前言
译文链接:http://websystique.com/spring/spring-4-hello-world-example-annotation-tutorial-full-example/
这个教程将展示一个基于Spring注解配置的Spring 4 Hello world例子,解释Spring 4的基本概念和使用方法。
同样也会提供基于XML配置的示例作为两者的一个比较,我们将创建一个基于maven工程,使用spring版本为4.0.6。
涉及的相关技术及开发工具
- Spring 4.0.6.RELEASE
- Maven 3
- JDK 1.6
- Eclipse JUNO Service Release 2
工程结构目录
如下是本工程的最终结构目录:
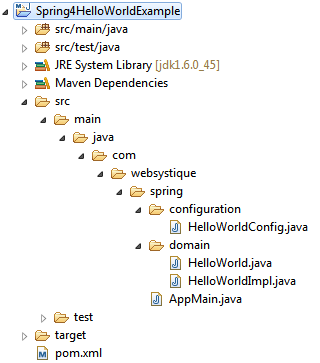
如果想要了解如何创建一个maven工程,请参考以下链接:Maven tutorial。里面包含了详细的步骤来说明如何创建maven工程。
那么,接下来,就让我们在以上目录结构上添加具体内容吧。
步骤一:在maven的pom.xml里添加spring依赖
我们可以通过pom.xml给maven工程添加所有依赖,如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.websystique.spring</groupId> <artifactId>Spring4HelloWorldExample</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>Spring4HelloWorldExample</name> <properties> <springframework.version>4.0.6.RELEASE</springframework.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <pluginManagement> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2</version> <configuration> <source>1.6</source> <target>1.6</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> </build> </project>
对于这个示例,我们只需要添加Spring core 和 Spring context依赖,其中spring注解是在spring-context里定义的。
步骤二:创建POJO类
Spring提倡低耦合和基于接口编程。
所以,我们首先创建一个POJO接口和它的实现类,这个POJO将作为一个spring bean。
package com.websystique.spring.domain; public interface HelloWorld { void sayHello(String name); }
package com.websystique.spring.domain; public class HelloWorldImpl implements HelloWorld{ public void sayHello(String name) { System.out.println("Hello "+name); } }
步骤三:创建Spring配置文件
Spring配置类包含工程中要用到的一些bean的定义。@Configuration注解声明这个类是一个Spring配置类,该类可以包含@Bean注解的方法,该方法创建bean交给spring容器管理。
package com.websystique.spring.configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Description; @Configuration public class HelloWorldConfig { @Bean(name="helloWorldBean") @Description("This is a sample HelloWorld Bean") public HelloWorld helloWorld() { return new HelloWorldImpl(); } }
@Description是Spring 4引入的新注解,用于描述bean的定义
以上基于注解的配置与如下的Spring XML配置达到的效果一样(我们把这个文件命名为helloworld-config.xml)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="helloWorldBean" class="com.websystique.spring.domain.HelloWorldImpl"> </beans>
步骤四:创建main方法执行该程序
package com.websystique.spring; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import com.websystique.spring.configuration.HelloWorldConfig; import com.websystique.spring.domain.HelloWorld; public class AppMain { public static void main(String args[]) { AbstractApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(HelloWorldConfig.class); HelloWorld bean = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorldBean"); bean.sayHello("Spring 4"); context.close(); } }
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext以我们的配置类(用@Configuration标注)作为入参创建spring应用上下文环境,在程序运行时注册所有在配置类中定义的bean。一旦我们创建了AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象,就可以通过其bean对象的方法执行一些操作。getBean方法从spring容器中得到指定的bean对象,并且可以调用该
HelloWorld bean = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorldBean");
bean.sayHello("Spring 4");
运行以上程序,会得到如下结果:
Hello Spring 4
如果使用基于XML的配置,上面的main方法应该这样写:
package com.websystique.spring; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.websystique.spring.domain.HelloWorld; public class AppMain { public static void main(String args[]) { AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloworld-config.xml"); HelloWorld bean = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorldBean"); bean.sayHello("Spring 4"); context.close(); } }
其中helloworld-config.xml文件是我们在步骤三中创建的,位于工程classpath下(如/src/main/resources)。
结语
下篇文章,我们将会看到一个bean的自动检测例子,该特性基于注解,可以自动找到应用环境中的所有bean,而不需要在配置类中一个个声明它们。
本例源码
http://websystique.com/?smd_process_download=1&download_id=778