一.摘要
分类:
- 单向链表
- 双向链表
优点:
- 采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出
- 链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量元素
- 插入和删除操作不会造成原有list迭代器失效,这在vector是不成立的
缺点:
- 链表灵活,但是空间(指针域)和时间(遍历)造成的额外消耗较大
- 不支持随机访问(迭代器不能直接加上偏移量)
二.构造函数
函数原型:
list<T> lst; //list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式: list(beg,end); //构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 list(n,elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 list(const list &lst); //拷贝构造函数。
示例代码:

1 /**list容器*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<list> 4 using namespace std; 5 void printList(const list<int>&l) { 6 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { 7 cout << *it << " "; 8 } 9 cout << endl; 10 } 11 int main() { 12 list<int>L1;//list<T> lst; //list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式: 13 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 14 L1.push_back(i); 15 } 16 cout << "L1:"; 17 printList(L1); 18 19 list<int>L2((++L1.begin()), (--L1.end()));//list(beg,end); //构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 20 cout << "L2:"; 21 printList(L2); 22 23 list<int>L3(4, 8);//list(n,elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 24 cout << "L3:"; 25 printList(L3); 26 27 list<int>L4(L1);//list(const list &lst); //拷贝构造函数。 28 cout << "L4:"; 29 printList(L4); 30 31 system("pause"); 32 return 0; 33 }
运行结果:

三.赋值和交换
函数原型:
assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。 list& operator=(const list &lst); //重载等号操作符 swap(lst); //将lst与本身的元素互换。
示例代码:

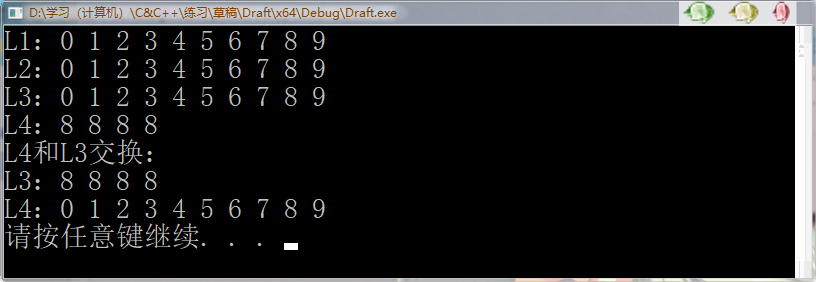
1 /*list赋值和交换*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<list> 4 using namespace std; 5 void printList(const list<int>&l) { 6 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { 7 cout << *it << " "; 8 } 9 cout << endl; 10 } 11 int main() { 12 list<int>L1; 13 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 14 L1.push_back(i); 15 } 16 cout << "L1:"; 17 printList(L1); 18 19 list <int>L2; 20 L2 = L1;//list& operator=(const list &lst); //重载等号操作符 21 cout << "L2:"; 22 printList(L2); 23 24 list<int>L3; 25 L3.assign(L1.begin(), L1.end());//assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 26 cout << "L3:"; 27 printList(L3); 28 29 list<int>L4; 30 L4.assign(4, 8);//assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。 31 cout << "L4:"; 32 printList(L4); 33 34 cout << "L4和L3交换:" << endl; 35 L4.swap(L3);//swap(lst); //将lst与本身的元素互换。 36 cout << "L3:"; 37 printList(L3); 38 cout << "L4:"; 39 printList(L4); 40 system("pause"); 41 return 0; 42 }
运行结果:
四.大小操作
函数原型:
size(); //返回容器中元素的个数 empty(); //判断容器是否为空 resize(num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
示例代码:

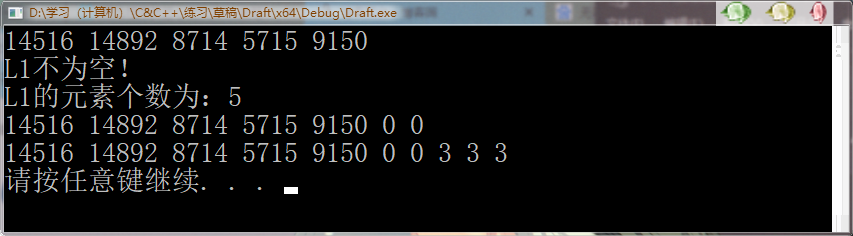
1 /*list大小操作*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<list> 5 using namespace std; 6 void printList(const list<int>&l) { 7 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { 8 cout << *it << " "; 9 } 10 cout << endl; 11 } 12 int main() { 13 srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 14 list<int>L; 15 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 16 L.push_back(rand()); 17 } 18 printList(L); 19 if (L.empty()) { //empty(); //判断容器是否为空 20 cout << "L1为空:" << endl; 21 } 22 else { 23 cout << "L1不为空!" << endl; 24 cout << "L1的元素个数为:" << L.size() << endl; //size(); //返回容器中元素的个数 25 } 26 L.resize(7);//resize(num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 27 printList(L); 28 L.resize(10, 3);//resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 29 printList(L); 30 system("pause"); 31 return 0; 32 }
运行结果:
五.插入和删除
函数原型:
push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素 pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素 push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素 pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素 insert(pos,elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。 insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。 insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。 clear();//移除容器的所有数据 erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
示例代码:

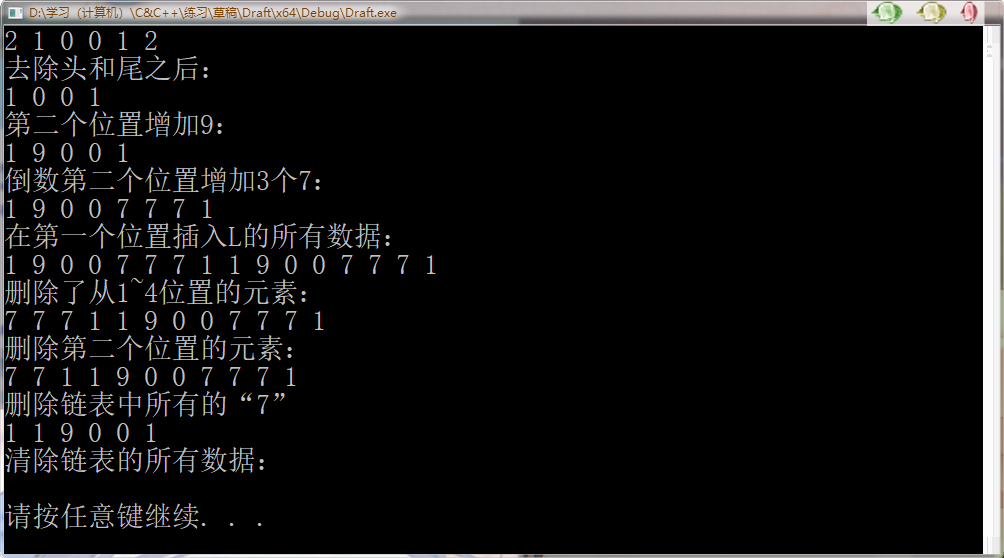
1 /*list插入和删除*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<list> 5 using namespace std; 6 void printList(const list<int>&l) { 7 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { 8 cout << *it << " "; 9 } 10 cout << endl; 11 }int main() { 12 srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 13 list<int>L; 14 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 15 L.push_back(i); //push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素 16 } 17 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 18 L.push_front(i); //push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素 19 } 20 printList(L); 21 L.pop_front(); //pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素 22 L.pop_back(); //pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素 23 cout << "去除头和尾之后:" << endl; 24 printList(L); 25 26 L.insert(++L.begin(), 9); //insert(pos, elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。 27 cout << "第二个位置增加9:" << endl; 28 printList(L); 29 L.insert(--L.end(), 3, 7); //insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。 30 cout << "倒数第二个位置增加3个7:" << endl; 31 printList(L); 32 L.insert(L.begin(), L.begin(), L.end()); //insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。 33 cout << "在第一个位置插入L的所有数据:" << endl; 34 printList(L); 35 list<int>::iterator it = L.begin(); 36 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 37 it++; 38 } 39 L.erase(L.begin(), it);//erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 40 cout << "删除了从1~4位置的元素:" << endl; 41 printList(L); 42 L.erase(++L.begin()); //erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 43 cout << "删除第二个位置的元素:" << endl; 44 printList(L); 45 L.remove(7); //remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。 46 cout << "删除链表中所有的“7”" << endl; 47 printList(L); 48 L.clear(); //clear();//移除容器的所有数据 49 cout << "清除链表的所有数据:" << endl; 50 printList(L); 51 52 system("pause"); 53 return 0; 54 }
运行结果:
六.数据存取
函数原型:
front(); //返回第一个元素。 back(); //返回最后一个元素。
示例代码:

1 /*list数据存取*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<list> 5 using namespace std; 6 void printList(const list<int>&l) { 7 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { 8 cout << *it << " "; 9 } 10 cout << endl; 11 }int main() { 12 srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 13 list<int>L; 14 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 15 L.push_back(rand()); 16 } 17 printList(L); 18 cout << "第一个元素为:" << endl; 19 cout << L.front() << endl; 20 cout << "最后一个元素为:" << endl; 21 cout << L.back() << endl; 22 23 cout << endl << "修改数据之后:" << endl; 24 L.front() = 6; 25 cout << "第一个元素为:" << endl; 26 cout << L.front() << endl; 27 L.back() = 9; 28 cout << "最后一个元素为:" << endl; 29 cout << L.back() << endl; 30 printList(L); 31 system("pause"); 32 return 0; 33 }
运行结果:

七.反转和排序
函数原型:
reverse(); //反转链表 sort(); //链表排序
示例代码:

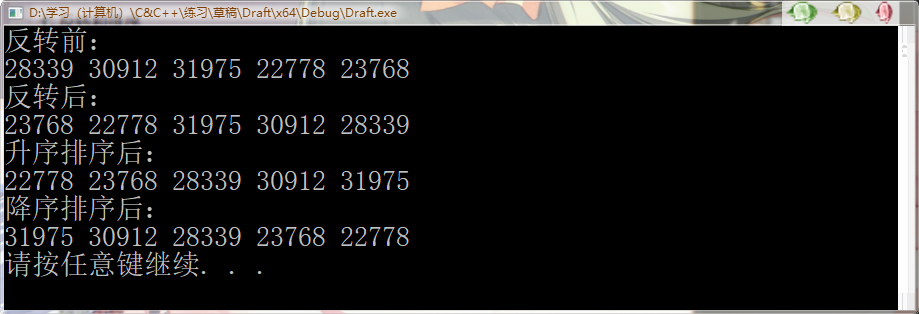
1 /*list数据存取*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<list> 5 using namespace std; 6 void printList(const list<int>&l) { 7 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { 8 cout << *it << " "; 9 } 10 cout << endl; 11 } 12 bool MyCompare(int x,int y) { 13 return x>y; //降序 14 } 15 16 int main() { 17 srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 18 list<int>L; 19 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 20 L.push_back(rand()); 21 } 22 cout << "反转前:" << endl; 23 printList(L); 24 L.reverse(); //reverse(); //反转链表 25 cout << "反转后:" << endl; 26 printList(L); 27 //所有不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,不可以用algorithm中的标准算法 28 L.sort(); //sort(); //链表排序(默认是升序) 29 cout << "升序排序后:" << endl; 30 printList(L); 31 L.sort(MyCompare); //降序 32 cout << "降序排序后:" << endl; 33 printList(L); 34 system("pause"); 35 return 0; 36 }
运行结果:
八.总结
也是些简单的操作,很容易上手~
