前言
译文链接:http://websystique.com/spring/spring-profile-example/
本文将探索Spring中的@Profile注解,可以实现不同环境(开发、测试、部署等)使用不同的配置。同样,除了使用注解也会给出基于XML配置的示例作为对比。
假设你有一个应用涉及数据库交互,你可能希望在开发环境上使用mysql数据库,在生产环境上使用oracle数据库,那么使用Spring的Profiles,可以轻松达到这个目的,接下来我们将给出一个实例详细介绍这种情况。
涉及技术及开发工具
- Spring 4.0.6.RELEASE
- Maven 3
- JDK 1.6
- Eclipse JUNO Service Release 2
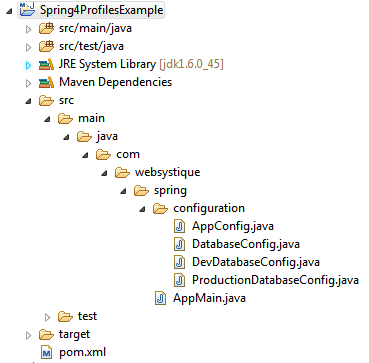
工程目录结构
步骤一:往pom.xml中添加依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.websystique.spring</groupId> <artifactId>Spring4ProfilesExample</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>Spring4ProfilesExample</name> <properties> <springframework.version>4.0.6.RELEASE</springframework.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <pluginManagement> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2</version> <configuration> <source>1.6</source> <target>1.6</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> </build> </project>
步骤二:创建Spring配置类
Spring配置类是指用@Configuration注解标注的类,这些类包含了用@Bean标注的方法。这些被@Bean标注的方法可以生成bean并交由spring容器管理。
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.websystique.spring") public class AppConfig { @Autowired public DataSource dataSource; }
以上配置只有一个属性被自动注入,接下来我们将展示这个dataSource属性可以根据不同的环境(开发环境或生产环境)注入不同的bean。
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import javax.sql.DataSource; public interface DatabaseConfig { DataSource createDataSource(); }
一个简单的接口,可以被所有可能的环境配置实现
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; @Profile("Development") @Configuration public class DevDatabaseConfig implements DatabaseConfig { @Override @Bean public DataSource createDataSource() { System.out.println("Creating DEV database"); DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); /* * Set MySQL specific properties for Development Environment */ return dataSource; } }
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; @Profile("Production") @Configuration public class ProductionDatabaseConfig implements DatabaseConfig { @Override @Bean public DataSource createDataSource() { System.out.println("Creating Production database"); DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); /* * Set ORACLE specific properties for Production environment */ return dataSource; } }
以上两个配置类都实现了DatabaseConfig接口,特殊的地方在于它们都用@Profile标注。
被@Profile标注的组件只有当指定profile值匹配时才生效。
可以通过以下方式设置profile值:
1、设置spring.profiles.active属性(通过JVM参数、环境变量或者web.xml中的Servlet context参数)
2、ApplicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles(“ProfileName”)
根据你的实际环境设置profile值,然后被profile标注(而且value=设置值)的bean才会被注册到spring容器。
步骤三:运行main方法测试
package com.websystique.spring; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class AppMain { public static void main(String args[]){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); //Sets the active profiles context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("Development"); //Scans the mentioned package[s] and register all the @Component available to Spring context.scan("com.websystique.spring"); context.refresh(); context.close(); } }
注意以上代码,context.scan("com.websystique.spring")扫描到该包并开始注册所有被@Component标注的bean时,如果同时遇到被@Profile注解标注的bean时,会与profile值做比较,profile值匹配则注册到spring容器,否则直接跳过。
在我们这个例子中,DevDatabaseConfig会被注册到Spring容器中。
运行以上程序,结果如下:
Creating DEV database
附:基于XML的配置
替换DevelopmentDatabaseConfig配置为dev-config-context.xml (src/main/resources/dev-config-context.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/websystique" /> <property name="username" value="myuser" /> <property name="password" value="mypassword" /> </bean> </beans>
替换ProductionDatabaseConfig配置为prod-config-context.xml (src/main/resources/prod-config-context.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value=" oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@PRODHOST:PRODPORT/websystique" /> <property name="username" value="myproduser" /> <property name="password" value="myprodpassword" /> </bean> </beans>
替换AppConfig配置为app-config.xml (src/main/resources/app-config.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.websystique.spring"/> <beans profile="Development"> <import resource="dev-config-context.xml"/> </beans> <beans profile="Production"> <import resource="prod-config-context.xml"/> </beans> </beans>
根据实际的profile配置,相应的config-context.xml文件会被加载,其它的会被忽略。
最后,main方法如下:
package com.websystique.spring; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AppMain { public static void main(String args[]){ AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app-config.xml"); //Sets the active profiles context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("Development"); /* * Perform any logic here */ context.close(); } }
运行程序,会得到相同的结果。
程序源码
http://websystique.com/?smd_process_download=1&download_id=799