最近在探索xgboost 调参事情,现在存在着几点问题:
1.调参方式,网上有多种调参方式,但是基本都是一个一个参数去调,贪心算法,只能满足局部最优,但是我们的参数都是相互影响的,局部最优,组合起来并非是最优的。
2.我基本都是确定几个参数的固定形式,比如说树的深度=3,最小叶节点=样本*5%,scale_pos_weight看好坏占比等等,最后使用train去得到最佳树的数量,但是这种也耗费时间,且不是自动化,还容易过拟合
3.模型的最优,首先模型的评判最优是模型的训练集,测试集,oot的KS的差距不能大于4%或者5%,且oot的KS不能与最优(比如说,我们尝试过多种建模方式,发现使用这些数据,oot的最优效果在0.35左右)差异过大。在这些条件下,去调参,去实现自动化
还是使用give-me-some-credit的数据:https://www.kaggle.com/brycecf/give-me-some-credit-dataset?select=cs-test.csv
除了调补缺失值-9999,基本 不对数据进行处理
#%%导入模块 import pandas as pd import numpy as np from scipy import stats import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline plt.rc("font",family="SimHei",size="12") #解决中文无法显示的问题 #%%导入数据 train=pd.read_csv('cs-training.csv') train.shape #(150000, 12) train.pop('Unnamed: 0') train.columns train = train.fillna(-9999) import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer, OneHotEncoder from sklearn_pandas import DataFrameMapper from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier, GradientBoostingRegressor from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression import warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #oot from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split train_x, oot_x, train_y, oot_y = train_test_split(train.drop(columns='SeriousDlqin2yrs'), \ train.SeriousDlqin2yrs, test_size=0.3, random_state=2021,stratify=train.SeriousDlqin2yrs) #训练集,测试集 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(train_x, \ train_y, test_size=0.3, random_state=2021,stratify=train_y) import xgboost as xgb from xgboost import plot_importance d_train = xgb.DMatrix(train_x,train_y,feature_names=train_x.columns) d_valid = xgb.DMatrix(test_x,test_y,feature_names=train_x.columns) watchlist = [(d_train,'train'),(d_valid,'valid')] #参数设置(未调箱前的参数) params={ 'eta':0.2, #特征权重,取值范围0~1,通常最后设置eta为0.01~0.2 'max_depth':3, #树的深度,通常取值3-10,过大容易过拟合,过小欠拟合 230 'min_child_weight':230, #最小样本的权重,调大参数可以繁殖过拟合 'gamma':0.4, #控制是否后剪枝,越大越保守,一般0.1、 0.2的样子 'subsample':0.8, #随机取样比例 'colsample_bytree':0.8 , #默认为1,取值0~1,对特征随机采集比例 'lambda':0.8, 'alpha':0.6, 'n_estimators':500, 'booster':'gbtree', #迭代树 'objective':'binary:logistic', #逻辑回归,输出为概率 'nthread':6, #设置最大的进程量,若不设置则会使用全部资源 'scale_pos_weight':10, #默认为0,1可以处理类别不平衡 'seed':1234, #随机树种子 'silent':1, #0表示输出结果 'eval_metric':'auc' #评分指标 } bst = xgb.train(params, d_train,1000,watchlist,early_stopping_rounds=100, verbose_eval=5) #最大迭代次数1000次 tree_nums = bst.best_ntree_limit print('最优模型树的数量:%s,最优迭代次数:%s,auc: %s' %(bst.best_ntree_limit,bst.best_iteration,bst.best_score)) bst = xgb.train(params, d_train,tree_nums,watchlist,early_stopping_rounds=1000, verbose_eval=10) #最优模型迭代次数去训练
预测
train_p = bst.predict(xgb.DMatrix(train_x)) test_p = bst.predict(xgb.DMatrix(test_x)) oot_p = bst.predict(xgb.DMatrix(oot_x))
画出ks 图形
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,auc def plot_roc(p1, p,string): ''' 目标:计算出分类模型的ks值 变量: self:模型fit(x,y),如(self=tree.fit(x,y)) data:一般是训练集(不包括label)或者是测试集(也是不包括label) y:label的column_name 返回:训练集(或者测试集)的auc的图片 ''' fpr, tpr, p_threshold = roc_curve(p1, p, drop_intermediate=False, pos_label=1) df = pd.DataFrame({'fpr': fpr, 'tpr': tpr, 'p': p_threshold}) df.loc[0, 'p'] = max(p) ks = (df['tpr'] - df['fpr']).max() roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(2.8, 2.8), dpi=140) ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=2, label='ROC curve\nAUC = %0.4f\nK-S = %0.4f' % (roc_auc, ks) ) ax.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--') ax.set_xlim([0.0, 1.0]) ax.set_ylim([0.0, 1.05]) ax.set_xlabel('False Positive Rate') ax.set_ylabel('True Positive Rate') ax.set_title(string) ax.legend(loc="lower right") plt.close() return fig
训练集
plot_roc(train_y, train_p,'训练集ROC Curve') #训练集
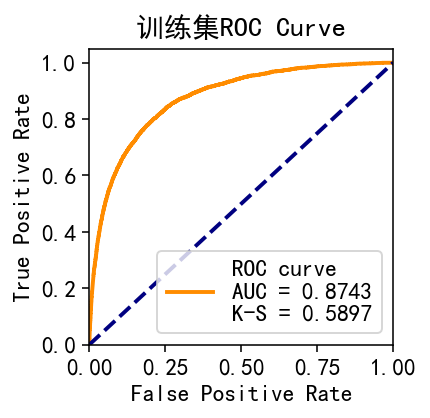
测试集
plot_roc(test_y, test_p,'测试集ROC Curve')
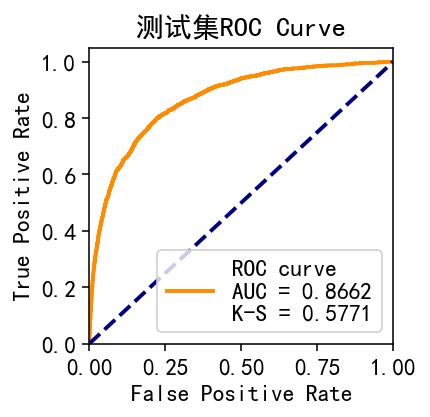
oot
plot_roc(oot_y, oot_p,'验证集ROC Curve')

像这种可以部署了,ks相差2%左右