看了下Java Tutorials中的fork/join章节,整理下。
什么是fork/join框架
fork/join框架是ExecutorService接口的一个实现,可以帮助开发人员充分利用多核处理器的优势,编写出并行执行的程序,提高应用程序的性能;设计的目的是为了处理那些可以被递归拆分的任务。
fork/join框架与其它ExecutorService的实现类相似,会给线程池中的线程分发任务,不同之处在于它使用了工作窃取算法,所谓工作窃取,指的是对那些处理完自身任务的线程,会从其它线程窃取任务执行。
fork/join框架的核心是ForkJoinPool类,该类继承了AbstractExecutorService类。ForkJoinPool实现了工作窃取算法并且能够执行 ForkJoinTask任务。
基本使用方法
在使用fork/join框架之前,我们需要先对任务进行分割,任务分割代码应该跟下面的伪代码类似:
if (任务足够小){ 直接执行该任务;
}else{ 将任务一分为二; 执行这两个任务并等待结果;
}
首先,我们会在ForkJoinTask的子类中封装以上代码,不过一般我们会使用更加具体的ForkJoinTask类型,如 RecursiveTask(可以返回一个结果)或RecursiveAction。
当写好ForkJoinTask的子类后,创建该对象,该对象代表了所有需要完成的任务;然后将这个任务对象传给ForkJoinPool实例的invoke()去执行即可。
例子-图像模糊
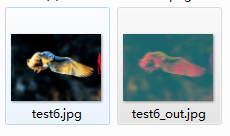
为了更加直观的理解fork/join框架是如何工作的,可以看一下下面这个例子。假定我们有一个图像模糊的任务需要完成,原始图像数据可以用一个整型数组表示,每一个整型元素包含了一个像素点的颜色值(RBG,存放在整型元素的不同位中)。目标图像同样是由一个整型数组构成,每个整型元素包含RBG颜色信息;
执行模糊操作需要遍历原始图像整型数组的每个元素,并对其周围的像素点做均值操作(RGB均值),然后将结果存放到目标数组中。由于图像是一个大数组,这个处理操作会花费一定的时间。但是有了fork/join框架,我们可以充分利用多核处理器进行并行计算。如下是一个可能的代码实现(图像做水平方向的模糊操作):
Tips:该例子仅仅是阐述fork/join框架的使用,并不推荐使用该方法做图像模糊,图像边缘处理也没做判断
public class ForkBlur extends RecursiveAction { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8032915917030559798L; private int[] mSource; private int mStart; private int mLength; private int[] mDestination; private int mBlurWidth = 15; // Processing window size, should be odd. public ForkBlur(int[] src, int start, int length, int[] dst) { mSource = src; mStart = start; mLength = length; mDestination = dst; } // Average pixels from source, write results into destination. protected void computeDirectly() { int sidePixels = (mBlurWidth - 1) / 2; for (int index = mStart; index < mStart + mLength; index++) { // Calculate average. float rt = 0, gt = 0, bt = 0; for (int mi = -sidePixels; mi <= sidePixels; mi++) { int mindex = Math.min(Math.max(mi + index, 0), mSource.length - 1); int pixel = mSource[mindex]; rt += (float) ((pixel & 0x00ff0000) >> 16) / mBlurWidth; gt += (float) ((pixel & 0x0000ff00) >> 8) / mBlurWidth; bt += (float) ((pixel & 0x000000ff) >> 0) / mBlurWidth; } // Re-assemble destination pixel. int dpixel = (0xff000000) | (((int) rt) << 16) | (((int) gt) << 8) | (((int) bt) << 0); mDestination[index] = dpixel; } } ...
现在,我们开始编写compute()的实现方法,该方法分成两部分:直接执行模糊操作和任务的划分;一个数组长度阈值sThreshold可以帮助我们决定任务是直接执行还是进行划分;
@Override protected void compute() { if (mLength < sThreshold) { computeDirectly(); return; } int split = mLength / 2; invokeAll(new ForkBlur(mSource, mStart, split, mDestination), new ForkBlur(mSource, mStart + split, mLength - split, mDestination)); }
接下来按如下步骤即可完成图像模糊任务啦:
1、创建图像模糊任务
ForkBlur fb = new ForkBlur(src, 0, src.length, dst);
2、创建ForkJoinPool
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
3、执行图像模糊任务
pool.invoke(fb);
完整代码如下:

/* * Copyright (c) 2010, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions * are met: * * - Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * - Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * * - Neither the name of Oracle or the names of its * contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived * from this software without specific prior written permission. * * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS * IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, * THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR * PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR * CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, * EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, * PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR * PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF * LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING * NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS * SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. */ import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; import java.io.File; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction; import javax.imageio.ImageIO; /** * ForkBlur implements a simple horizontal image blur. It averages pixels in the * source array and writes them to a destination array. The sThreshold value * determines whether the blurring will be performed directly or split into two * tasks. * * This is not the recommended way to blur images; it is only intended to * illustrate the use of the Fork/Join framework. */ public class ForkBlur extends RecursiveAction { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8032915917030559798L; private int[] mSource; private int mStart; private int mLength; private int[] mDestination; private int mBlurWidth = 15; // Processing window size, should be odd. public ForkBlur(int[] src, int start, int length, int[] dst) { mSource = src; mStart = start; mLength = length; mDestination = dst; } // Average pixels from source, write results into destination. protected void computeDirectly() { int sidePixels = (mBlurWidth - 1) / 2; for (int index = mStart; index < mStart + mLength; index++) { // Calculate average. float rt = 0, gt = 0, bt = 0; for (int mi = -sidePixels; mi <= sidePixels; mi++) { int mindex = Math.min(Math.max(mi + index, 0), mSource.length - 1); int pixel = mSource[mindex]; rt += (float) ((pixel & 0x00ff0000) >> 16) / mBlurWidth; gt += (float) ((pixel & 0x0000ff00) >> 8) / mBlurWidth; bt += (float) ((pixel & 0x000000ff) >> 0) / mBlurWidth; } // Re-assemble destination pixel. int dpixel = (0xff000000) | (((int) rt) << 16) | (((int) gt) << 8) | (((int) bt) << 0); mDestination[index] = dpixel; } } protected static int sThreshold = 10000; @Override protected void compute() { if (mLength < sThreshold) { computeDirectly(); return; } int split = mLength / 2; invokeAll(new ForkBlur(mSource, mStart, split, mDestination), new ForkBlur(mSource, mStart + split, mLength - split, mDestination)); } // Plumbing follows. public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String srcName = "C:\test6.jpg"; File srcFile = new File(srcName); BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(srcFile); System.out.println("Source image: " + srcName); BufferedImage blurredImage = blur(image); String dstName = "C:\test6_out.jpg"; File dstFile = new File(dstName); ImageIO.write(blurredImage, "jpg", dstFile); System.out.println("Output image: " + dstName); } public static BufferedImage blur(BufferedImage srcImage) { int w = srcImage.getWidth(); int h = srcImage.getHeight(); int[] src = srcImage.getRGB(0, 0, w, h, null, 0, w); int[] dst = new int[src.length]; System.out.println("Array size is " + src.length); System.out.println("Threshold is " + sThreshold); int processors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); System.out.println(Integer.toString(processors) + " processor" + (processors != 1 ? "s are " : " is ") + "available"); ForkBlur fb = new ForkBlur(src, 0, src.length, dst); ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); pool.invoke(fb); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Image blur took " + (endTime - startTime) + " milliseconds."); BufferedImage dstImage = new BufferedImage(w, h, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB); dstImage.setRGB(0, 0, w, h, dst, 0, w); return dstImage; } }
测试了一下,执行效果如下:
Source image: C: est6.jpg
Array size is 120000
Threshold is 10000
4 processors are available
Image blur took 10 milliseconds.
Output image: C: est6_out.jpg
JDK中使用fork/join的例子
除了我们上面提到的使用fork/join框架并行执行图像模糊任务之外,在JAVA SE中,也已经利用fork/join框架实现了一些非常有用的特性。其中一个实现是在JAVA SE8 中java.util.Arrays 类的parallelSort()方法。这些方法和sort()方法类似,但是可以通过fork/join框架并行执行。对于大数组排序,在多核处理器系统中,使用并行排序方法比顺序排序更加高效。当然,关于这些排序方法是如何利用fork/join框架不在本篇文章讨论范围,更多信息可以查看JAVA API文档。
另一个fork/join框架的实现是在JAVA SE8中的java.util.streams包内,与Lambda表达式相关,更多信息,可以查看https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/javaOO/lambdaexpressions.html链接。
参考链接:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/concurrency/forkjoin.html
