Redis是一个事件驱动内存数据库,服务器需要处理一下两类事件:
- 文件事件:Redis服务器通过套接字和客户端进行连接,而文件事件就是服务器对套接字操作的抽象。服务器与客户端的通信会产生相应的文件事件,而服务器则通过监听并处理这些事件来完成一系列网络通信操作。
- 时间事件:Redis服务器中的一些操作需要在给定的时间点执行,而时间事件就是服务器对这类定时操作的抽象。
- 文件事件
Redis基于reactor模式开发了自己的网络事件处理器,称为文件事件处理器。。
- 文件事件处理器使用I/O多路复用程序同时监听多个套接字,并根据套接字目前执行的任务来为套接字关联不同的事件处理器。
- 当被监听的套接字准备好执行链接应答(accept)、读取(read)、写入(write)、关闭(close)等操作时,与操作相应的文件事件就会产生,这时文件事件处理器就会调用套接字之前关联好的事件处理器来处理这些事件。
虽然文件事件处理器以单线程运行,但是通过使用I/O多路复用程序来监听多个套接字,文件事件处理器及实现了高性能的网络通信模型,又可以很好的和Redis服务器中其他同样以单线程运行的模块进行对接,这保持了Redis内部单线程设计的简单性。
文件事件处理器由四个部分组成,分别是套接字、I/O多路复用、文件事件分派器、事件处理器。结构如下
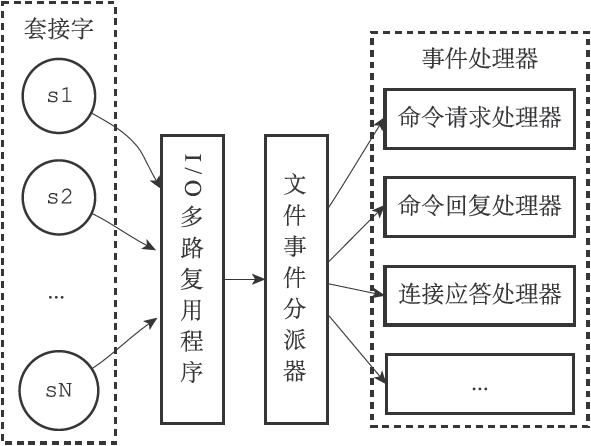
- 套接字:每当一个套接字准备好执行应答、写入、读取、关闭等操作时,就会产生一个文件事件。因为一个服务器通常会链接多个套接字,所以多个文件事件有可能会并发出现。
- I/O多路复用:负责监听多个套接字,并将产生事件的套接字都放到队列中,然后通过队列,以有序、同步、每次一个套接字的方式,向文件事件分派器传送产生了事件的套接字。
- 文件事件分派器:接收I/O多路复用程序传来的套接字,并根据套接字产生的事件的类型,调用相应的事件处理器。
- 事件处理器:服务器会为不同的套接字关联不同的事件处理器,某个事件发生时,服务器就执行该动作。
-
- 关于I/O多路复用
Redis使用的IO多路复用技术主要有:select、epoll、evport和kqueue等。每个IO多路复用函数库在Redis源码中都对应一个单独的文件,比如ae_select.c,ae_epoll.c, ae_kqueue.c等。程序会在编译时选择系统中性能最高的作为I/O多路复用程序的底层实现。
#ifdef HAVE_EVPORT #include "ae_evport.c" #else #ifdef HAVE_EPOLL #include "ae_epoll.c" #else #ifdef HAVE_KQUEUE #include "ae_kqueue.c" #else #include "ae_select.c" #endif #endif #endif
文件事件结构
/* File event structure */ //文件事件 typedef struct aeFileEvent { //文件时间类型 int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */ //可读处理函数 aeFileProc *rfileProc; //可写处理函数 aeFileProc *wfileProc; //客户端传入的数据 void *clientData; } aeFileEvent;
- 时间事件
- 定时事件:让程序在指定的事件之后执行一次。
- 周期性事件:让一段程序每隔指定时间就执行一次。
一个时间事件是定时时间还是周期性事件取决于时间事件处理器的返回值:
- 如果事件处理器返回AE_NOMORE,那么这个事件为定时事件:该事件在到达一次后会被删除。
- 如果返回一个非AE_NOMORE,那么这个事件为周期性事件,当一个时间事件到达后,服务器会根据事件处理器的返回值,对时间事件的when进行更新,让这个事件在一段时间后再次到达。
时间事件结构
//时间事件结构 typedef struct aeTimeEvent { //时间事件的id long long id; /* time event identifier. */ //时间事件到达的时间的秒数 long when_sec; /* seconds */ //时间事件到达的时间的毫秒数 long when_ms; /* milliseconds */ //时间事件处理函数 aeTimeProc *timeProc; //时间事件终结函数 aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc; //客户端传入的数据 void *clientData; //指向下一个时间事件 struct aeTimeEvent *next; } aeTimeEvent;
- 事件的调度与执行
事件状态结构
/* A fired event */ //就绪事件 typedef struct aeFiredEvent { //就绪事件的文件描述符 int fd; //就绪事件类型 int mask; } aeFiredEvent; /* State of an event based program */ //事件状态结构 typedef struct aeEventLoop { //当前已注册的最大的文件描述符 int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered */ //文件描述符监听集合的大小 int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked */ //下一个时间事件的ID long long timeEventNextId; //最后一次执行事件的时间 time_t lastTime; /* Used to detect system clock skew */ //注册的文件时间表 aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */ //已就绪的文件事件表 aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */ //时间事件的头结点指针 aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead; //事件处理开关 int stop; //多路复用库的事件状态数据 void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data */ //执行处理事件之前的函数 aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep; } aeEventLoop;
-
- epoll的底层实现
//在epfd标识的事件表上注册fd事件 static int aeApiAddEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; //apidata 多路复用库额时事件状态数据 struct epoll_event ee; /* If the fd was already monitored for some event, we need a MOD * operation. Otherwise we need an ADD operation. */ int op = eventLoop->events[fd].mask == AE_NONE ? EPOLL_CTL_ADD : EPOLL_CTL_MOD; //EPOLL_CTL_ADD 向epfd注册fd上的event //EPOLL_CTL_MOD 修改fd已注册的event //AE_NONE 0 未设置 //AE_READABLE 事件可读 //AE_WRITEABLE 事件可写 ee.events = 0; mask |= eventLoop->events[fd].mask; /* Merge old events */ if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN; if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT; ee.data.u64 = 0; /* avoid valgrind warning */ ee.data.fd = fd; if (epoll_ctl(state->epfd,op,fd,&ee) == -1) return -1; return 0; } //等待所监听文件描述符上有事件发生 static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; int retval, numevents = 0; retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,eventLoop->setsize, tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec*1000 + tvp->tv_usec/1000) : -1); //通过epoll_wait 返回有事件发生的套接字链表 if (retval > 0) { int j; numevents = retval; //遍历事件表 for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { int mask = 0; struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j; if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLERR) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; //将有事件发生的套接字加入到就绪事件表中 eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd; eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask; } } return numevents; }
-
- 事件调度
事件循环监控由aeMain实现
//事件轮训的主函数 void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 0; //一直处理 while (!eventLoop->stop) { //执行处理事件之前的函数 if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL) eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); //处理到时的时间事件和文件事件 aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS); } }
aeMain中调用aeProcessEvents监控所有事件的触发。
/* Process every pending time event, then every pending file event * (that may be registered by time event callbacks just processed). * Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event * fires, or when the next time event occurs (if any). * * If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns. * if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed. * if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed. * if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed. * if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set the function returns ASAP until all * the events that's possible to process without to wait are processed. * * The function returns the number of events processed. */ //根据flag不同 处理不同的时间 //flag AE_ALL_EVENTS 表示处理所有的文件事件和时间事件 //AE_FILE_EVENTS 表示处理所有的文件事件 //AE_TIME_EVENTS 表示处理所有的时间事件 //AE_DONT_WAIT 表示调用多路复用时,不会阻塞等待事件的触发,将所有已触发的时间处理完成后立即返回 int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags) { int processed = 0, numevents; /* Nothing to do? return ASAP */ if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0; /* Note that we want call select() even if there are no * file events to process as long as we want to process time * events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready * to fire. */ //如果已经注册过文件事件 或者需要处理时间事件且不是AE_DONT_WAIT 则需要调用底层的aeApiPoll //等待所监听文件描述符上有时间发生 函数底层调用epoll_wait //标识当前 if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 || ((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) { int j; aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL; struct timeval tv, *tvp; //如果设置了时间事件 但不是AE_DONT_WAIT 需要阻塞 if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT)) //获取最近到时的时间事件 shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop); if (shortest) { long now_sec, now_ms; /* Calculate the time missing for the nearest * timer to fire. */ //获取当前时间 aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms); tvp = &tv; tvp->tv_sec = shortest->when_sec - now_sec; if (shortest->when_ms < now_ms) { tvp->tv_usec = ((shortest->when_ms+1000) - now_ms)*1000; tvp->tv_sec --; } else { tvp->tv_usec = (shortest->when_ms - now_ms)*1000; } if (tvp->tv_sec < 0) tvp->tv_sec = 0; if (tvp->tv_usec < 0) tvp->tv_usec = 0; } else { //没有获取到最早到时的时间事件,时间事件列表为空 /* If we have to check for events but need to return * ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout * to zero */ //如果设置了不阻塞 if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) { tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0; tvp = &tv; } else { /* Otherwise we can block */ tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */ //tvp = NULL epoll_wait的等待时间是-1 表示一直等待下去 } } //eventLoop->fired 存储就绪的事件表 //等待监听文件描述符上有事件发生 //如果tvp为null 则阻塞 否则tvp设置阻塞时间 就会有时间事件到时 //返回来就绪文件事件的个数 numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp); for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd]; int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask; int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd; int rfired = 0; /* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed * event removed an element that fired and we still didn't * processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */ //如果文件是可读事件 设置可读事件标识 调用读事件方法处理读事件 if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) { rfired = 1; fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); } //如果文件时可写事件 设置可写事件标识 调用可写事件处理写事件 if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) { if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); } processed++; //执行的事件次数+1 } } /* Check time events */ //执行时间事件 if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop); return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */ }
对于文件事件和时间事件的处理都是同步、有序、院子地执行的,服务器不会中途中断事件处理,也不会对事件进行抢占,因此,不管是文件事件的处理器,还是时间事件的处理器,它们都会尽可能的减少程序的阻塞事件,并在有需要时主动让出执行权,从而降低造成事件饥饿的可能性。比如,在命令回复回调函数中,将一个命令回复写入到客户端套接字时,如果写人字节数超过了一个预设常量的话,命令回复函数就会主动用break跳出写人循环,将余下的数据留到下次再写。另外,时间事件也会将非常耗时的持久化操作放到子线程或者子进程执行。并且时间事件是在文件事件之后执行,并且事件之间不会出现抢占,所以时间事件的实际处理时间,通常会比时间事件设置的到达时间稍微晚一些。
-
- 执行时间事件
/* Process time events */ //执行时间事件 // static int processTimeEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { int processed = 0; aeTimeEvent *te; long long maxId; time_t now = time(NULL); /* If the system clock is moved to the future, and then set back to the * right value, time events may be delayed in a random way. Often this * means that scheduled operations will not be performed soon enough. * * Here we try to detect system clock skews, and force all the time * events to be processed ASAP when this happens: the idea is that * processing events earlier is less dangerous than delaying them * indefinitely, and practice suggests it is. */ //如果系统时间被调整到过去 将所有时间的触发事件的秒数清0 提前处理比延后处理危险性低 if (now < eventLoop->lastTime) { te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; while(te) { te->when_sec = 0; te = te->next; } } //设置上一次时间事件处理的时间为当前时间 eventLoop->lastTime = now; te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; //时间事件头结点指针 maxId = eventLoop->timeEventNextId-1; //当前时间事件表中的最大ID 下一个时间的id //遍历时间事件列表 while(te) { long now_sec, now_ms; long long id; //表示该事件在之前已经触发的时间事件的回调函数中注册的 //因为时间事件总是插入到链表的表头,所以时间事件分别按照id的逆序排列 if (te->id > maxId) { te = te->next; continue; } aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms); //判断当前时间是否已经超过来触发时间 if (now_sec > te->when_sec || (now_sec == te->when_sec && now_ms >= te->when_ms)) { int retval; id = te->id; //调用触发回调函数 retval = te->timeProc(eventLoop, id, te->clientData); processed++; /* After an event is processed our time event list may * no longer be the same, so we restart from head. * Still we make sure to don't process events registered * by event handlers itself in order to don't loop forever. * To do so we saved the max ID we want to handle. * * FUTURE OPTIMIZATIONS: * Note that this is NOT great algorithmically. Redis uses * a single time event so it's not a problem but the right * way to do this is to add the new elements on head, and * to flag deleted elements in a special way for later * deletion (putting references to the nodes to delete into * another linked list). */ //如果时间事件时AE_NOMORE说明触发的时间事件时一次性事件 //直接从链表中删除 //否则为周期性事件 则将其触发时间改为当前时间+retval if (retval != AE_NOMORE) { aeAddMillisecondsToNow(retval,&te->when_sec,&te->when_ms); } else { aeDeleteTimeEvent(eventLoop, id); } te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; } else { te = te->next; } } return processed; }