
98 } catch (IOException e) {
99 e.printStackTrace();
100 }
101 }
102 }
103
104 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
105 ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient("127.0.0.1", 9000);
106 chatClient.start();
107 }
108 }
控制台
9. 参考