Redis 中,字典是基础结构。Redis 数据库数据、过期时间、哈希类型都是把字典作为底层结构。
字典的结构
哈希表
哈希表的实现代码在:dict.h/dictht ,Redis 的字典用哈希表的方式实现。
typedef struct dictht {
// 哈希表数组,俗称的哈希桶(bucket)
dictEntry **table;
// 哈希表的长度
unsigned long size;
// 哈希表的长度掩码,用来计算索引值,保证不越界。总是 size - 1
// h = dictHashKey(ht, he->key) & n.sizemask;
unsigned long sizemask;
// 哈希表已经使用的节点数
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
table是一个哈希表数组,每个节点的实现在dict.h/dictEntry,每个dictEntry保存一个键值对。size属性记录了向系统申请的哈希表的长度,不一定都用完,有预留空间的。sizemask属性主要是用来计算索引值 = 哈希值 & sizemask,这个索引值决定了键值对放在table的哪个位置。它的值总是size - 1,其实我有点不明白为啥计算的时候不直接用size - 1,知道的大佬请明示。used属性用来记录已经使用的节点数,size-use就是未使用的节点啦。
下图展示了一个大小为 4 的空哈希表结构,没有任何键值对
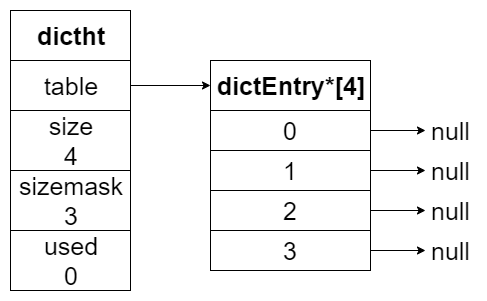
哈希节点
哈希表 dictht 的 table 的元素由哈希节点 dictEntry 组成,每一个 dictEntry 就是一个键值对
typedef struct dictEntry {
// 键
void *key;
// 值
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
// 下一个哈希节点,用于哈希冲突时拉链表用的
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
next 指针是用于当哈希冲突的时候,可以形成链表用的。后续会将
字典
Redis 的字典实现在: dict.h/dict 。
typedef struct dict {
// 哈希算法
dictType *type;
// 私有数据,用于不同类型的哈希算法的参数
void *privdata;
// 两个哈希表,用两个的原因是 rehash 扩容缩容用的
dictht ht[2];
// rehash 进行到的索引值,当没有在 rehash 的时候,为 -1
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
// 正在跑的迭代器
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
// dictType 实际上就是哈希算法,不知道为啥名字叫 dictType
typedef struct dictType {
// hash方法,根据 key 计算哈希值
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
// 复制 key
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
// 复制 value
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
// key 比较
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
// 销毁 key
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
// 销毁 value
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
dictType 属性表示字典类型,实际上这个字典类型就是一组操作键值对算法,里面规定了很多函数。
privdata 则是为不同类型的 dictType 提供的可选参数。
如果有需要,在创建字典的时候,可以传入dictType 和 privdata。
dict.c
// 创建字典,这里有 type 和 privdata 可以传
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, void *privDataPtr) {
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
// 初始化字典
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type, void *privDataPtr) {
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->iterators = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
下图是比较完整的普通状态下的 dict 的结构(没有进行 rehash,也没有迭代器的状态):

哈希算法
当字典中需要添加新的键值对时,需要先对键进行哈希,算出哈希值,然后在根据字典的长度,算出索引值。
// 使用哈希字典里面的哈希算法,算出哈希值
hash = dict->type->hashFunction(key)
// 使用 sizemask 和 哈希值算出索引值
idx = hash & d->ht[table].sizemask;
// 通过索引值,定位哈希节点
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
哈希冲突
哈希冲突指的是多个不同的 key,算出的索引值一样。
Redis 解决哈希冲突的方法是:拉链法。就是每个哈希节点后面有个 next 指针,当发现计算出的索引值对应的位置有其他节点,那么直接加在前面节点后即可,这样就形成了一个链表。
下图展示了 {k1, v1} 和 {k2, v2} 哈希冲突的结构。
假设 k1 和 k2 算出的索引值都是 3,当 k2 发现 table[3] 已经有 dictEntry{k1,v1},那就 dictEntry{k1,v1}.next = dictEntry{k2,v2}。
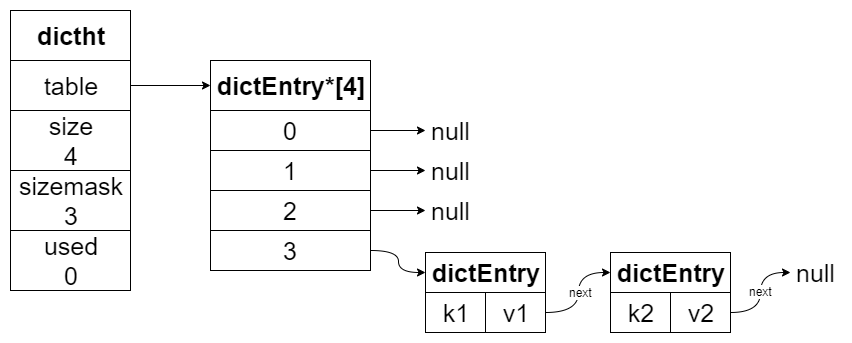
rehash
随着操作的不断进行,哈希表的长度会不断增减。哈希表的长度太长会造成空间浪费,太短哈希冲突明显导致性能下降,哈希表需要通过扩容或缩容,让哈希表的长度保持在一个合理的范围内。
Redis 通过 ht[0] 和 ht[1] 来完成 rehash 的操作,步骤如下:
- 为 ht[1] 分配空间,分配的空间长度有两种情况:
- 扩容:第一个大于等于
ht[0].used * 2的 (2^n) 的数,例如 ht[0].used = 3,那么分配的是距离 6 最近的 (2^3=8) - 缩容:第一个大于等于
ht[0].used / 2的 (2^n) 的数,例如 ht[0].used = 6,那么分配的是距离 3 最近的 (2^2=4)
- 扩容:第一个大于等于
- 将 h[0] 上的键值对都迁移到 h[1],迁移的时候都是重新计算索引值的。由于 h[1] 的长度较长,之前在 h[0] 拉链的元素大概率会被分到不同的位置。
- ht[0] 所有的键值对迁移完之后,h[0] 释放,然后
h[0] = h[1],并把 h[1] 清空,为下次 rehash 准备
渐进式 rehash
上面说的 rehash 中的第二步,迁移的过程不是一次完成的。如果哈希表的长度比较小,一次完成很快。但是如果哈希表很长,例如百万千万,那这个迁移的过程就没有那么快了,会造成命令阻塞!
下面来说说,redis 是如何渐进式地将 h[0] 中的键值对迁移到 h[1] 中的:
- 为 h[1] 开辟空间,字典同时持有 h[0] 和 h[1]
- 字典中的
rehashidx维护了 rehash 的进度,设置为 0 的时候,开始 rehash - 字典每次增删改查的时候,除了完成指定操作之外,还会顺带把
rehashidx上的整条链表迁移到h[1]中。迁移完之后rehashidx + 1 - 随着字典的不断读取、操作,最终
h[0]上的所有键值对都会迁移到h[1]中。全部迁移完成之后rehashidx = -1
这种渐进式 rehash 的方式的好处在于,将庞大的迁移工作,分摊到每次的增删改查中,避免了一次性操作带来的性能的巨大损耗。
缺点就是迁移过程中 h[0] 和 h[1] 同时存在的时间比较长,空间利用率较低。
下面一系列的图,演示了字典是如何渐进式地 rehash ( 图片来自 《Redis 设计与实现》图片集 )
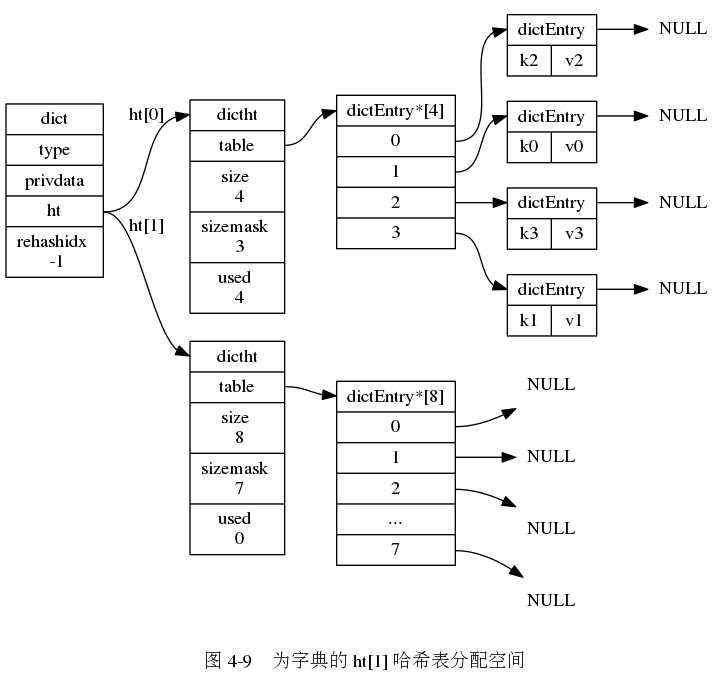
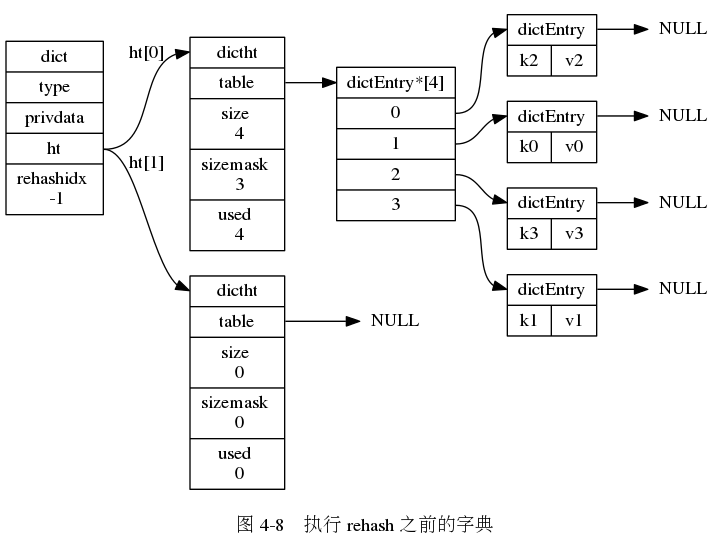
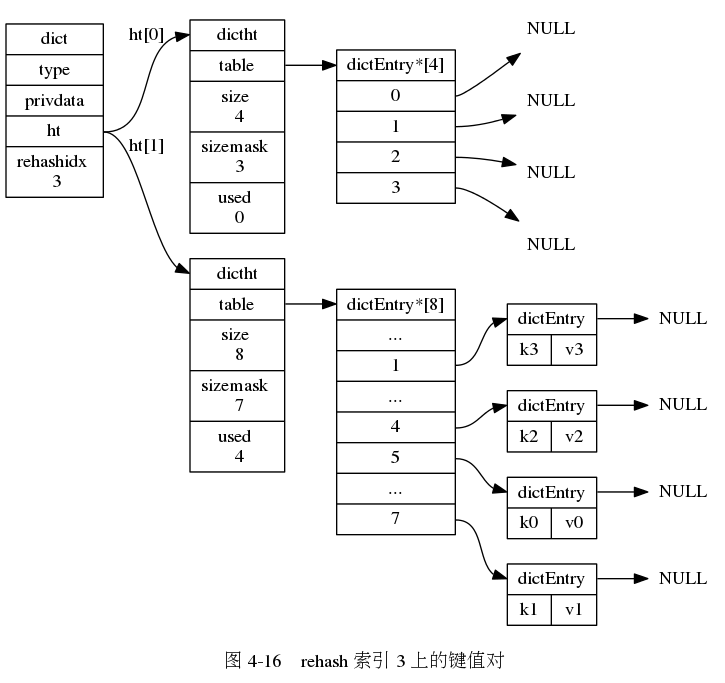
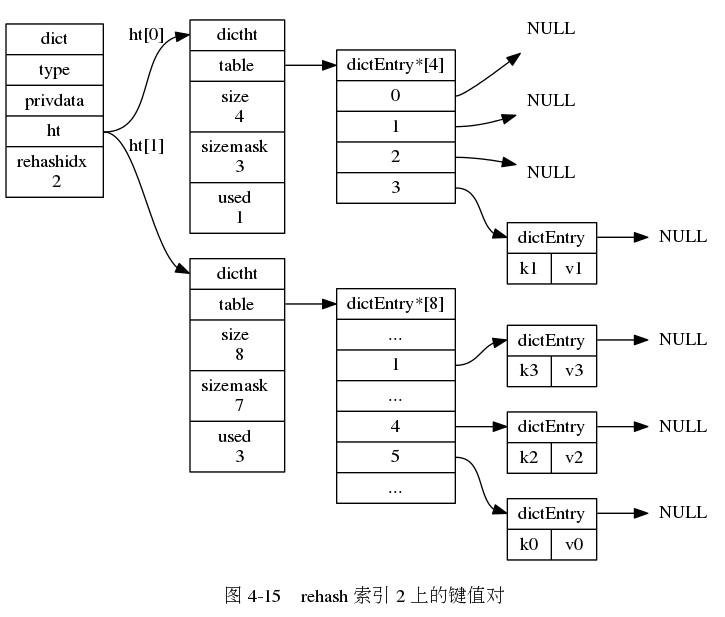
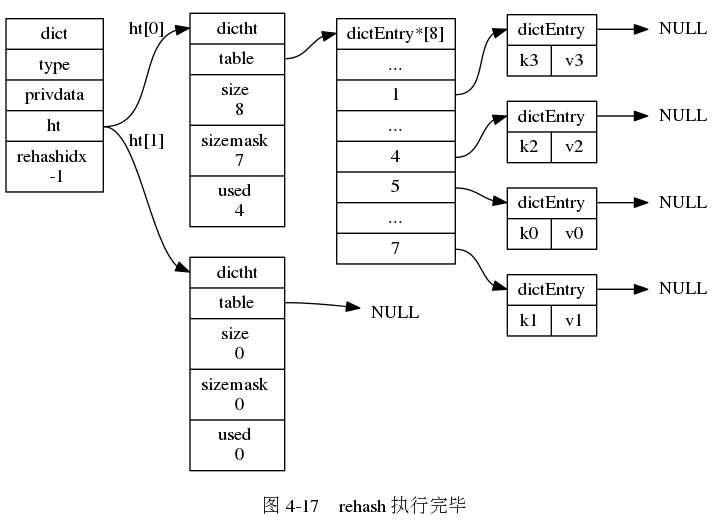
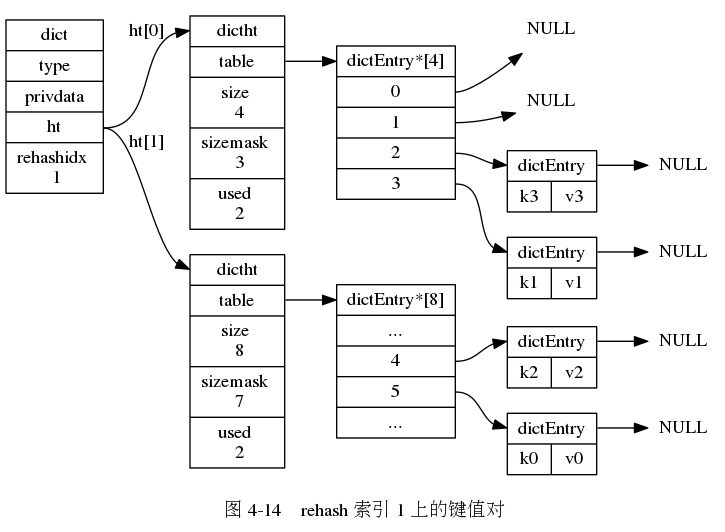
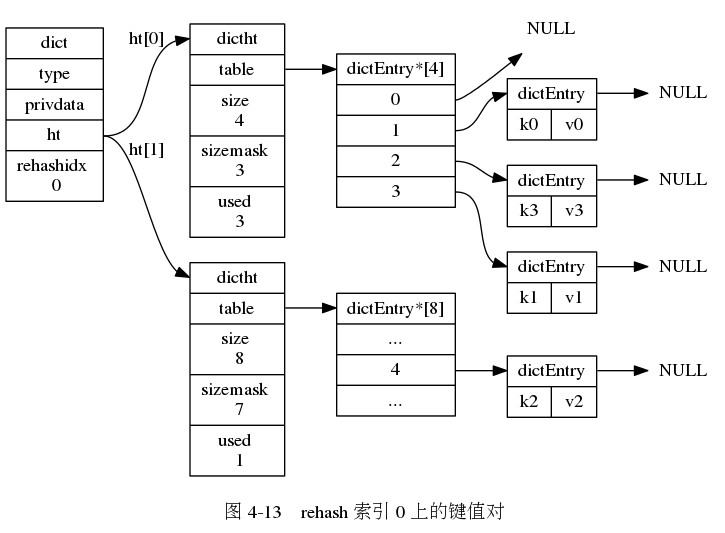



字典的常用操作
1. 查找节点
查找的代码实现在 dict.c:
#define dictHashKey(d, key) (d)->type->hashFunction(key)
// ...
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key) {
dictEntry *he;
uint64_t h, idx, table;
// 空字典直接返回 NULL
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
// 如果状态是正在 rehash,则渐进式 rehash 一步
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 调用字典的哈希算法进行哈希,算出哈希码
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
// 算出在哈希桶中的 index
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
// 找到对应的哈希槽
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
// 哈希槽是个链表
while(he) {
// 遍历链表,找到跟 key 相等的节点
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
// 如果没有在 rehash,就不找 ht[1] 了
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
2. 添加节点
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val) {
// 底层添加节点的方法
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d, key, NULL);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
// 给节点设置值
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
// 添加节点的方法
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing) {
long index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
// 国际惯例,rehash 一波
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 查看插入的 key 是否已经存在,已经在则返回 NULL
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;
// 如果正在 rehash,那就放在 ht[1] 就行了
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
// 把节点放到对应的哈希槽
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
// 节点的 key 赋值
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
3. 删除节点
删除的代码实现在 dict.c,整体来说,前半部分跟查找类似,找到对应的节点之后,再进行删除:
static dictEntry *dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) {
uint64_t h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
// 如果是空的,返回
if (d->ht[0].used == 0 && d->ht[1].used == 0) return NULL;
// 国际惯例,rehash 一波
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 根据字典的哈希算法,算出哈希码
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
// 算出索引
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
// 找到哈希槽
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
/* Unlink the element from the list */
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
// 释放节点。
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
}
d->ht[table].used--;
return he;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return NULL; /* not found */
}
nofree 参数的意思是"是否要释放找到的节点的内存",为什么需要这个参数呢?
因为有一些情况,需要在删除之前先找到节点的值。
例如 skiplist 编码的 zset 在删除之前,需要拿到这个节点对应的 score,再去删除跳表中的节点,这个后面会有文章专门说。
int zsetDel(robj *zobj, sds ele) {
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
// ...
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
// `skiplist` 编码
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
dictEntry *de;
double score;
// 找到要删除的哈希节点,但是先不释放内存
de = dictUnlink(zs->dict,ele);
if (de != NULL) {
// 拿到节点的分数,用于删掉链表节点
/* Get the score in order to delete from the skiplist later. */
score = *(double*)dictGetVal(de);
// 释放节点内存
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(zs->dict,de);
// 删链表节点
int retval = zslDelete(zs->zsl,score,ele,NULL);
// ...
}
}
// ...
}