201871010104-陈园园 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第四周学习总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://www.cnblogs.com/lily-2018/p/11441372.html |
| 作业学习目标 |
|
第一部分:总结第四章理论知识
1.类与对象概念
(1)类是构造对象的模板或蓝图,由类构造对象的过程称为创建类的实例。
(2)对象:即数据,对象有三个特性,行为、状态、标识。
2.类与对象的关系
(1)类是对象,事物的描述和抽象,是具有相同属性和行为的对象集合。对象则是该类事物的实例。
(2)类是一个静态的概念,类本身不携带任何数据。当没有为类创建任何对象时,类本身不存在于内存空间 中。对象是一个动态的概念。每一个对象都存在着有别于其它对象的属于自己的独特的属性和行为。对象的属性可以随着它自己的行为而发生改变。
3.对象与对象变量的关系
(1).Java中想使用对象就必须先构造对象,并指定其初始状态。
4.通过实验掌握了预定义类的基本使用方法,熟悉Math类、String类、math类、Scanner 类、LocalDate类的常用API。
5.掌握用户自定义类的语法规则,包括实例域、静态域、构造器方法、更改器方法、访问器方法、静态方法、main方法、方法参数的定义要求
(1)实例域:可将实例域定义为final,构建对象时必须初始化这样的域。
(2)静态域:绝大多数面向对象程序设计语言中,静态域被称为类域。如果将域定义为static,每个类中只有一个这样的域。而每个对象对于所有的实例域却都有自己的一份拷贝。
(3)静态方法:静态方法是一种不能向对象实时操作的方法。可以使用对象调用静态方法。
(4)构造器方法:构造器与类同名。构造器总是伴随着new操作符的执行被调用,而不能对一个已经存在的对象调用构造器来达到重新设置实例域的目的。
(5)更改器方法:调用更改器方法后对象的状态会改变。
(6)访问器方法:只访问对象而不修改对象的方法。
(7)main方法:main方法不对任何对象进行操作。静态的main方法将执行并创建程序所需要的对象。
6.重载
多个方法有相同的名字、不同的参数、便产生了重载。Java允许重载任何方法,而不只是构造器方法。
7.包
Java允许使用包将类组织起来。借助包可以方便地组织自己的代码,并将自己的代码与别人提供的代码库分开管理。而且使用包可以确保类名的唯一性。
8.文档注释技术
包括类注释,方法注释,域注释,通用注释,包与概述注释等。
第二部分:实验部分
实验名称:实验三 类与对象的定义及使用
1. 实验目的:
(1) 熟悉PTA平台线上测试环境;
(2) 理解用户自定义类的定义;
(3) 掌握对象的声明;
(4) 学会使用构造函数初始化对象;
(5) 使用类属性与方法的使用掌握使用;
(6) 掌握package和import语句的用途。
3. 实验步骤与内容:
实验1 任务1
公民身份证号码按照GB11643—1999《公民身份证号码》国家标准编制,由18位数字组成:前6位为行政区划分代码,第7位至14位为出生日期码,第15位至17位为顺序码,第18位为校验码。从键盘输入1个身份证号,将身份证号的年月日抽取出来,按年-月-日格式输出。注意:输入使用Scanner类的nextLine()方法,以免出错。
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = in.nextLine();
String s2,s3,s4;
s2 = s1.substring(6,10);
s3 = s1.substring(10,12);
s4 = s1.substring(12,14);
System.out.println(s2+"-"+s3+"-"+s4);
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验1 任务2
tudentfile.txt文件内容是某班同学的学号与姓名,利用此文件编制一个程序,将studentfile.txt文件的信息读入到内存,并提供两类查询功能:
(1)输入姓名查询学号;
(2)输入学号查询姓名。要求程序具有友好人机交互界面。 编程建议:
(1)从文件中读入学生信息,可以编写如下函数: public static void StudentsFromFile(String fileName))
(2)输入姓名查找学生学号,可以编写如下函数: public static String findStudentName(String name)
(3)输入学号查找学生姓名,可以编写如下函数: public static String findStudentID(String ID)。
代码如下:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main1 {
// private static Student students[];
private static ArrayList<Student> list;
public static void main(String[] args) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
readFile("studentfile.txt");
System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出");
int i;
while ((i = in.nextInt()) != 3) {
switch (i) {
case 1:
System.out.println("请输入姓名");
String name = in.next();
Student student = findStudentByName(name);
if (student == null) {
System.out.println("没找到");
} else {
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("请输入学号");
String id = in.next();
Student student1 = findStudentById(id);
if (student1 == null) {
System.out.println("没找到");
} else {
System.out.println(student1.toString());
}
System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出");
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
in.close();
}
}
public static void readFile(String path) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
String result;
while ((result = br.readLine()) != null) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(result.substring(13));
student.setID(result.substring(0,12));
list.add(student);
}
br.close();
}
public static Student findStudentByName(String name) {
for (Student student : list) {
if (student.getName().equals(name)) {
return student;
}
}
return null;
}
public static Student findStudentById(String Id) {
for (Student student : list) {
if (student.getID().equals(Id)) {
return student;
}
}
return null;
}
}
class Student {
private String name;
private String ID;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getID() {
return ID;
}
public void setID(String iD) {
ID = iD;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return "姓名是:" + name + "学号是:" + ID;
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验2
测试程序1
参考教材104页EmployeeTest.java,设计StudentTest.java,定义Student类,包含name(姓名)、sex(性别)序1:
1)编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-2(教材104页);
2)结合程序运行结果,掌握类的定义与类对象的用法,并在程序代码中添加类与对象知识应用的注释;
3) 尝试在项目中编辑两个类文件(Employee.java、 EmployeeTest.java ),编译并运行程序。
4)javascore(java成绩)三个字段,编写程序,从键盘输入学生人数,输入学生信息,并按以下表头输出学生信息表:
姓名 性别 java成绩
代码如下:
import java.time.*;
/**
* This program tests the Employee class.
* @version 1.13 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EmployeeTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array with three Employee objects
Employee[] staff = new Employee[3];//构造了一个Employee数组,并填入了三个雇员对象。
staff[0] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);
staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1);
staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15);
// raise everyone's salary by 5%
for (Employee e : staff)//利用Employee中的raiseSalary方法将每一个雇员的薪水提高5%
e.raiseSalary(5);
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)//调用getName方法、getSalary方法和getHireDay方法将每个雇员的信息打印出来
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
+ e.getHireDay());
}
}
class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay;
public Employee(String n, double s, int year, int month, int day)
{
name = n;
salary = s;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
运行结果如下:

设计StudentTest.java,定义Student类,包含name(姓名)、sex(性别)序1:
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class cyy {
String 姓名;
String 性别;
double java成绩;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private String 姓名3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入学生人数");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int totalStudent = sc.nextInt();
cyy[] stus = new cyy[totalStudent];
for(int i=0;i<totalStudent;i++){
cyy s = new cyy();
stus[i]=s;
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个学生的姓名");
s.set姓名3(sc.next());
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个学生的性别");
s.性别 = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个学生的Java成绩");
s.java成绩 = sc.nextDouble();
}
printcyy(stus);
sc.close();
}
private static void printcyy(cyy[] stus) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public static void printtudents(cyy[] s){
System.out.println("姓名\t性别\tJava成绩");
for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++){
System.out.println(s[i].姓名+"\t"+s[i].性别+"\t"+s[i].java成绩);
}
}
public String get姓名3() {
return 姓名;
}
public void set姓名3(String 姓名3) {
this.姓名 = 姓名3;
}
}
运行结果如下:

测试程序2:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-3(教材116);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握静态域(netxtId)与静态方法(getNextId)的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
l 理解Java单元(类)测试的技巧。
代码如下:
/**
* This program demonstrates static methods.
* @version 1.02 2008-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class StaticTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array with three Employee objects
var staff = new Employee[3];//构造Employee数组,并有三个雇员对象;
staff[0] = new Employee("Tom", 40000);
staff[1] = new Employee("Dick", 60000);
staff[2] = new Employee("Harry", 65000);
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
{
e.setId(); //打印每个雇员的信息;
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary="
+ e.getSalary());
}
int n = Employee.getNextId(); // calls static method
System.out.println("Next available id=" + n);
}
}
//打印每个雇员的信息;
class Employee
{
private static int nextId = 1;
private String name;
private double salary;
private int id;
public Employee(String n, double s)
{//构造Employee类的对象,并声明局部变量name,salary,hireday;
name = n;
salary = s;
id = 0;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public int getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId()
{
id = nextId; // set id to next available id
nextId++;
}
public static int getNextId()
{
return nextId; // returns static field
}
public static void main(String[] args) // unit test
{
var e = new Employee("Harry", 50000);
System.out.println(e.getName() + " " + e.getSalary());
}
}
运行结果如下:

测试程序3:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-4(教材121);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java方法参数的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
代码如下:
/**
* This program demonstrates parameter passing in Java.
* @version 1.01 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ParamTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
* Test 1: Methods can't modify numeric parameters//测试方法不能修改数值参数
*/
System.out.println("Testing tripleValue:");
double percent = 10;
System.out.println("Before: percent=" + percent);
tripleValue(percent);//调用 tripleValue
System.out.println("After: percent=" + percent);
/*
* Test 2: Methods can change the state of object parameters//调用 tripleValue
*/
System.out.println("\nTesting tripleSalary:");
var harry = new Employee("Harry", 50000);
System.out.println("Before: salary=" + harry.getSalary());
tripleSalary(harry);
System.out.println("After: salary=" + harry.getSalary());
/*
* Test 3: Methods can't attach new objects to object parameters
*/
System.out.println("\nTesting swap:");
var a = new Employee("Alice", 70000);
var b = new Employee("Bob", 60000);
System.out.println("Before: a=" + a.getName());
System.out.println("Before: b=" + b.getName());
swap(a, b);//用交换函数交换a,b
System.out.println("After: a=" + a.getName());
System.out.println("After: b=" + b.getName());
}
public static void tripleValue(double x) // doesn't work
{
x = 3 * x;
System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x);
}
public static void tripleSalary(Employee x) // works
{
x.raiseSalary(200);
System.out.println("End of method: salary=" + x.getSalary());
}
public static void swap(Employee x, Employee y)
{
Employee temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x.getName());
System.out.println("End of method: y=" + y.getName());
}
}
class Employee // simplified Employee class
{
private String name;
private double salary;//类的实例域定义来存放的需要操作的数据;
public Employee(String n, double s)
{
name = n;
salary = s;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
运行结果如下:

测试程序4:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-5(教材129);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java用户自定义类的用法,掌握对象构造方法及对象使用方法,在相关代码后添加注释。
代码如下:
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates object construction.
* @version 1.02 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ConstructorTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array with three Employee objects
var staff = new Employee[3];
//构造Employee数组,并有三个雇员对象;
staff[0] = new Employee("Harry", 40000);
staff[1] = new Employee(60000);
staff[2] = new Employee();
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff) //打印每个雇员的信息
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary="
+ e.getSalary());
}
}
class Employee
{
private static int nextId;
private int id;
private String name = ""; // instance field initialization
private double salary;
// static initialization block
static
{
var generator = new Random();
// set nextId to a random number between 0 and 9999 将nextId设置为0到999之间的随机值
nextId = generator.nextInt(10000);
}
// object initialization block
{
id = nextId;
nextId++;
}
// three overloaded constructors //三个重载的构造
public Employee(String n, double s)
{
name = n;
salary = s;
}
public Employee(double s)
{
// calls the Employee(String, double) constructor
this("Employee #" + nextId, s);
}
// the default constructor
public Employee()
{
// name initialized to ""--see above
// salary not explicitly set--initialized to 0
// id initialized in initialization block
}
public String getName()
{
return name; //实例域name的访问器方法
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary; //实例域salary的访问器方法
}
public int getId()
{
return id; //实例域id的访问器方法
}
}
运行结果如下:
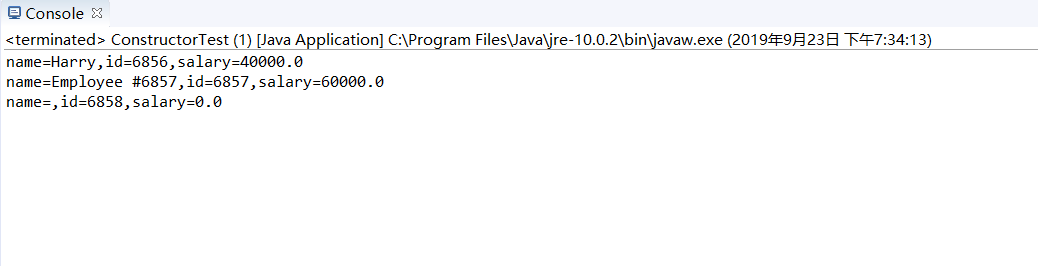
测试程序5:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-6、4-7(教材135);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java包的定义及用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
4-6代码如下:
import com.horstmann.corejava.*;
// the Employee class is defined in that package
import static java.lang.System.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of packages.
* @version 1.11 2004-02-19
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PackageTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// because of the import statement, we don't have to use
// com.horstmann.corejava.Employee here import语句,不需要使用com.horstmann.corejava
var harry = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1);
harry.raiseSalary(5);
// because of the static import statement, we don't have to use System.out here
out.println("name=" + harry.getName() + ",salary=" + harry.getSalary());
//由于使用了静态导入语句,在这里不需要使用System.out
}
}
4-6运行结果如下:
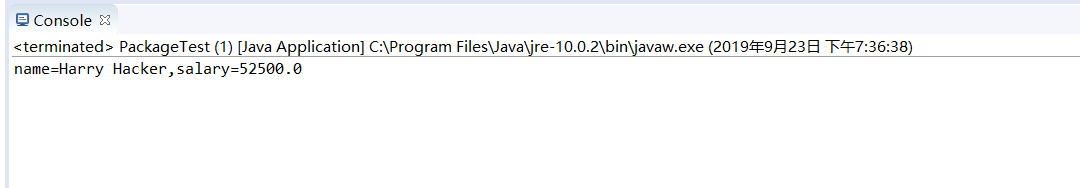
4-7代码如下:
package com.horstmann.corejava; //将类放入包中
// the classes in this file are part of this package
import java.time.*; //java.time包的导入
// import statements come after the package statement 导入语句位于PACKAGE语句之后
/**
* @version 1.11 2015-05-08
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay;
public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name; //this用来引用当前对象
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
4-7运行结果如下:
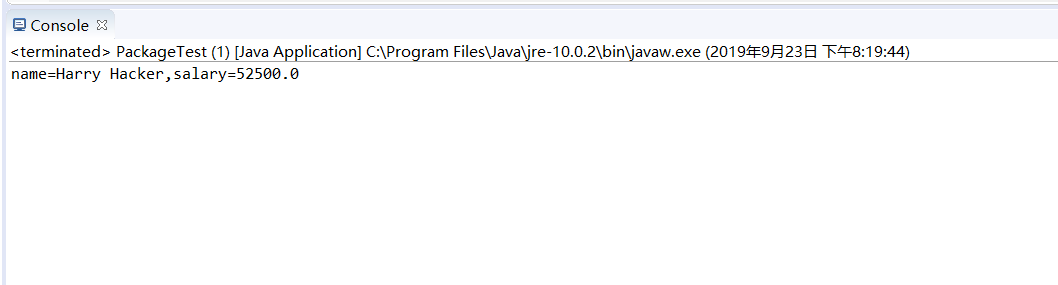
实验总结:
通过这次实验,我初步了解了java中OOP的概念,学习了如何自定义类去编程,加深了对java面向对象的特点的理解。 经过过本章《对象与类》的学习 ,首先对于本章的理论知识有了初步的了解。如使用预定义类,用户自定义类,静态域与静态方法,还有方法参数,包以及文档注释等等。另外,通过实验测试程序也对本章知识有了更多的认识。在学习了类之后,有学习了静态域和静态方法的用法,在这一次的学习过程当中,觉得颇有收获,觉得比较简单易懂,了解了静态域、静态常量、静态方法、工厂方法和main方法的概念,并通过实例程序去真正理解了这些概念。希望在以后老师的讲解过程中有更大的进步。