双列集合
Map:用于存储具有键、值映射关系的元素,每一个元素都包含一对键值,可以通过指定的键找到对应的值
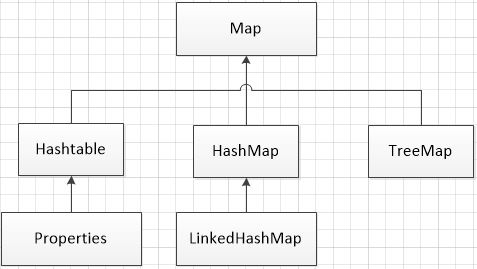
关系图
1.HashMap集合
(1)HashMap的介绍
HashMap:Map接口的实现类,用于存储键值映射关系
HashMap特点:键相同,值覆盖
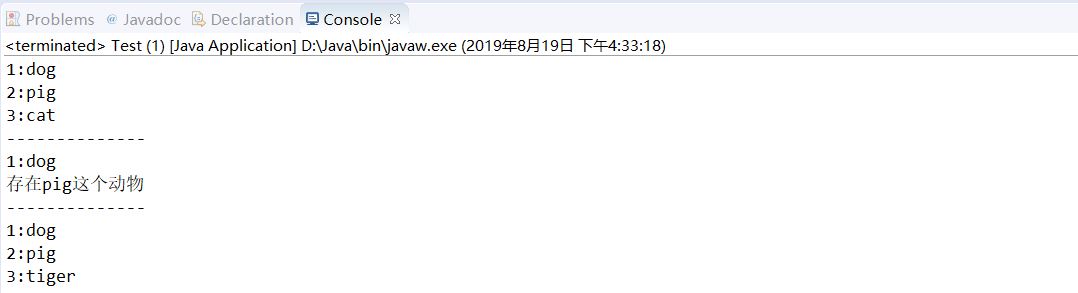
(2)HashMap简单应用
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 //向集合中添加key,value 5 map.put(1,"dog"); 6 map.put(2, "pig"); 7 map.put(3, "cat"); 8 //map.get():通过键得到对应的值 9 System.out.println("1:"+map.get(1)); 10 System.out.println("2:"+map.get(2)); 11 System.out.println("3:"+map.get(3)); 12 System.out.println("--------------"); 13 //判断是否包含存在的键,存在返回true,不存在返回false 14 if (map.containsKey(1)) { 15 System.out.println("1:"+map.get(1)); 16 } 17 //判断是否包含存在的键,存在返回true,不存在返回false 18 if (map.containsValue("pig")) { 19 System.out.println("存在"+map.get(2)+"这个动物"); 20 } 21 System.out.println("--------------"); 22 map.put(3, "tiger"); 23 System.out.println("1:"+map.get(1)); 24 System.out.println("2:"+map.get(2)); 25 System.out.println("3:"+map.get(3)); 26 } 27 }
(3)HashMap的遍历:
————通过遍历集合中所有的键,再根据键得到对应的值
迭代器遍历:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 map.put(1,"dog"); 5 map.put(2, "pig"); 6 map.put(3, "cat"); 7 //获取所有的key 8 Set keys = map.keySet(); 9 Iterator integer = keys.iterator(); 10 while(integer.hasNext()) { 11 //得到key 12 Object key = integer.next(); 13 //通过key得到value 14 Object value = map.get(key); 15 System.out.println(key+":"+value); 16 } 17 } 18 }
foreach遍历:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 map.put(1,"dog"); 5 map.put(2, "pig"); 6 map.put(3, "cat"); 7 //获取所有的key 8 Set keys = map.keySet(); 9 for(Object key:keys) { 10 Object value = map.get(key); 11 System.out.println(key+":"+value); 12 } 13 } 14 }
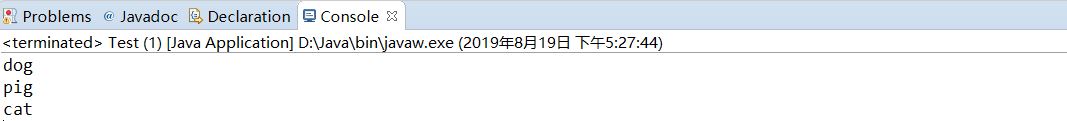
结果相同,下图:

————获取集合中所有的映射关系,再从映射关系中取出键和值
迭代器遍历:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 map.put(1,"dog"); 5 map.put(2, "pig"); 6 map.put(3, "cat"); 7 Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); 8 Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator(); 9 while(iterator.hasNext()) { 10 //获取映射关系 11 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next(); 12 Object key = entry.getKey(); 13 Object value = entry.getValue(); 14 System.out.println(key+":"+value); 15 } 16 } 17 }
foreach遍历:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 map.put(1,"dog"); 5 map.put(2, "pig"); 6 map.put(3, "cat"); 7 Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); 8 for(Object es:entrySet) { 9 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)es; 10 Object key = entry.getKey(); 11 Object value = entry.getValue(); 12 System.out.println(key+":"+value); 13 } 14 } 15 }
结果相同,下图:

————通过Map集合中values()方法获取Map中存储所有值的Collection集合
迭代器遍历:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 map.put(1,"dog"); 5 map.put(2, "pig"); 6 map.put(3, "cat"); 7 Collection values = map.values(); 8 Iterator iterator = values.iterator(); 9 while(iterator.hasNext()) { 10 Object value = iterator.next(); 11 System.out.println(value); 12 } 13 } 14 }
foreach遍历:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map map = new HashMap(); 4 map.put(1,"dog"); 5 map.put(2, "pig"); 6 map.put(3, "cat"); 7 Collection values = map.values(); 8 for(Object value:values) { 9 System.out.println(value); 10 } 11 } 12 }
结果相同,下图: