1,概述
linux设备驱动分为三种:字符驱动设备、块驱动设备、网络设备
架构:
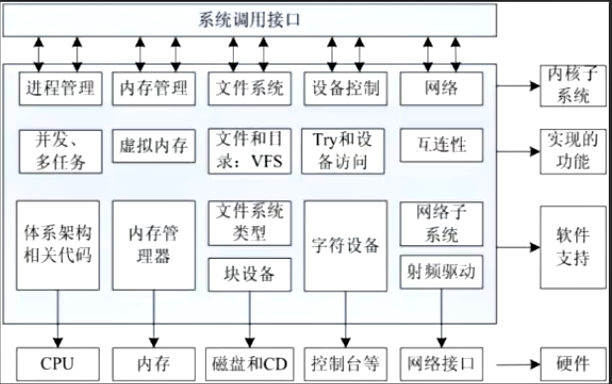
1,字符设备驱动
是指只能一个字节一个字节读写的设备,不能随机读取设备内存中的某一数据,读取数据需要按照先后数据。字符设备是面向流的设备,常见的字符设备有鼠标、键盘、串口、控制台和LED设备等。
2.块设备驱动
是指可以从设备的任意位置读取一定长度数据的设备。块设备包括硬盘、磁盘、U盘和SD卡等。
3网络设备驱动
网卡驱动,CAN驱动等
2,驱动的静态加载和动态加载
区别:
1,编译选择不一样。选择 * 就是编入内核镜像 ,选择 M 是单独编为一个驱动模块,独立存在于文件系统上;
2,静态加载,在内核中加载时间靠前;动态加载,在文件系统中为 .ko的文件,需要等到系统跑起来之后,手动用insmod 命令加载,时间相对靠后 。
动态加载的优势:
1,支持热插拔
2,有利于驱动调试
3,开机优化。界面启动快
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
字符设备驱动:

1,概念
(1)设备号
内核中通过类型 dev_t 来描述设备号,其实质是 unsigned int 32位整数,其中高12位为主设备号(用来区分不同类别的设备),低20位为次设备号(用来区分同一类别的不同设备)
注册函数:
1. 静态申请:
int register_chrdev_region (dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
/** * register_chrdev_region() - register a range of device numbers * @from: the first in the desired range of device numbers; must include * the major number. * @count: the number of consecutive device numbers required * @name: the name of the device or driver. * * Return value is zero on success, a negative error code on failure. */
2.动态分配:
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name);
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name); /** * alloc_chrdev_region() - register a range of char device numbers * @dev: output parameter for first assigned number * @baseminor: first of the requested range of minor numbers * @count: the number of minor numbers required * @name: the name of the associated device or driver * * Allocates a range of char device numbers. The major number will be * chosen dynamically, and returned (along with the first minor number) * in @dev. Returns zero or a negative error code. */
3.注销设备号:
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count);
获取设备号 :
#define MINORBITS 20 #define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1) #define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS)) #define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK)) #define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
(2)设备信息的描述
struct cdev { struct kebject kobj; //由内核中设备管理模型来操作 struct module *owner; //为了加载驱动实现的,都会给它赋值 const struct file_operations *ops; //函数集 struct list_head list; //链表 dev_t dev; //设备号 unsignde int count; //支持的设备 };
(3)设备行为的描述
/include/linux/fs.h struct file_openrations { struct module *owner; ………… ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *); ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *); ………… }
从下一节开始,我们手动编写一个字符驱动。